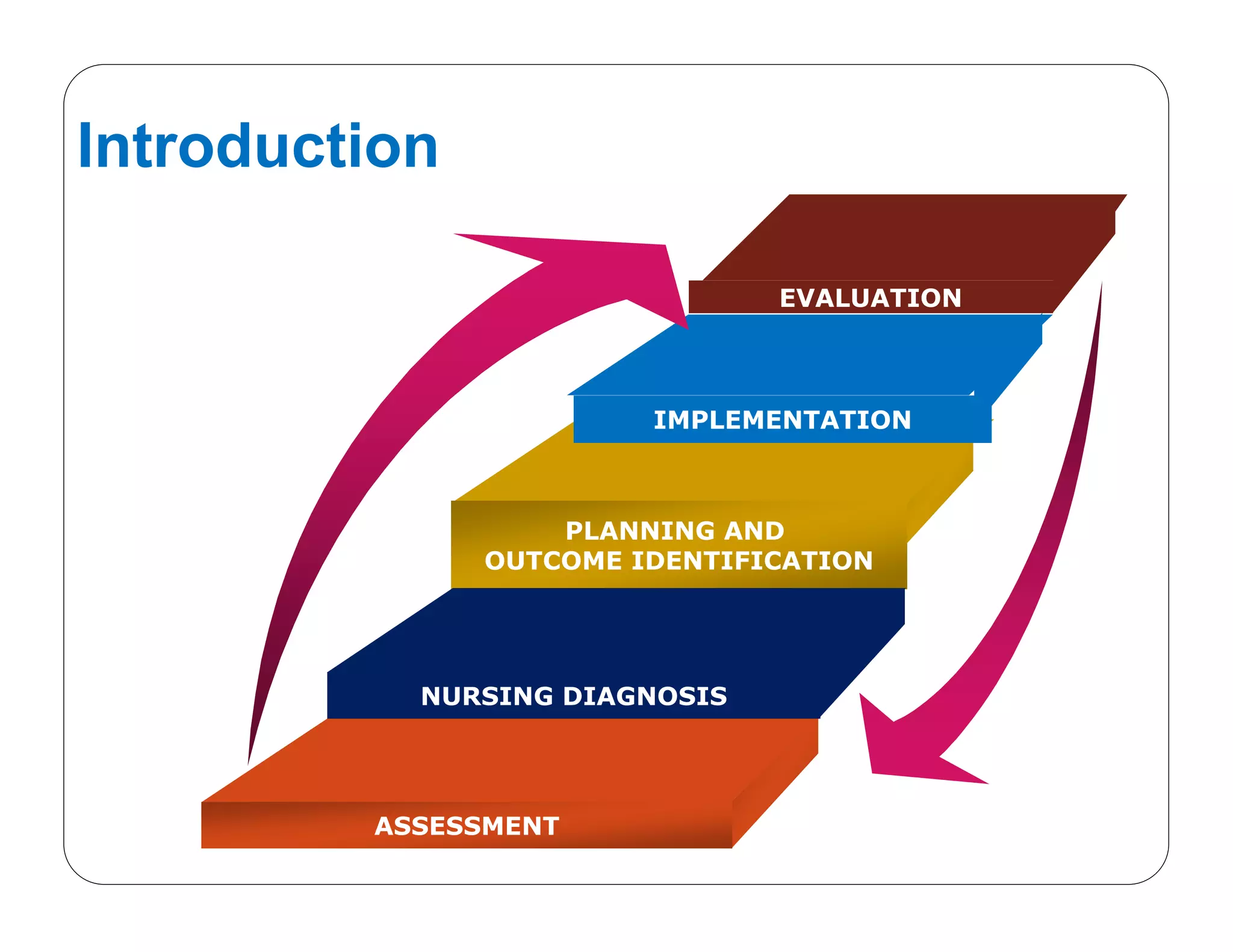
