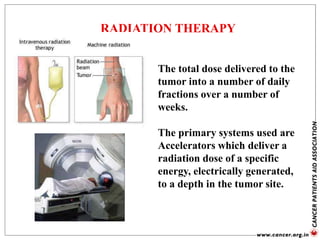
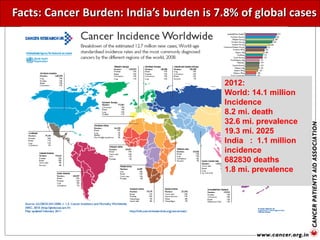
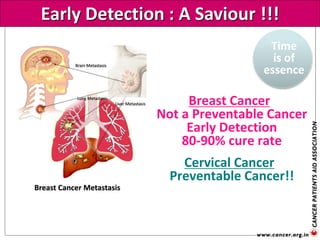
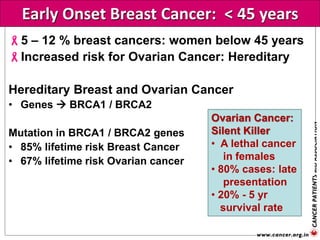
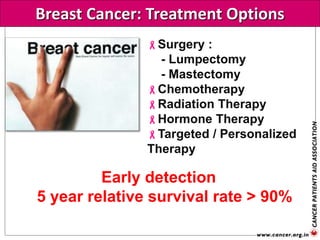
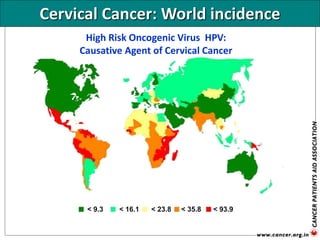
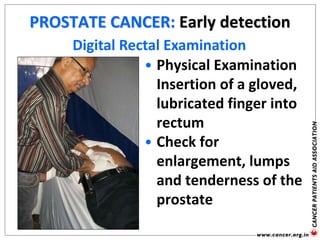
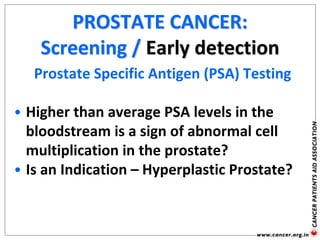
The document provides an extensive overview of cancer awareness, prevention, early detection, treatment options, and support systems in India. It emphasizes the importance of education, stigma removal, insurance for patients, and rehabilitation programs, highlighting statistics on cancer incidence and survival rates. Key cancers addressed include breast, cervical, and prostate, with detailed information on risk factors, signs, and prevention strategies.










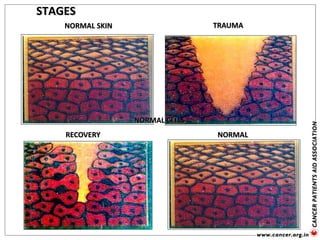
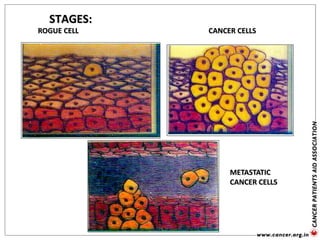
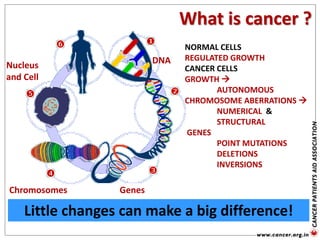
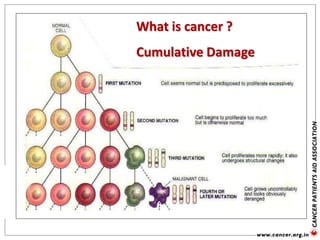





































![Genetic Cancer Etiology
Sporadic [70-75%
]
Strong hereditary
component [5-
10% ]
Familial or
Multifactorial [15-20%
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cancerawareness2014-150806060610-lva1-app6892/85/Cancer-Awareness-68-320.jpg)