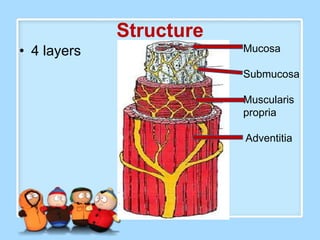
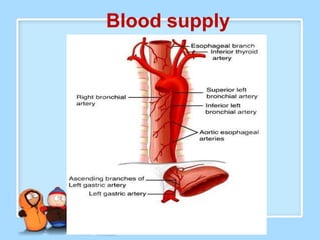
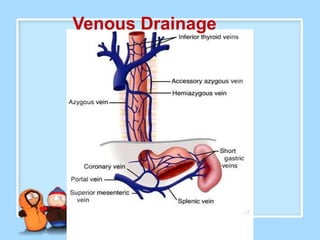
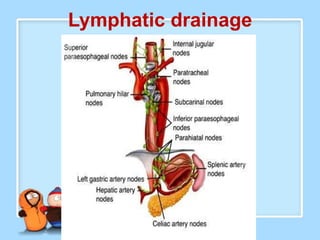
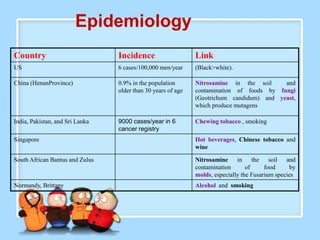
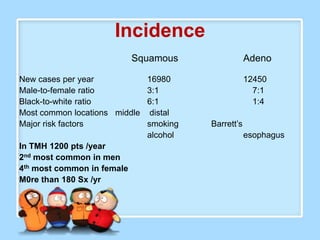
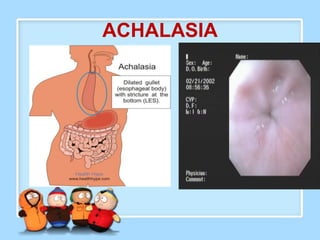
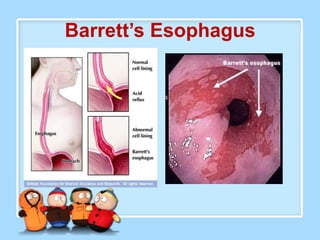
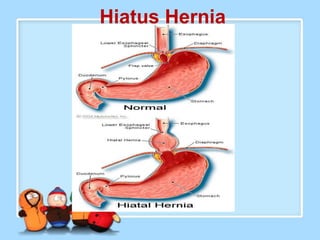
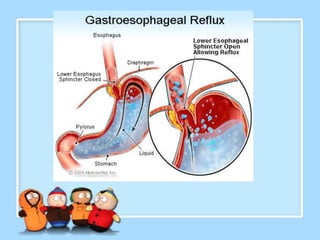
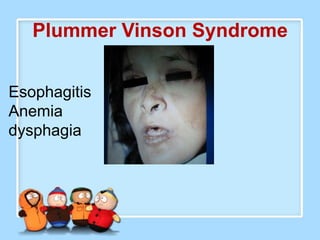
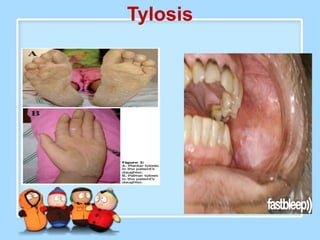
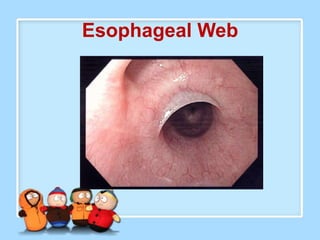
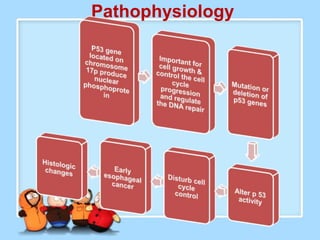
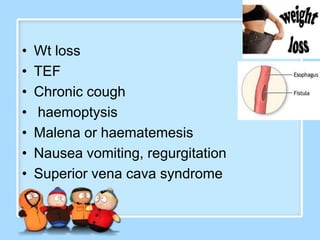
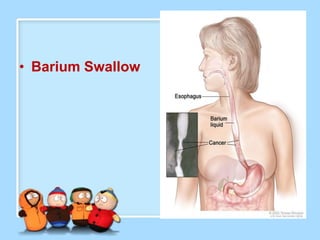
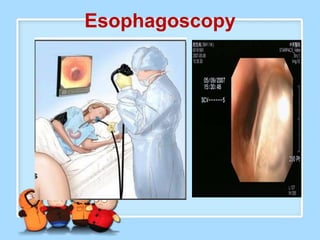
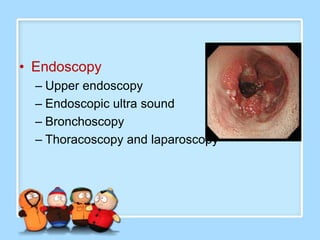
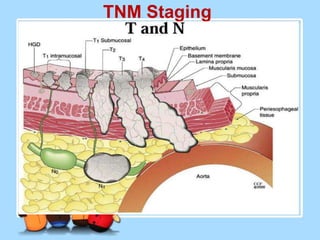
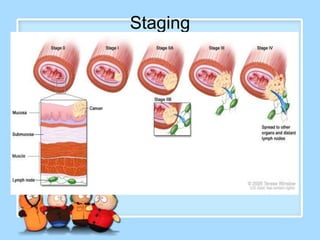
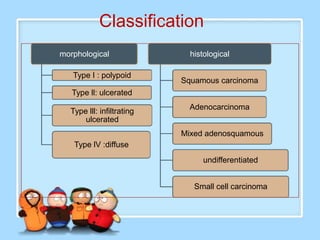
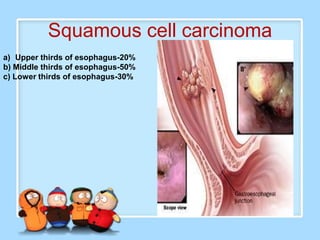
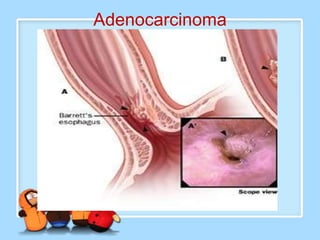
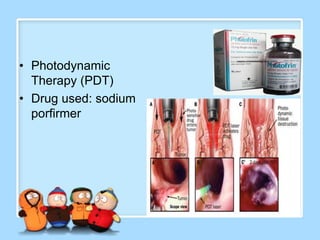
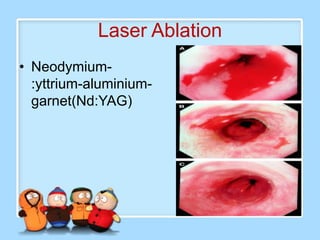