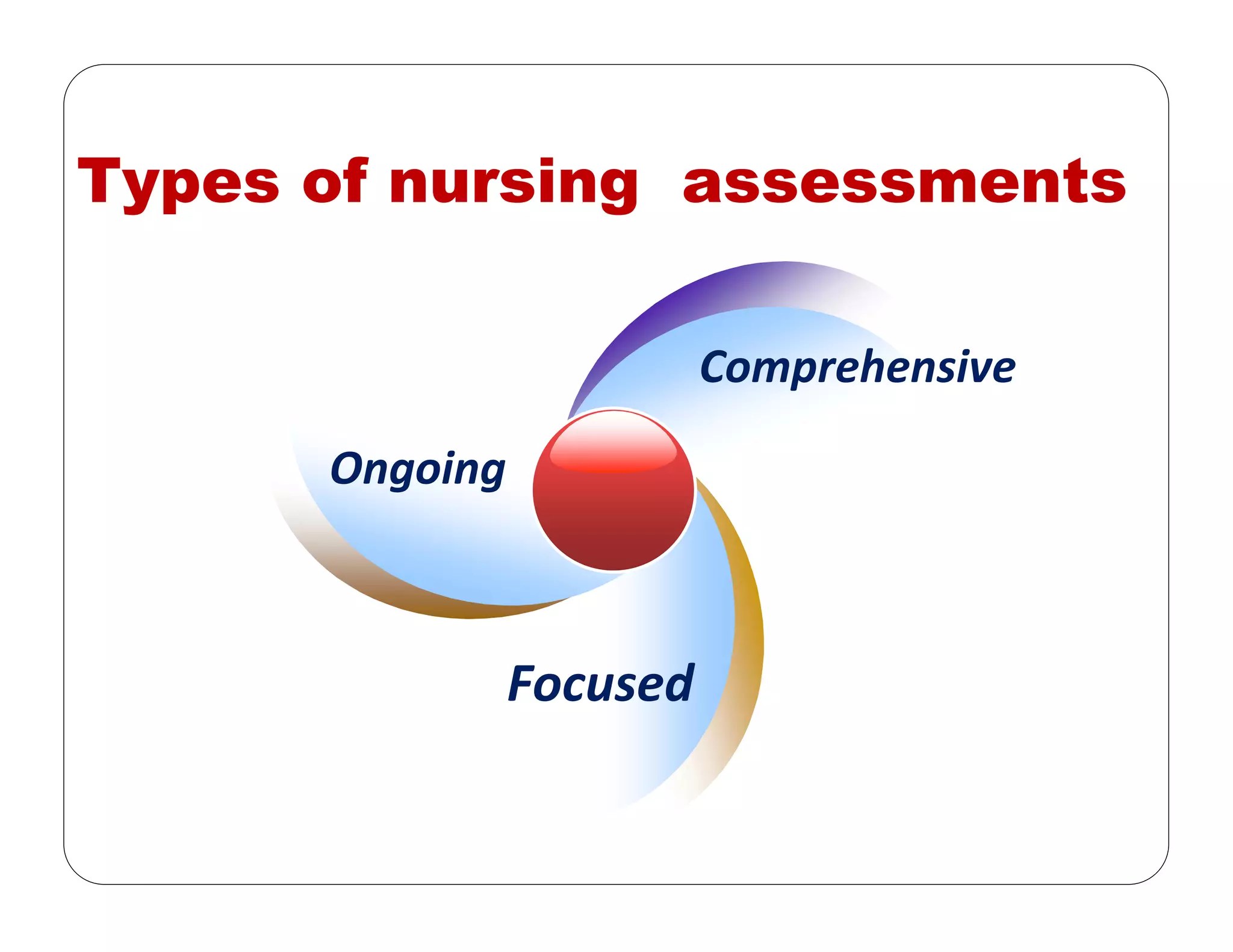
