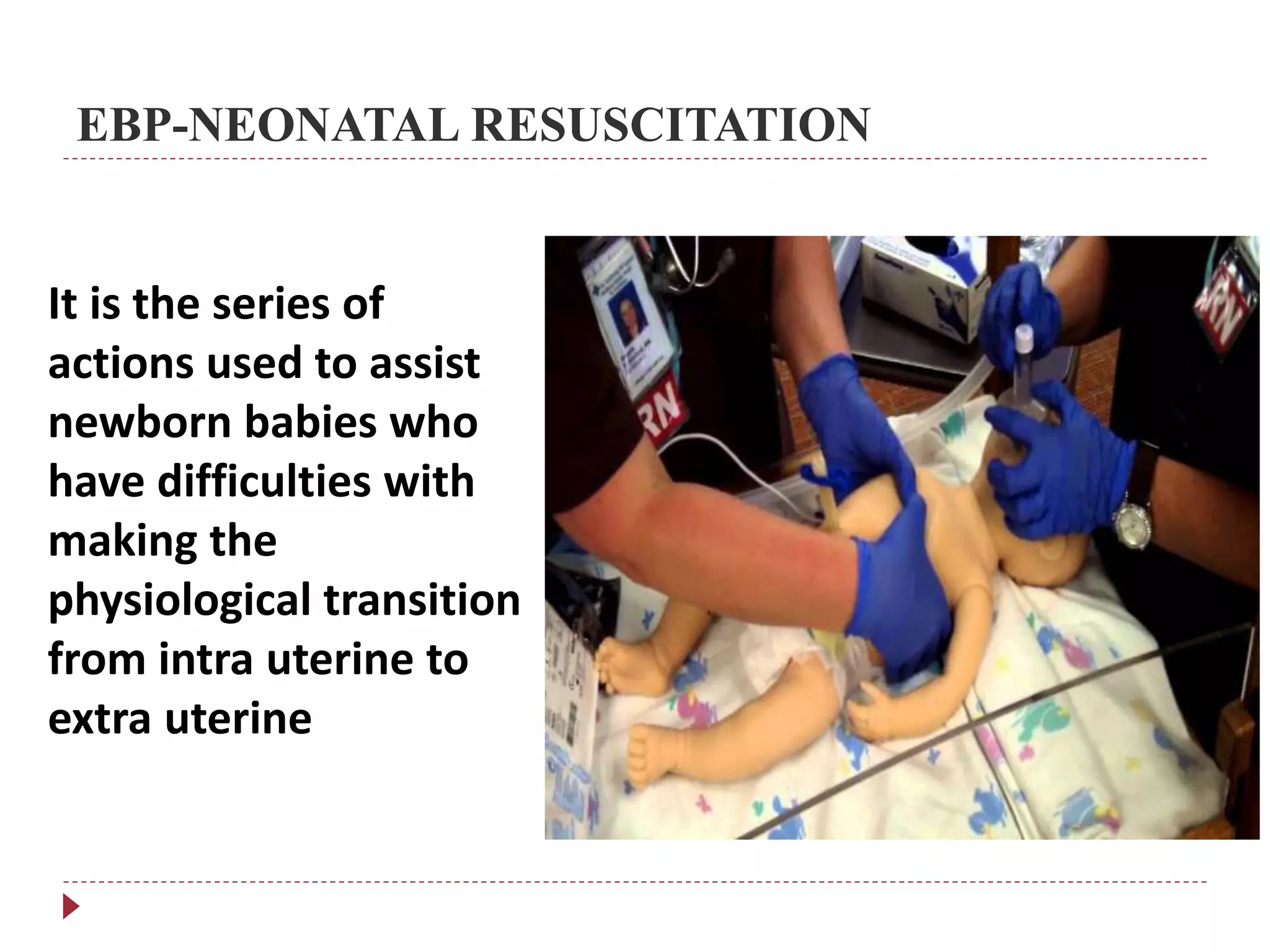
The document discusses evidence-based neonatal care, highlighting the significant risk of newborn deaths occurring within the first 28 days of life, primarily due to factors such as preterm birth and birth complications. It outlines the India Newborn Action Plan aimed at reducing neonatal mortality rates by 2030 and emphasizes the importance of quality antenatal care and skilled attendance at birth. Furthermore, it covers best practices for neonatal resuscitation, thermoregulation, and promotes innovations to enhance maternal and infant health.