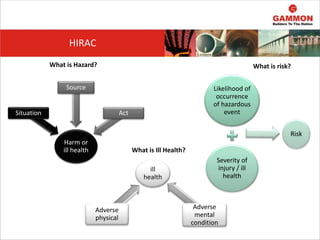
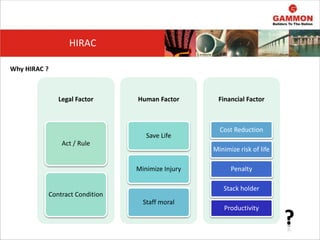
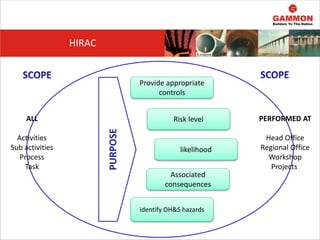
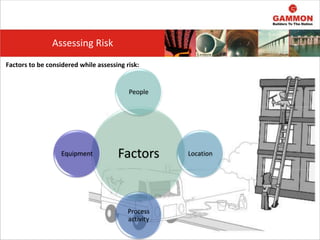
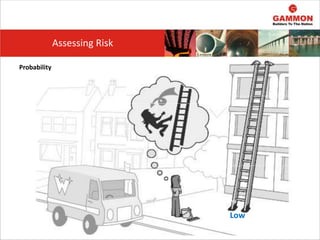
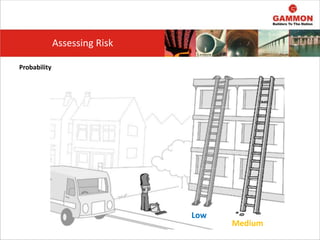
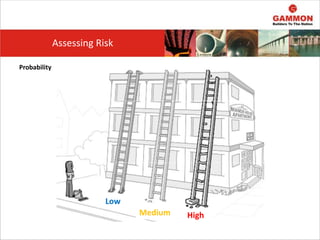
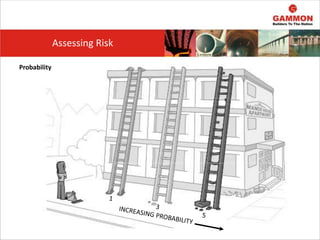
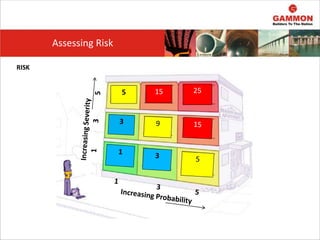
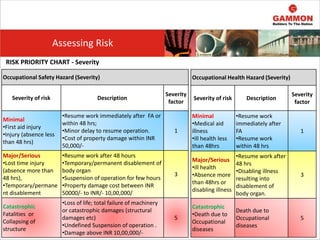
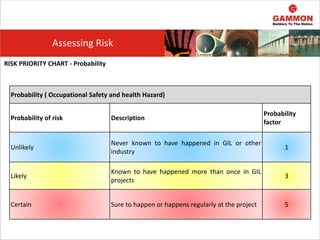
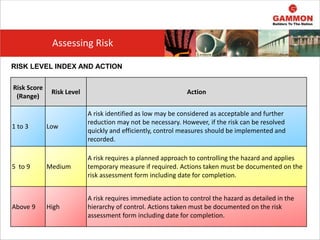
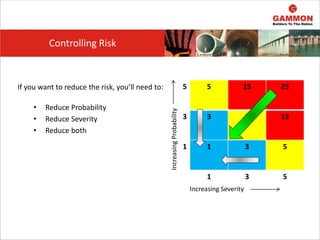
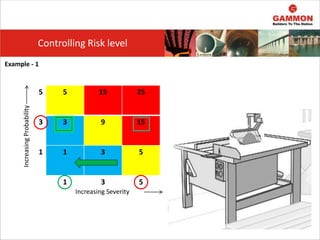
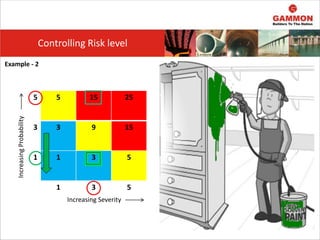
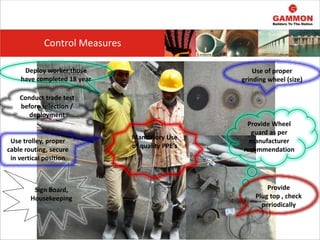
This document provides information on Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Control (HIRAC). It defines risk, hazard, and ill health. It explains why HIRAC is important from both legal and financial perspectives. Key aspects of risk assessment are discussed, including factors to consider, evaluating likelihood and severity, and developing a risk matrix. The hierarchy of controls for reducing risk is outlined. Examples of potential hazards, consequences, and control measures are given. Guidance is provided on reviewing risk assessments, including triggers for when a review is needed. Related HIRAC procedures and documentation are listed.