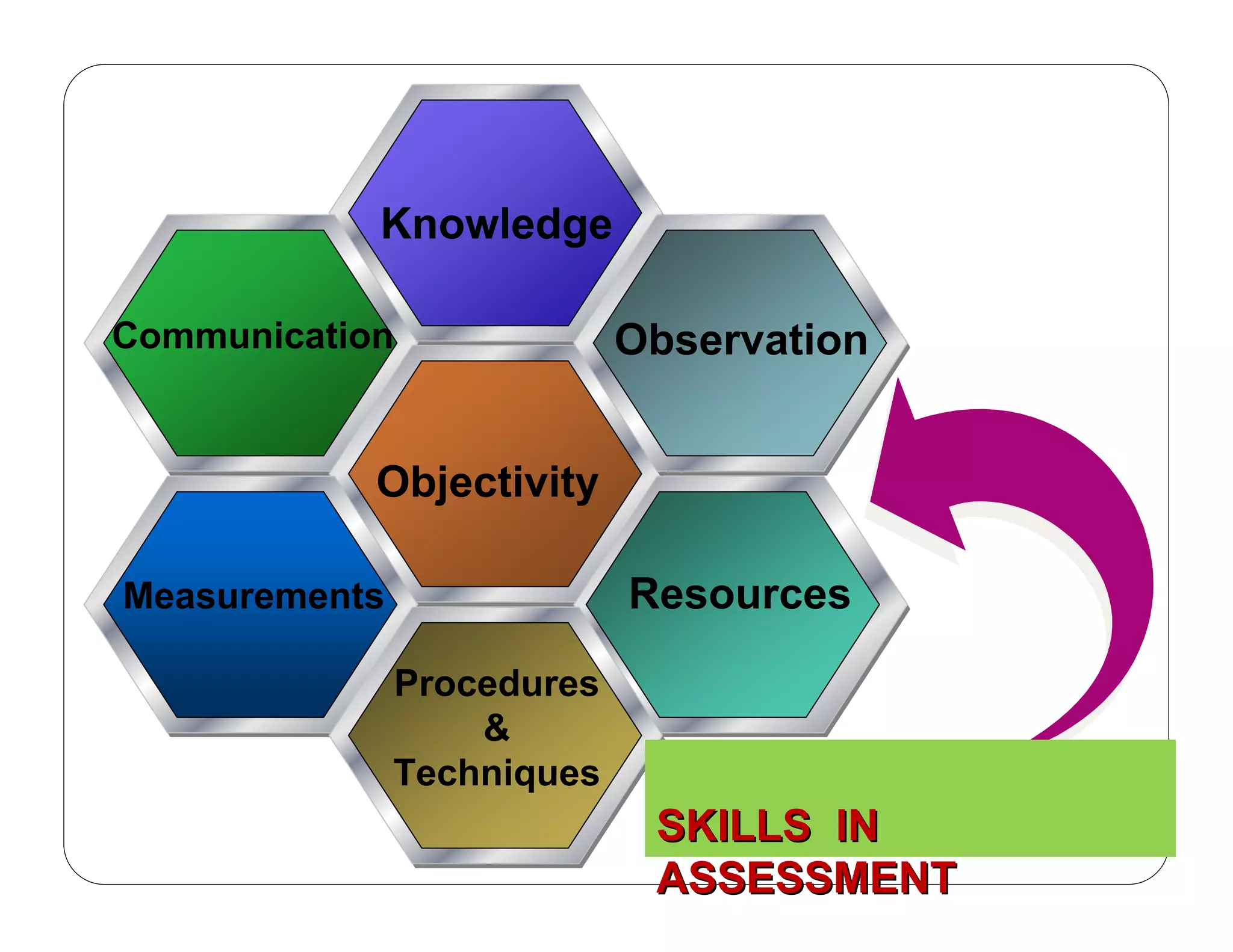
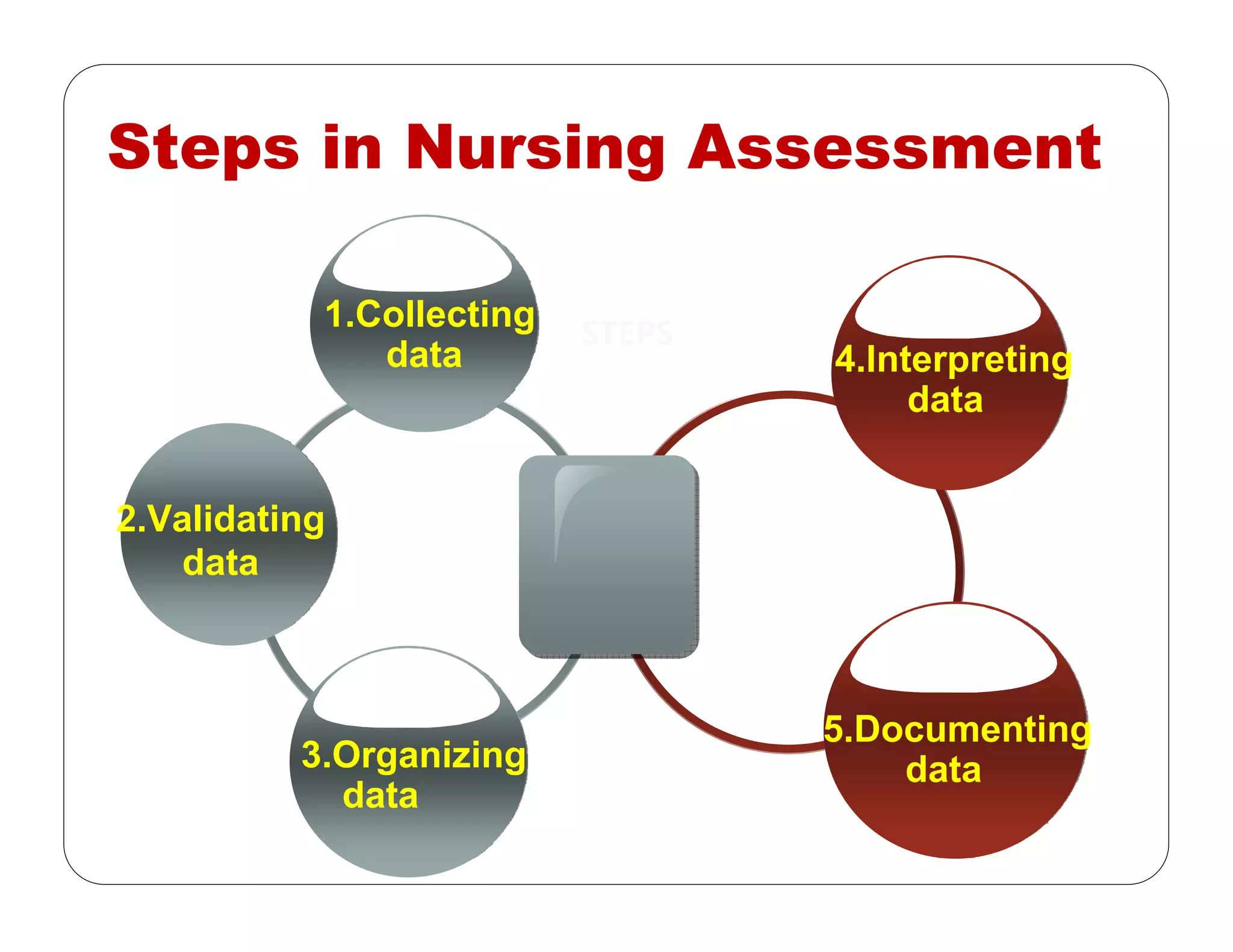
