This document provides an overview of the syllabus for a course on industrial safety engineering. It includes:
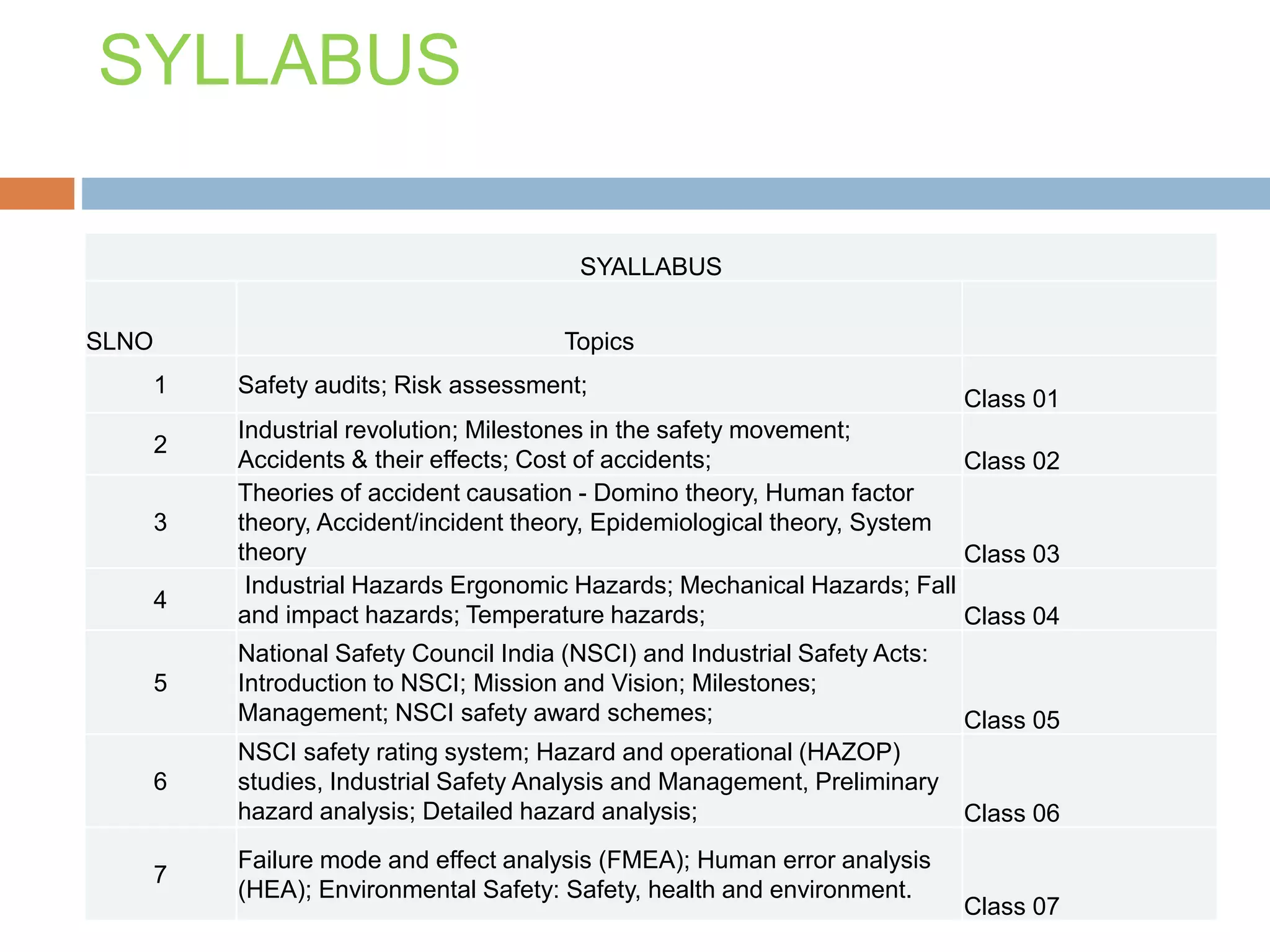
1. A list of 7 topics to be covered in the course, including safety audits, accident causation theories, industrial hazards, and risk assessment methods.
