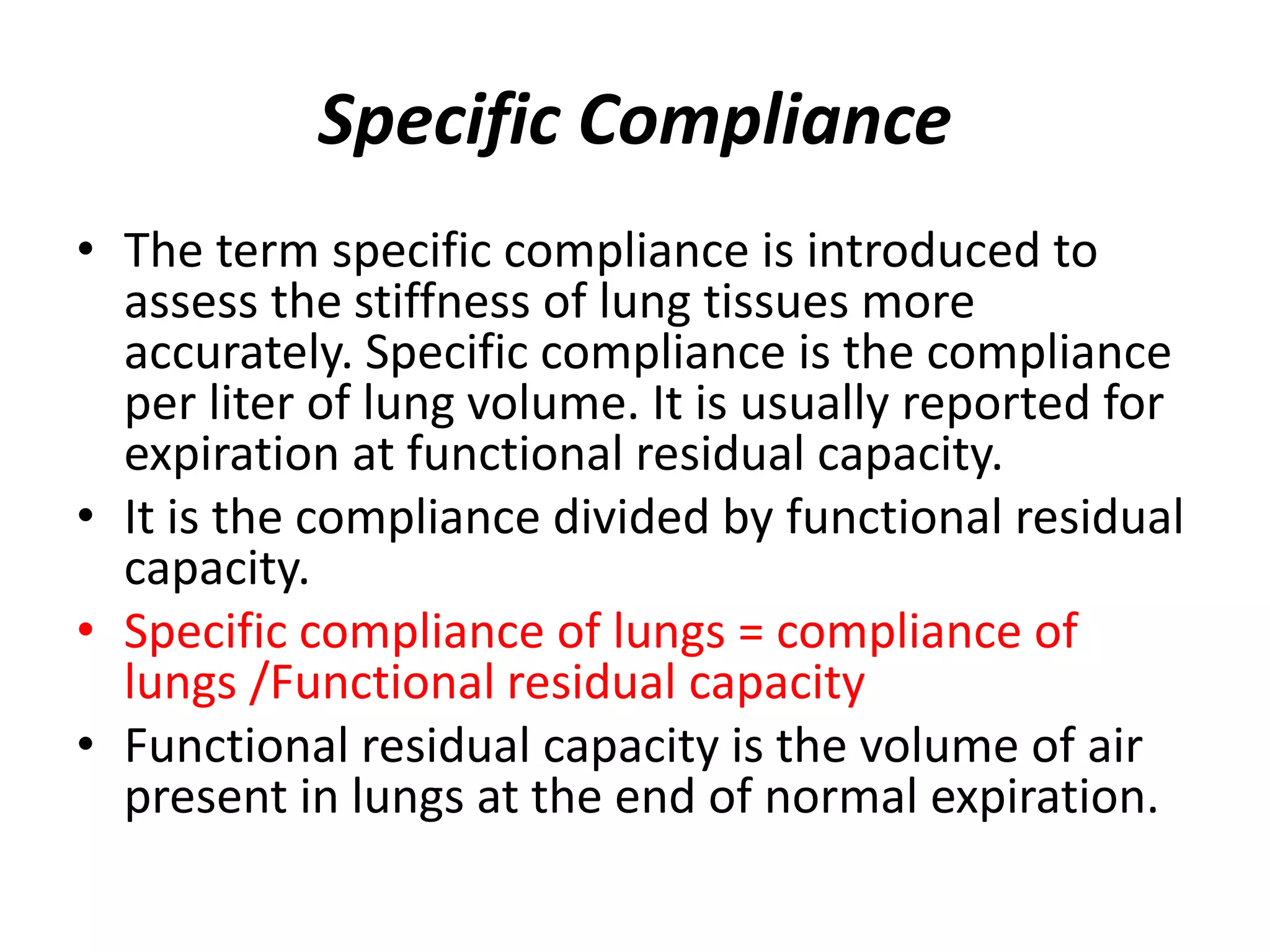
Compliance refers to the expansibility of the lungs and thorax, or the change in their volume with changes in pressure. Determining compliance provides a measure of lung stiffness. Normal compliance values are 130 mL/1 cm H2O for lungs and thorax together and 100 mL/1 cm H2O for lungs alone. Compliance can be measured statically without breathing or dynamically during breathing, and diseases may decrease dynamic compliance more than static compliance. Compliance is measured by determining volume and pressure changes in the lungs during inspiration and expiration.