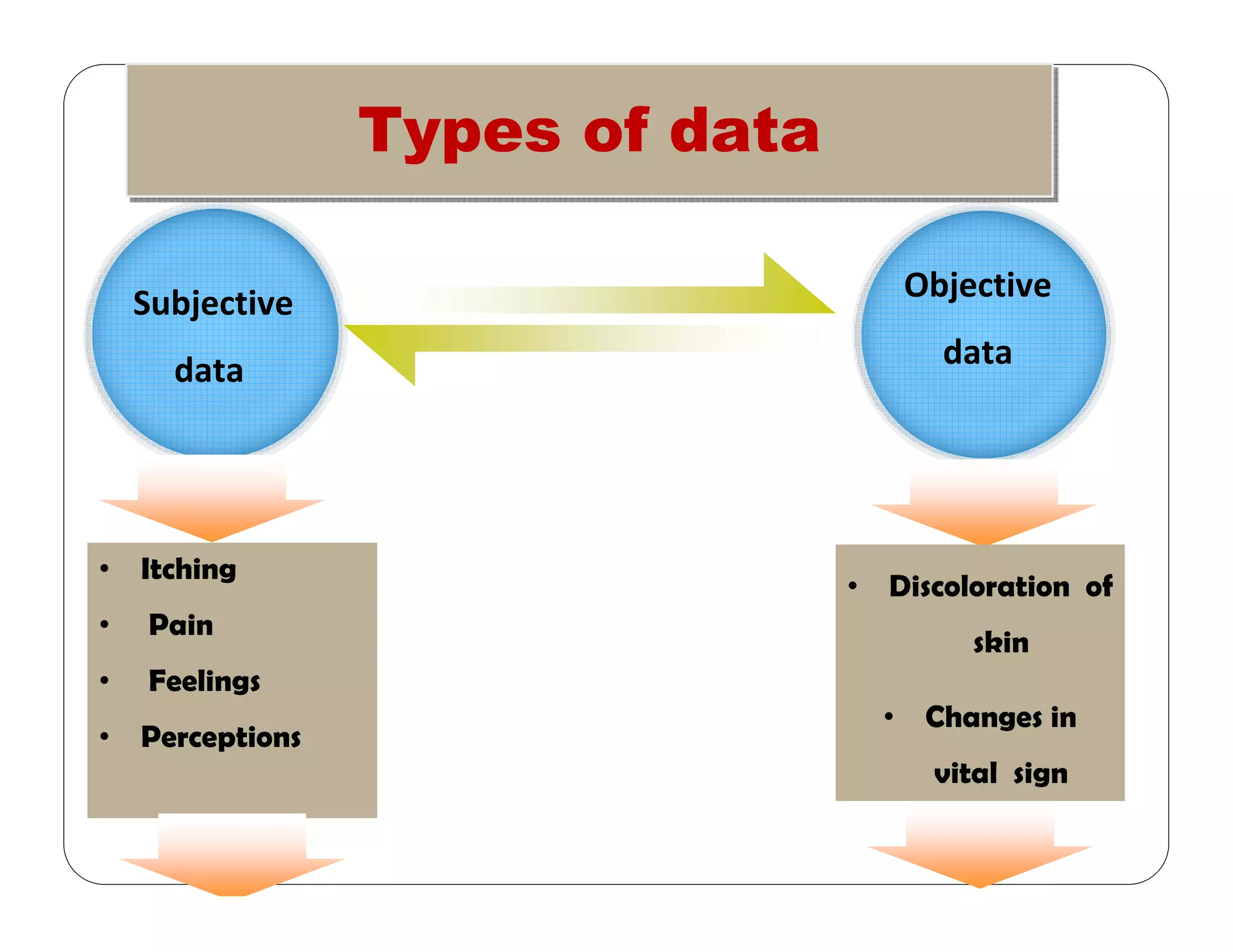
