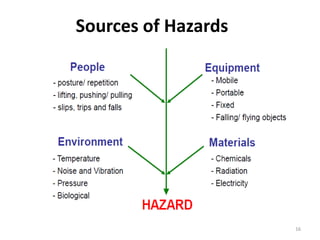
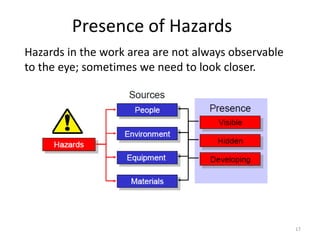
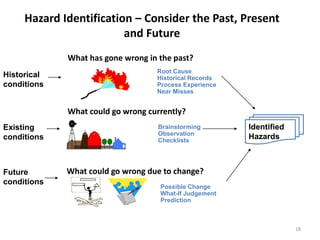
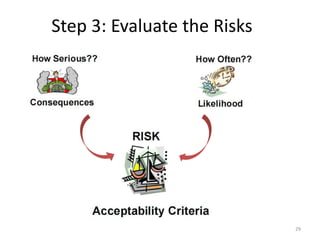
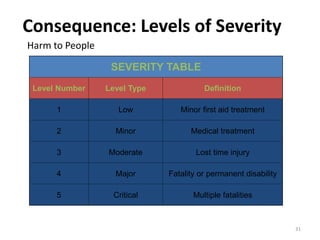
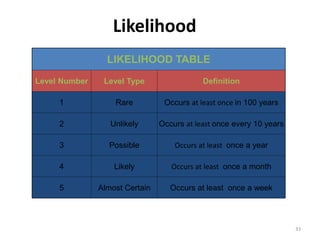
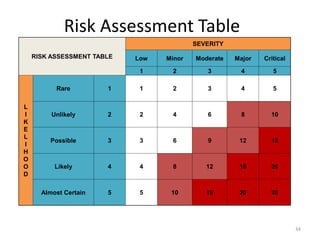
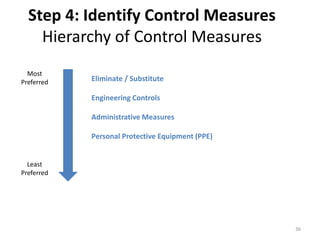
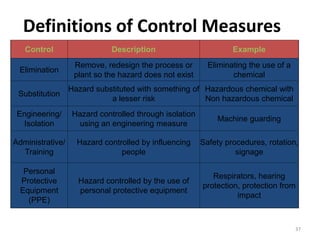
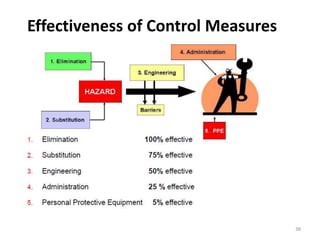
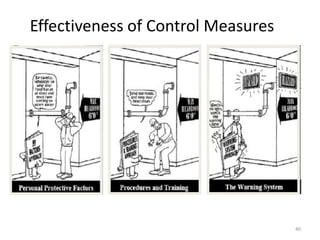
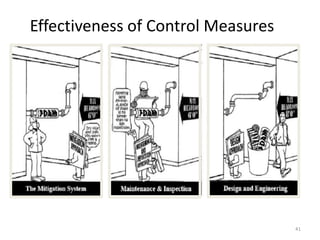
The document outlines the objectives and processes of hazard identification and risk assessment (HIRA), emphasizing the importance of recognizing hazards and conducting risk assessments to manage risks effectively. It categorizes hazards into ergonomic, physical, chemical, biological, and psychosocial types while detailing the steps involved in risk assessment, including identifying hazards, evaluating risks, and implementing control measures. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of effective communication and training for employees to ensure safety in the workplace.