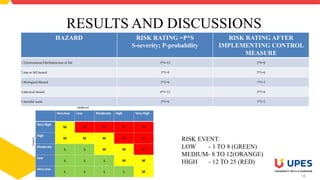
This document outlines the methodology for conducting a hazard identification and risk assessment (HIRA). It describes the objectives of a HIRA as helping to prepare for the most likely hazards, isolate any hazards that cannot affect the community, and create emergency plans based on high risk scenarios. The methodology involves identifying hazards, assessing their risks through analysis of frequency and consequences, determining control measures, implementing controls, and ongoing monitoring and review. As an example, several hazards identified for one site are listed along with their original and residual risk ratings after implementing controls.