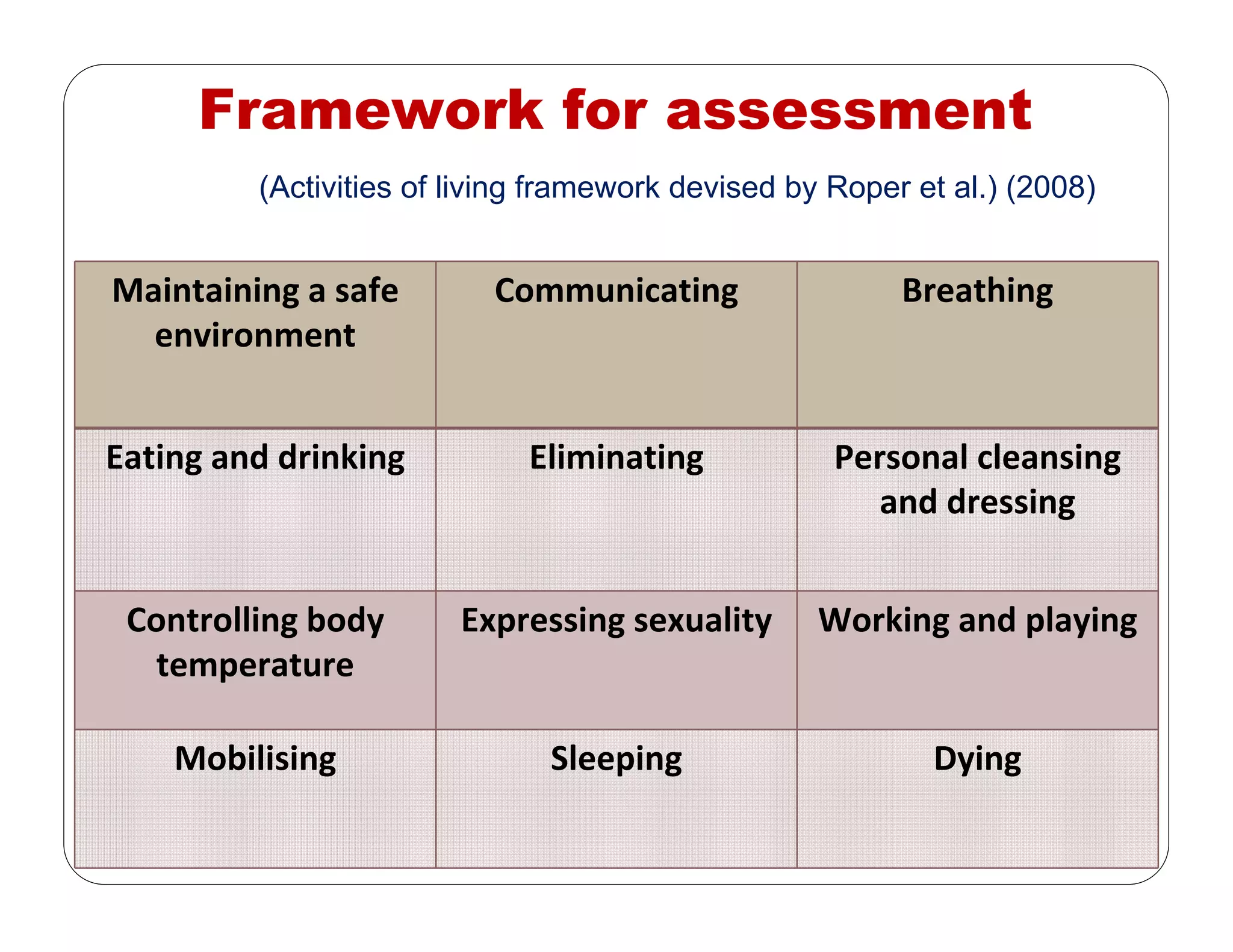
