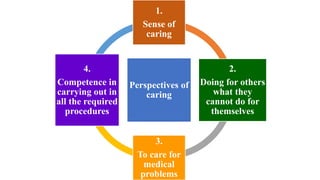
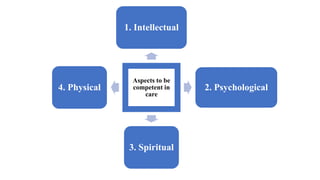
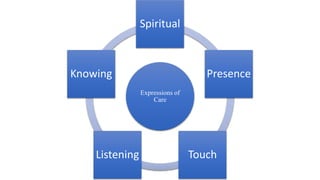
This document discusses the importance of caring in nursing. It defines caring from four perspectives: having a sense of caring, doing for others what they cannot do for themselves, caring for medical problems, and competence in carrying out procedures. The document emphasizes that caring involves being physically present with patients, engaging in dialogue, active listening, maintaining confidentiality, and believing in patients. Caring involves competence in intellectual, psychological, spiritual and physical aspects of care, and can be expressed through spiritual presence, touch, listening and knowing patients.