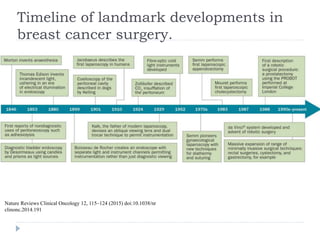
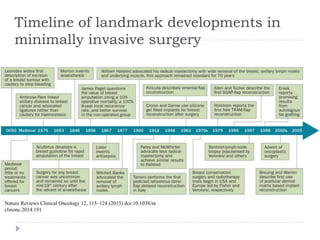
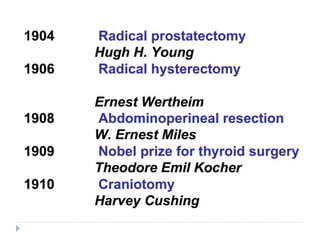
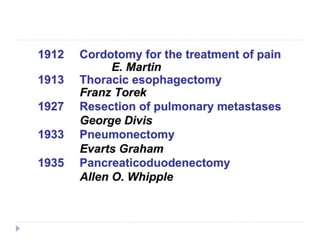
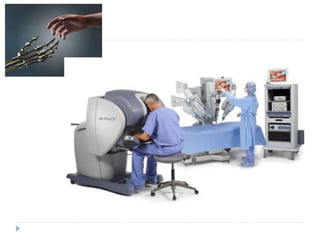
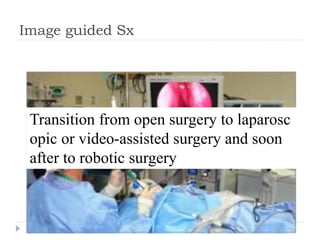
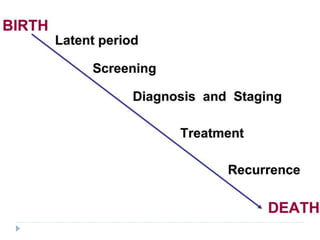
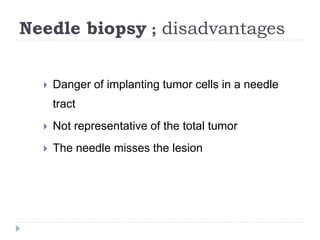
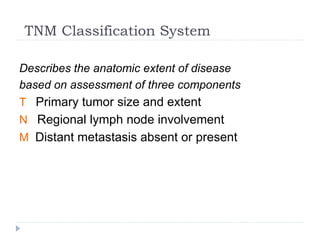
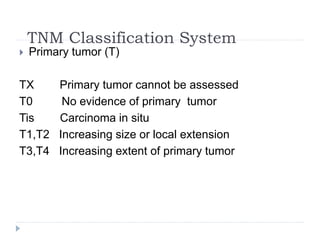
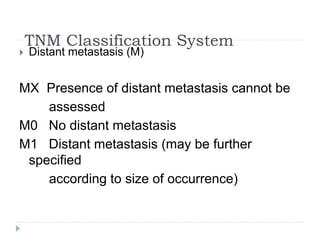
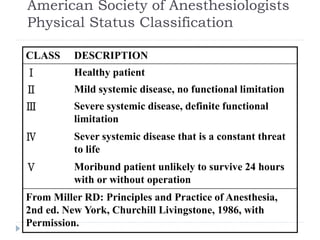
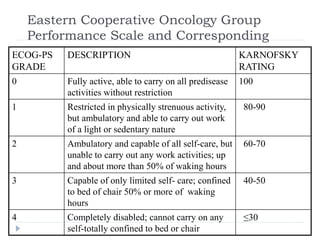
This document discusses the role and history of surgical oncology. It outlines how surgery has evolved from open procedures to minimally invasive and robotic techniques. Key developments include the transition to laparoscopic surgery and increased use of intraoperative navigation and genomic testing. The roles of the surgical oncologist include prevention, diagnosis through biopsy techniques, definitive and palliative treatment, and rehabilitation. Challenges include identifying curable patients and balancing treatment efficacy with quality of life. The field continues to advance through multidisciplinary care, research, and education.