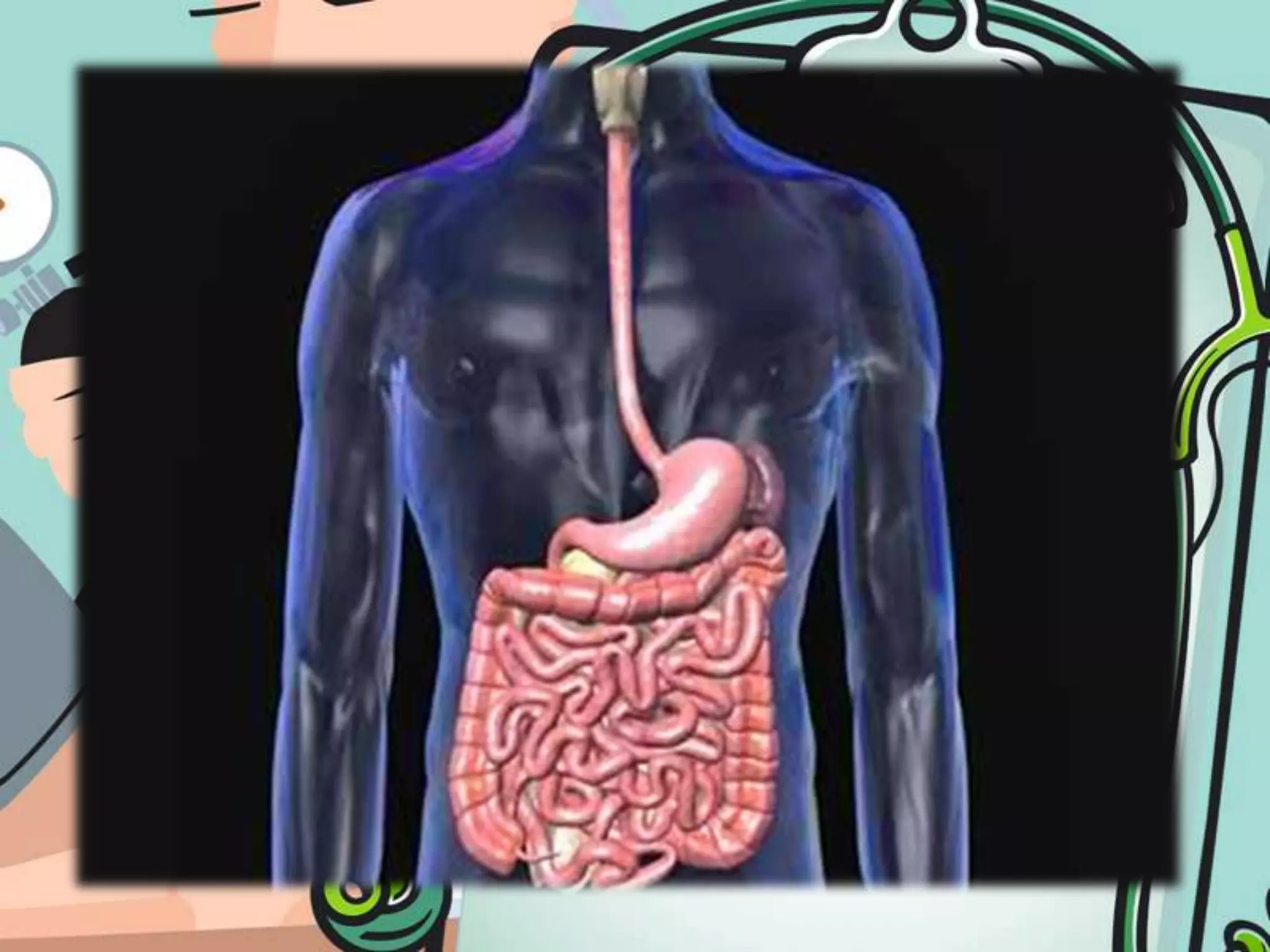
The document provides instructions for placing a nasogastric tube, including preparing the necessary equipment, explaining the procedure to the patient, inserting the tube into the stomach, confirming proper placement, securing the tube, feeding the patient through the tube, and removing the tube. It also describes how to check gastric aspirate to evaluate for abnormalities and how to care for the tube and patient during use of the nasogastric tube.