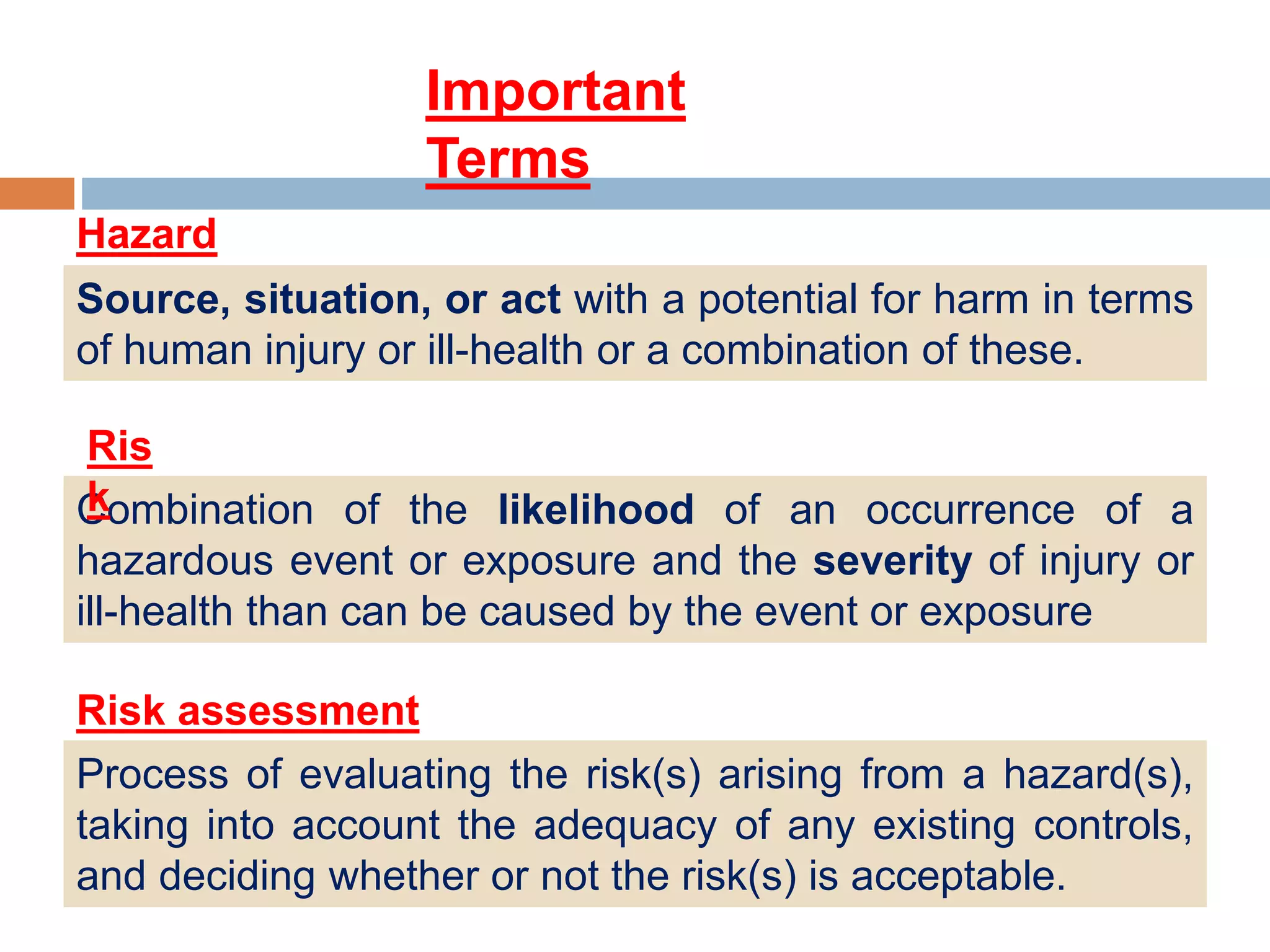
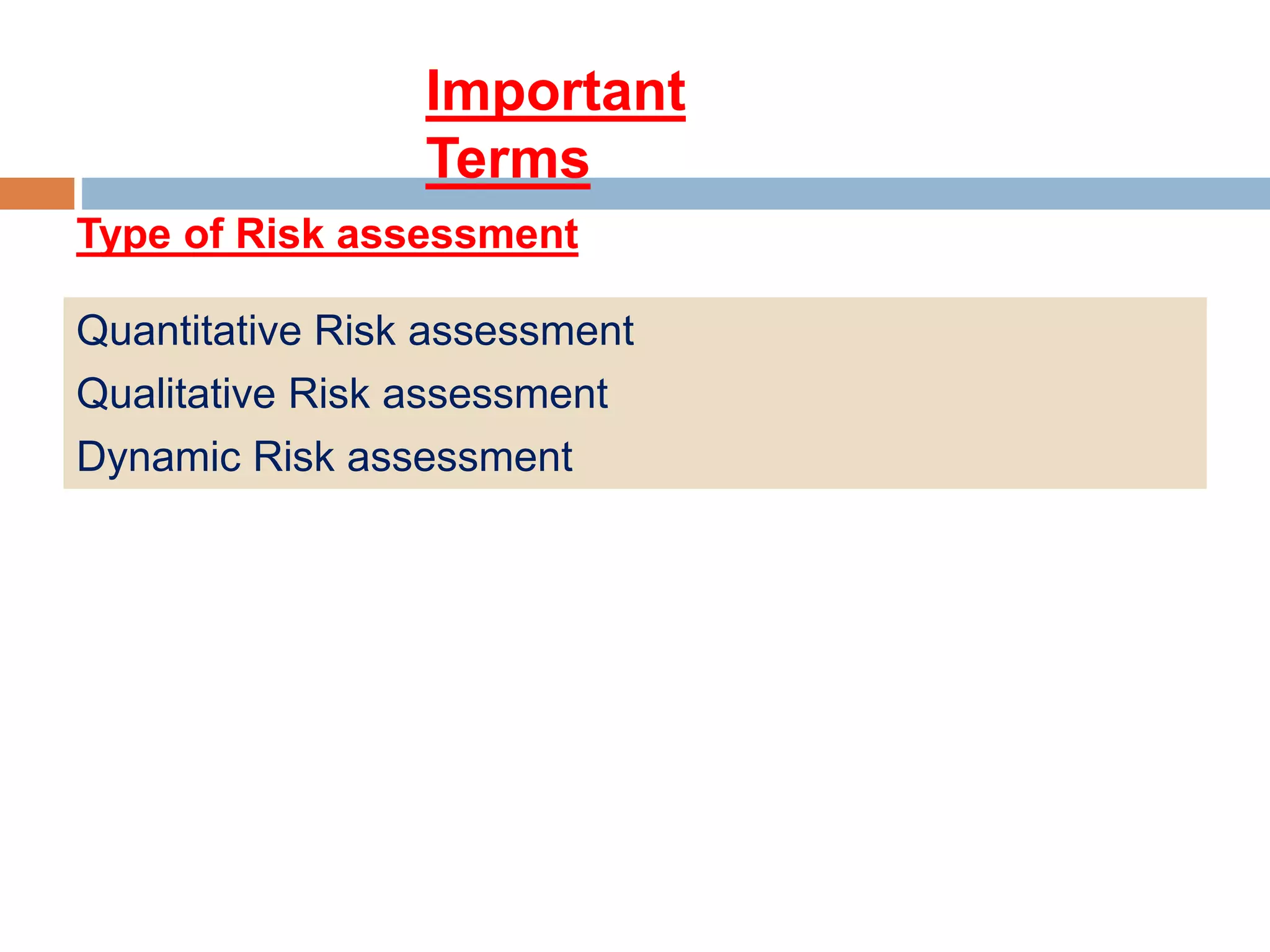
