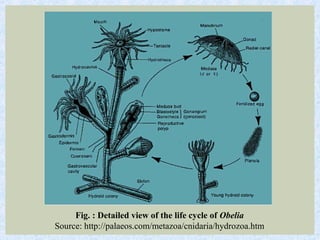
Metagenesis is a life cycle where a diploid asexual phase alternates with another diploid sexual phase, as seen in Obelia. Obelia exists as polyps that reproduce asexually through budding, producing medusa that are sexual and free-swimming. The medusa then sexually reproduce to form new polyps, completing the alternation between the two diploid phases known as metagenesis. Polymorphism in Obelia results in three distinct types of individuals - nutritive polyps, asexual reproductive polyps, and sexual reproductive medusa - that have different structures and functions.