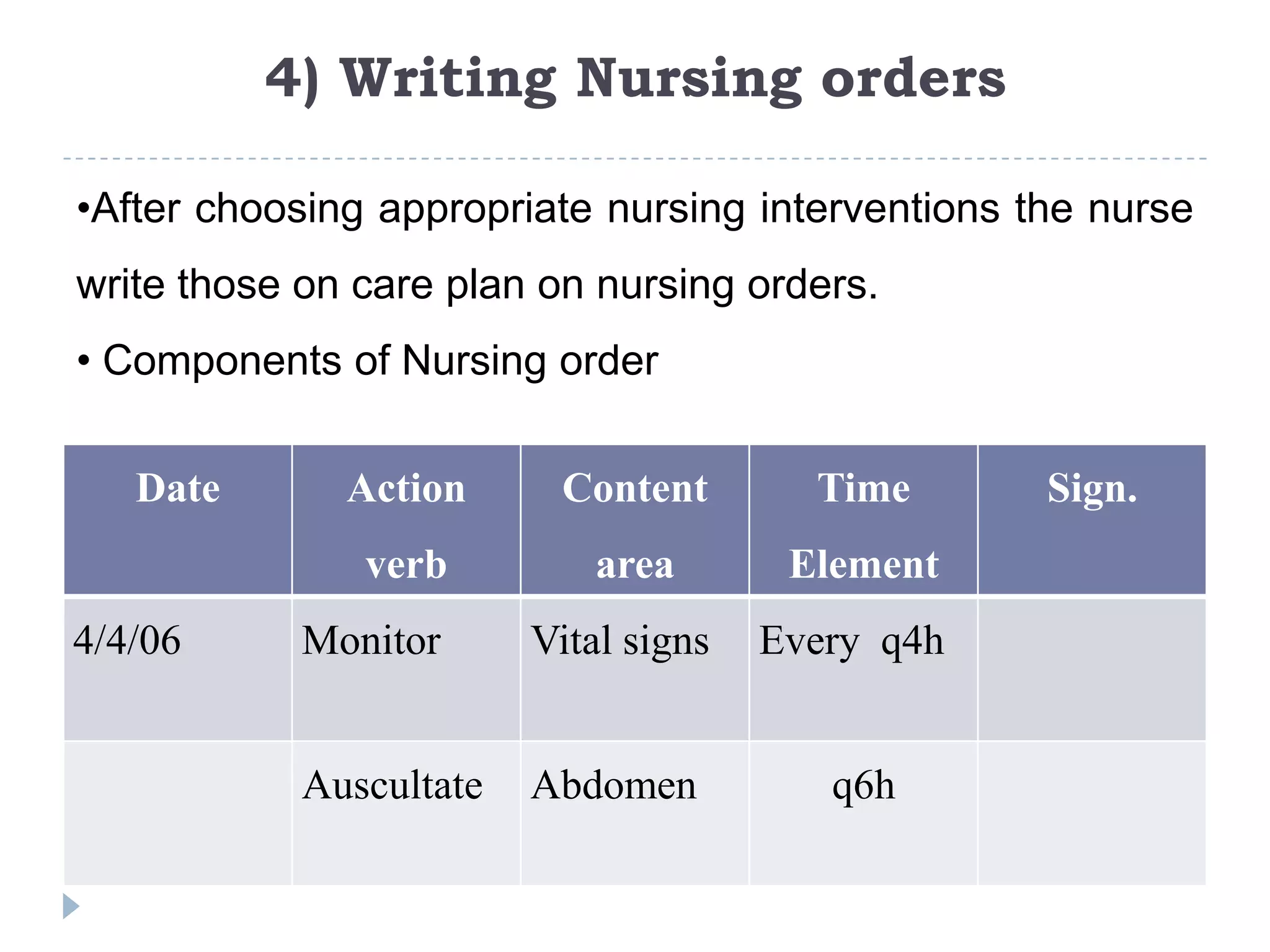
This document discusses the planning phase of the nursing process. Planning involves setting priorities, establishing goals, and selecting interventions. It describes initial planning, ongoing planning, and discharge planning. Guidelines are provided for developing different types of nursing care plans such as informal, formal, standardized, and individualized plans. The planning process involves setting priorities, establishing goals and desired outcomes, selecting nursing interventions, and writing nursing orders.


![Types of Planning
1] Initial planning
2] Ongoing Planning
3] Discharge planning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-3-2048.jpg)
![1] Initial planning
Admission assessment based on the initial care.
As nurse obtain new information and evaluate the
clients responses to care, they can individualize the
initial care plan further.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-4-2048.jpg)
![2] Ongoing Planning
Done by all nurses who work with the client.
Ongoing planning also occurs at the beginning of a
shift as the nurse plans the care.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-5-2048.jpg)
![3] Discharge planning
Is the process of anticipating and planning for needs
after discharge,
Is a crucial part of comprehensive health care and
should be addressed in each client’s care plan to be
given that day.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-6-2048.jpg)
![Purposes of ongoing planning
1] To determine any changes in client’s health status.
2] To set priorities for the client’s care
3] To decide which problems to focus on during the
shift
4] To Co-ordinate the nurse’s activities so that more
than one problem can be addressed at each client
contact.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-7-2048.jpg)





![Guidelines for writing Nursing Care plans
1] Date and sign the plan
2]Use category headings assessment/ nursing diagnoses/
planning /Implementation /Evaluation.
3] Use standardized Medical or English symbols and key
words rather than complete sentences to communicate
your ideas.
Eg. Clean wound with H2O2 b.i.d rather than “clean the
client’s wound morning & evening with Hydrogen
peroxide twice a day.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-13-2048.jpg)
![Guidelines for writing Nursing Care plans
4] Be specific. Because Nurses are now working shifts
of different lengths, some working 12 hrs. & some
working 8 hour shifts it is even more to be specific
about expected timing of an intervention. If the order
reads “change incision dressing q shift”
5] Refer to procedure books or other sources of
information rather than including all the steps on a
written plan.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-14-2048.jpg)
![Guidelines for writing Nursing Care plans
6] Tailor the plan to the unique characteristics of the
client by ensuring that the client’s choices, such as
preferences about the times of care & the methods
used are included.
7] Ensure that the nursing plan incorporates preventive
and health maintenance aspects as well as
restorative ones.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-15-2048.jpg)
![Guidelines for writing Nursing Care plans
8] Ensure that the plan contains interventions for
ongoing assessment of the client (eg. Inspect
incision q8h)
9] Include collaborative and co-ordination activities in
the plan.
10] Include plans for the client’s discharge and home
care needs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-16-2048.jpg)





![3) Selecting Nursing interventions &
activities
Nursing interventions & activities are the action not a nurse performs to
achieve client goals.
Types of nursing interventions
1] Independent Interventions: - activities that are nurses are licensed to
initiate. Eg. Physical care, ongoing assessment, counseling, Emotional
support, environmental Management.
2] Dependent Interventions: - activities carried out under physicians order.
Eg. Medications, diagnostic tests, diet Activity.
3] Collaborative Interventions: - Nurse carries out in collaboration with other
health team members - Such as physiotherapies social workers, dietitians,
physicians, Eg. Crutch walking.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingprocess-planning-111105020329-phpapp02/75/Nursing-process-planning-22-2048.jpg)