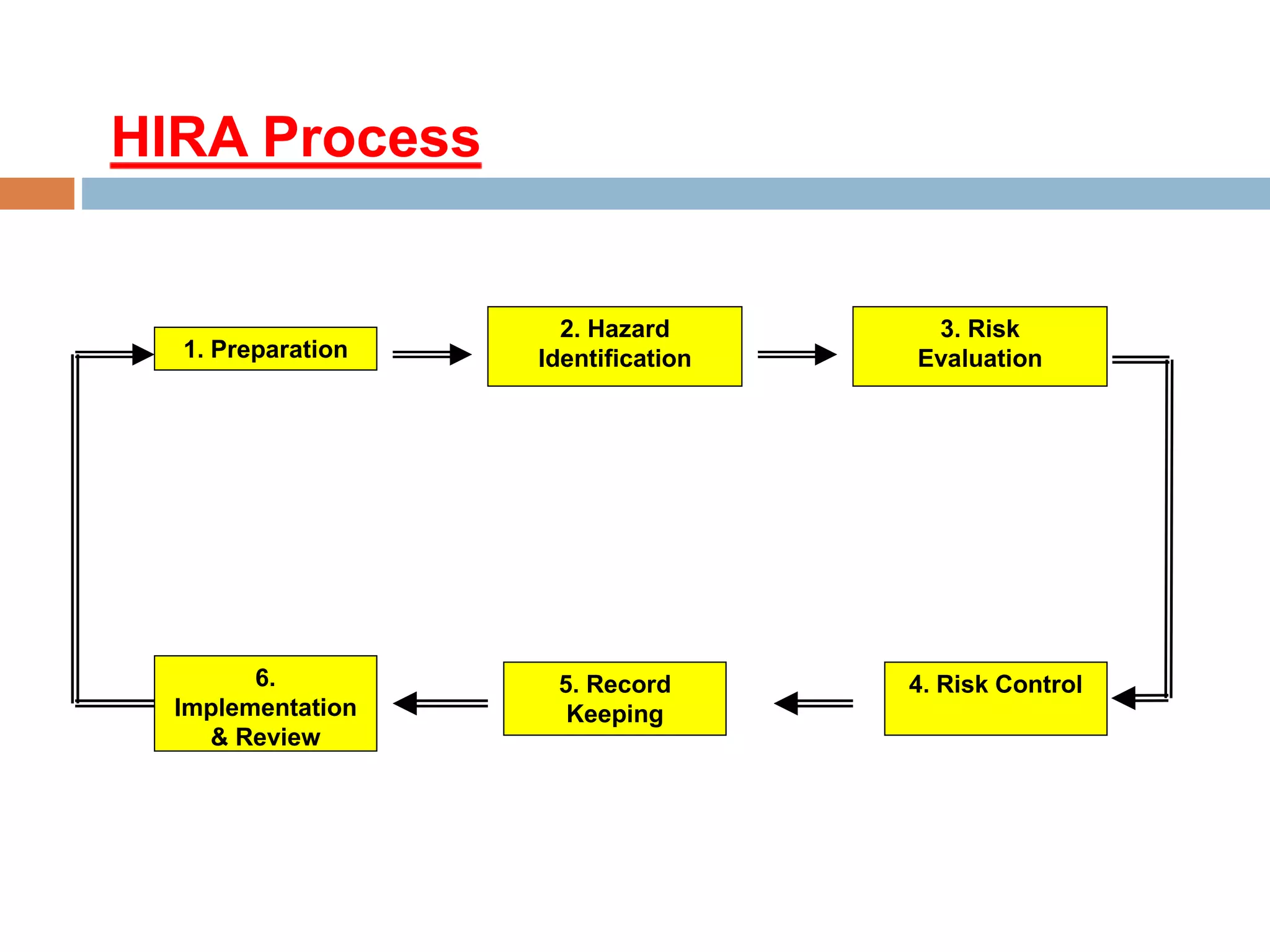
2. Descriptions of key terms related to hazard identification and risk assessment, such as hazard, risk, risk assessment types, and the risk assessment process.
