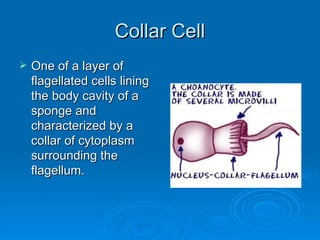
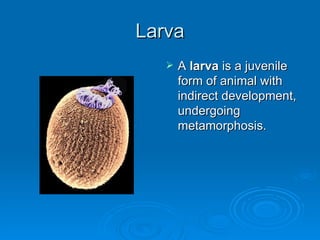
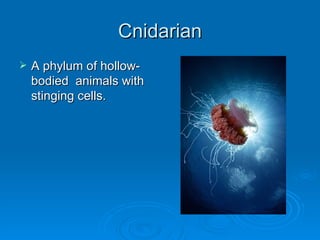
Sponges and cnidarians are sessile animals that are permanently attached and feed by filtering suspended particles and food from water. They have structures like collar cells, tentacles, and the ability to regenerate lost parts. Some are hermaphrodites and have both male and female reproductive organs. Their life cycle involves larval and polyp or medusa forms.