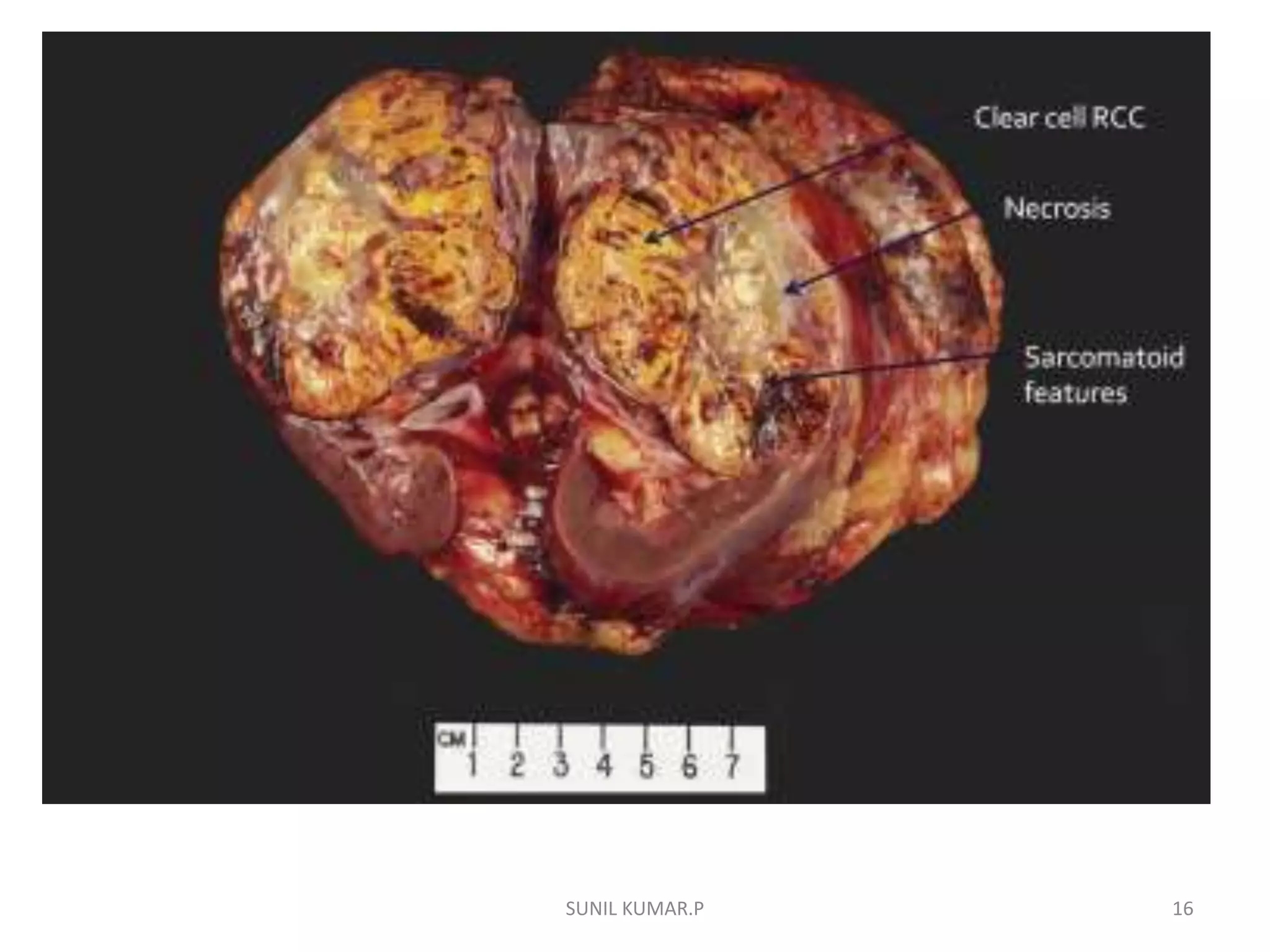
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, originating from the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule. Risk factors include tobacco use, genetic factors, cystic kidney diseases, and exposure to certain chemicals. RCC is typically diagnosed through imaging tests and biopsy. Surgical removal of the kidney is the main treatment for localized RCC, while advanced or metastatic RCC may be treated with targeted drugs or immunotherapy. Prognosis depends on the stage, with localized RCC having high survival rates.