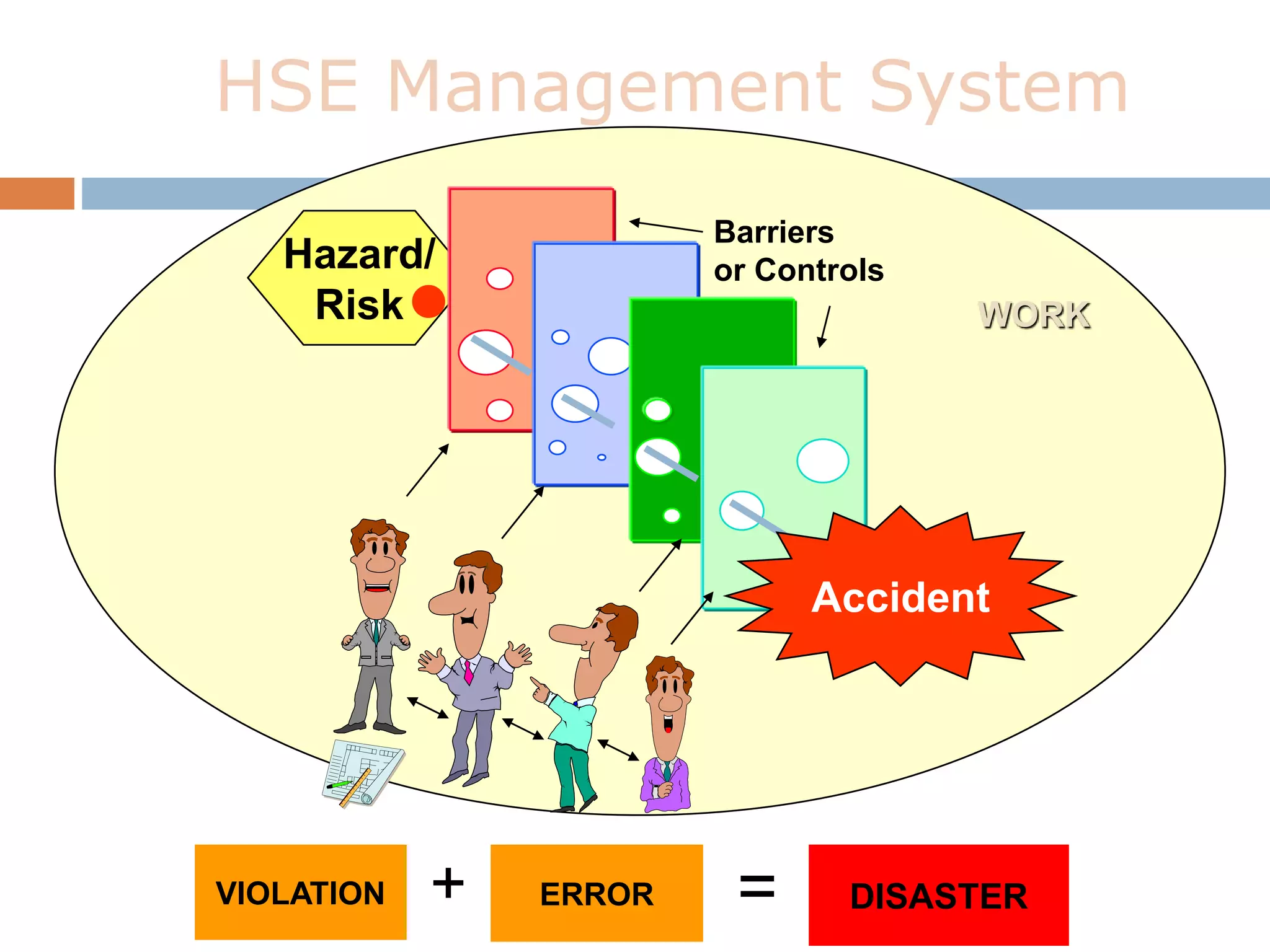
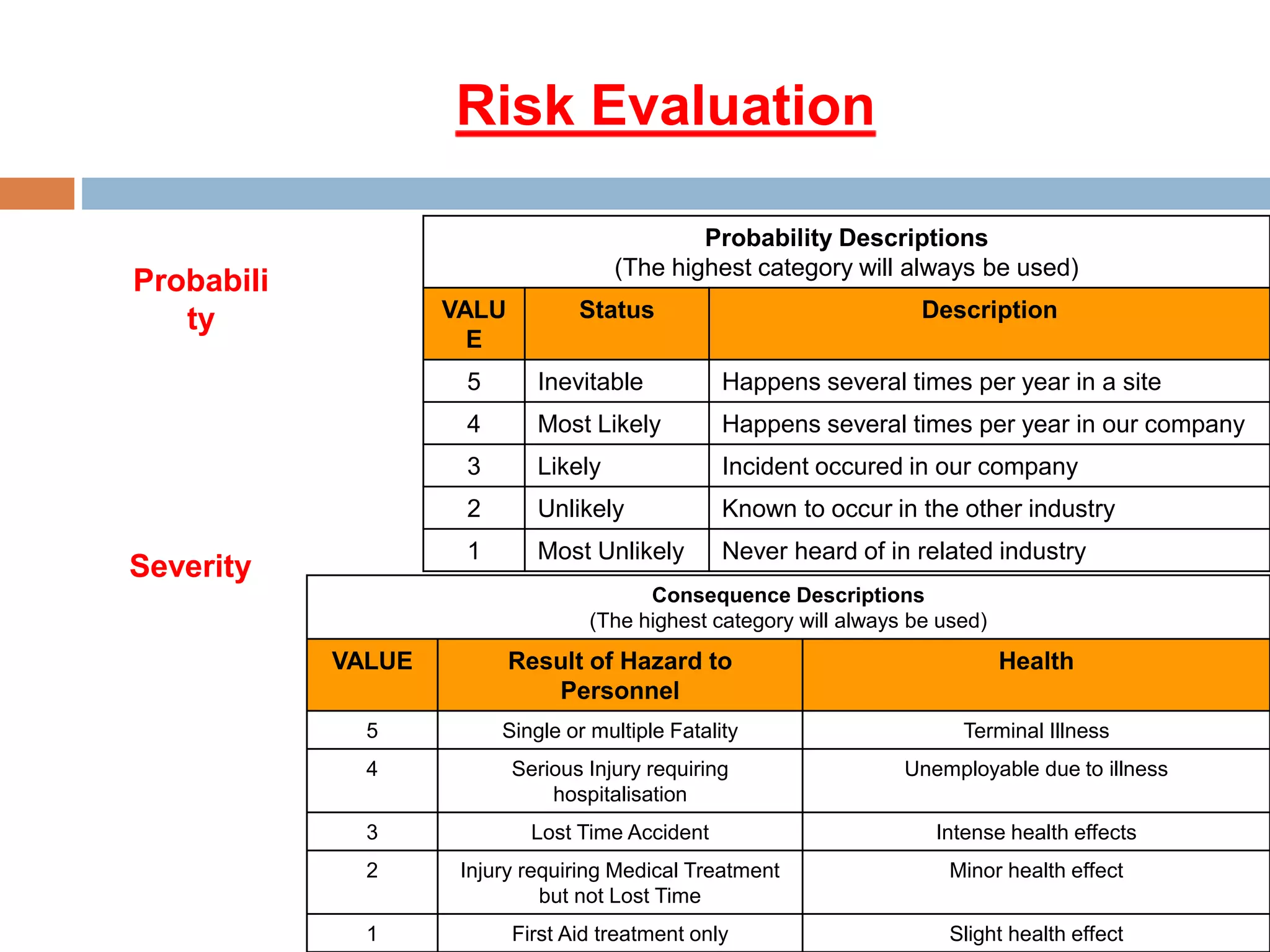