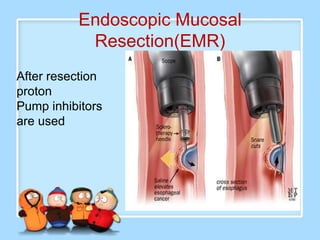
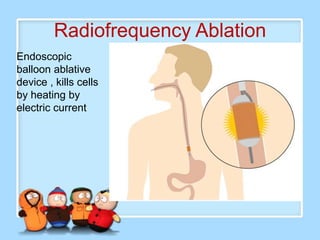
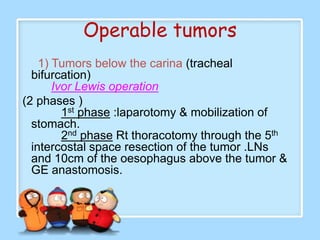
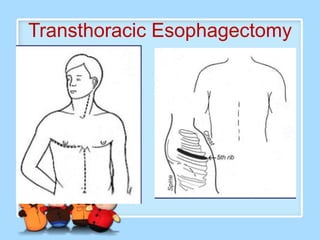
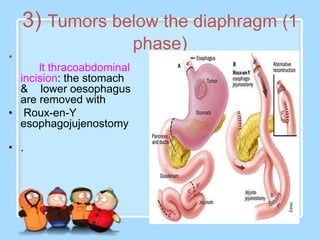
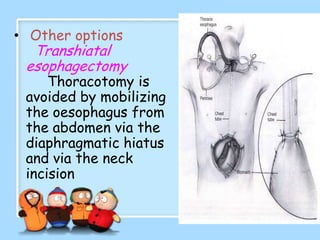
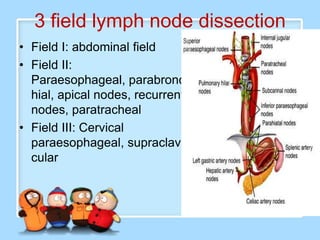
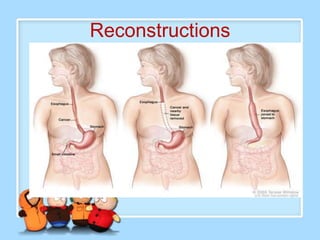
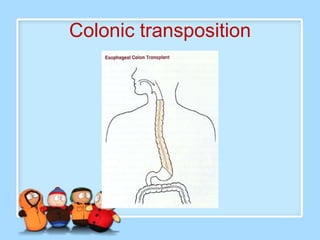
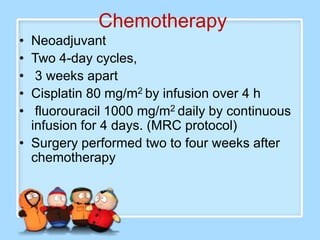
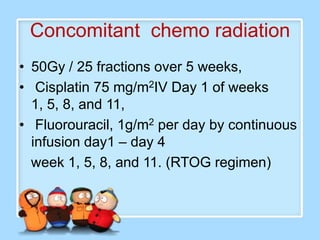
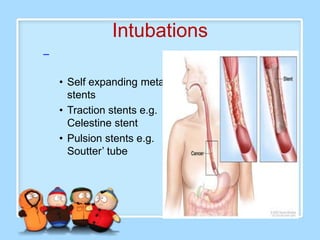
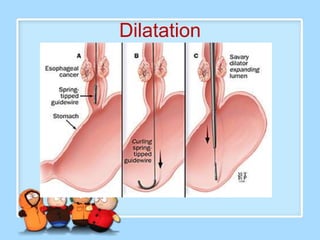
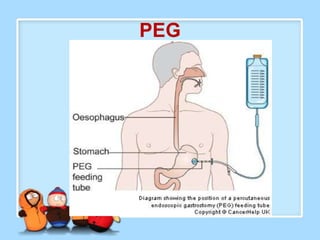
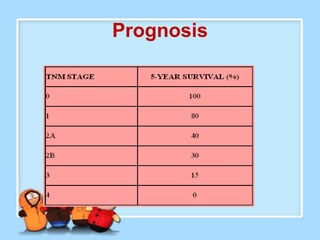
The document discusses Ms. Sujata Desai, Ms. Sarita Kumari, and Ms. Shiney Sam and provides information on the anatomy, epidemiology, etiology, clinical manifestations, investigations, staging, treatment including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and palliative care, and complications of esophageal cancer. It also describes the classification, spread, prevention and screening recommendations for esophageal cancer.