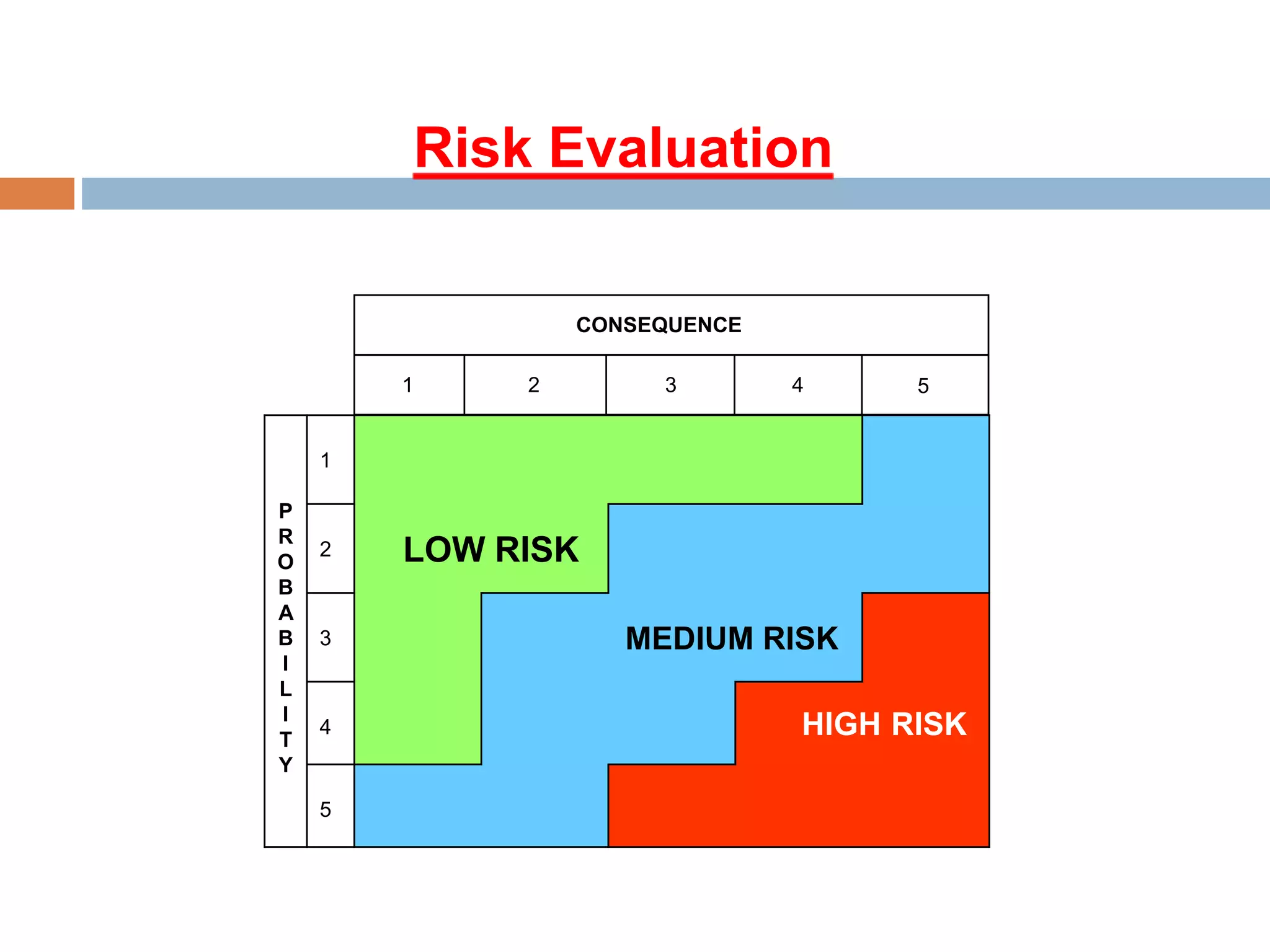
3. An explanation of the risk evaluation process, including assessing probability and severity of hazards to determine risk levels.
4. An overview of risk mitigation measures and the hierarchy of hazard controls.
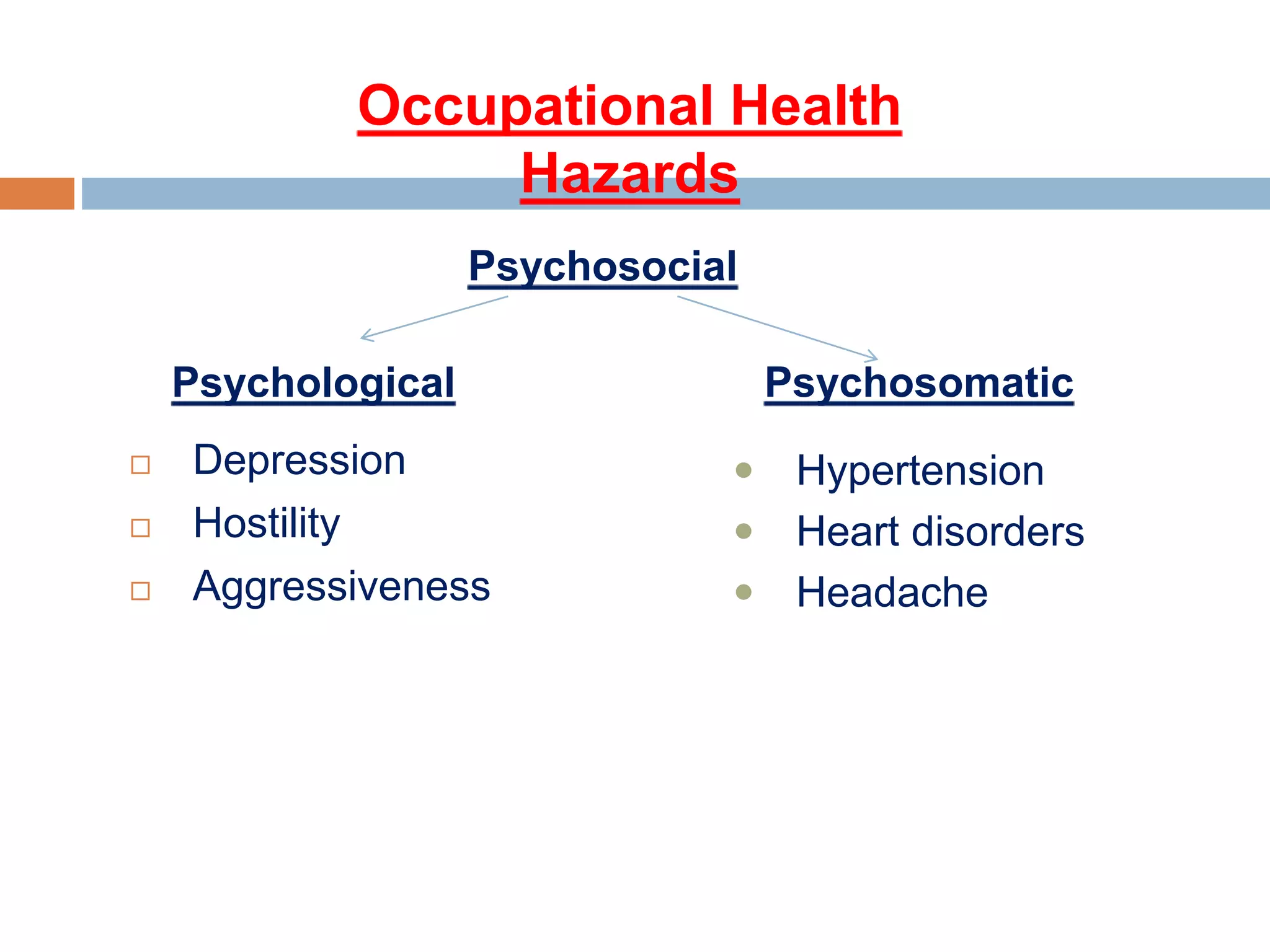
5. A review of occupational health hazards including physical, chemical, biological,