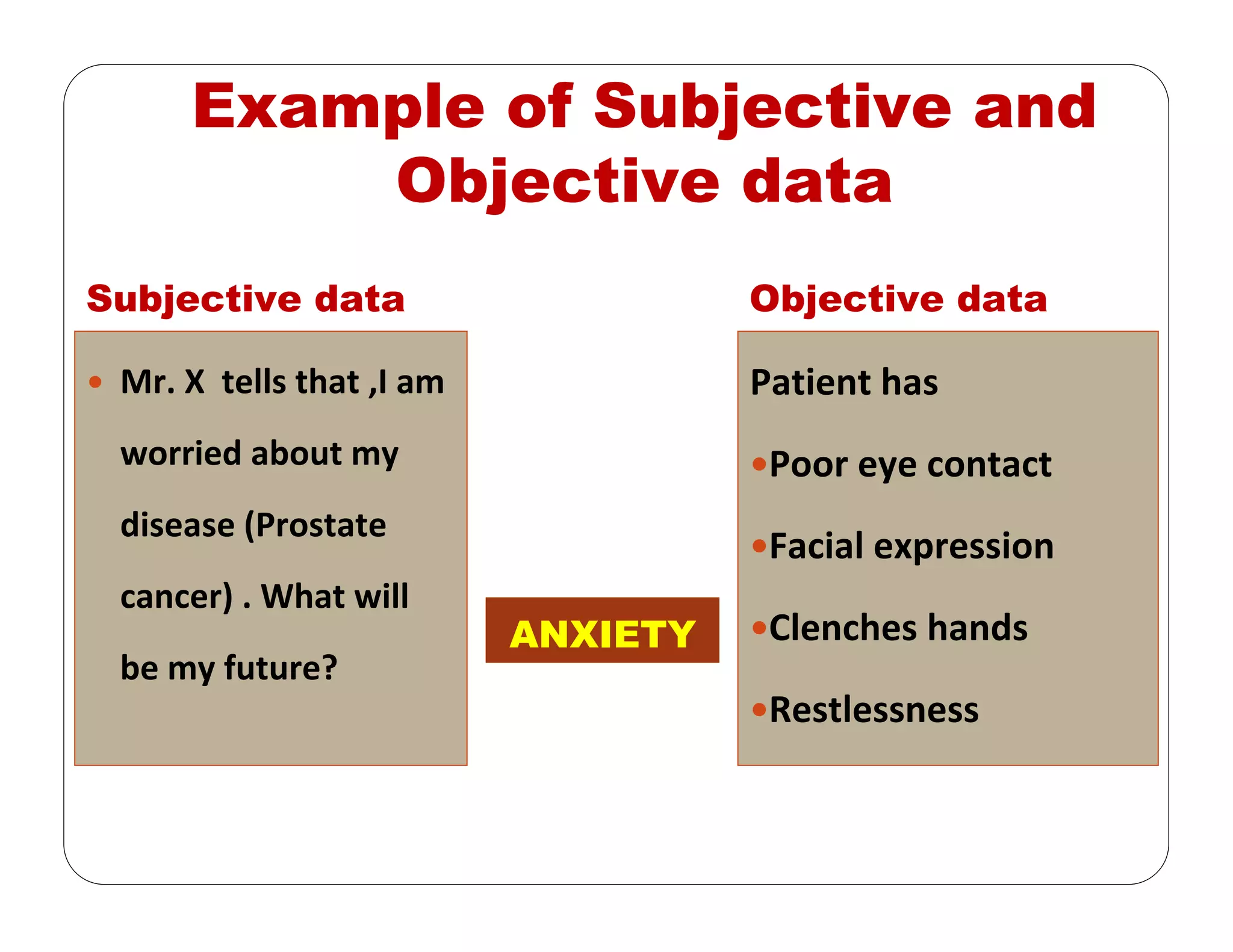
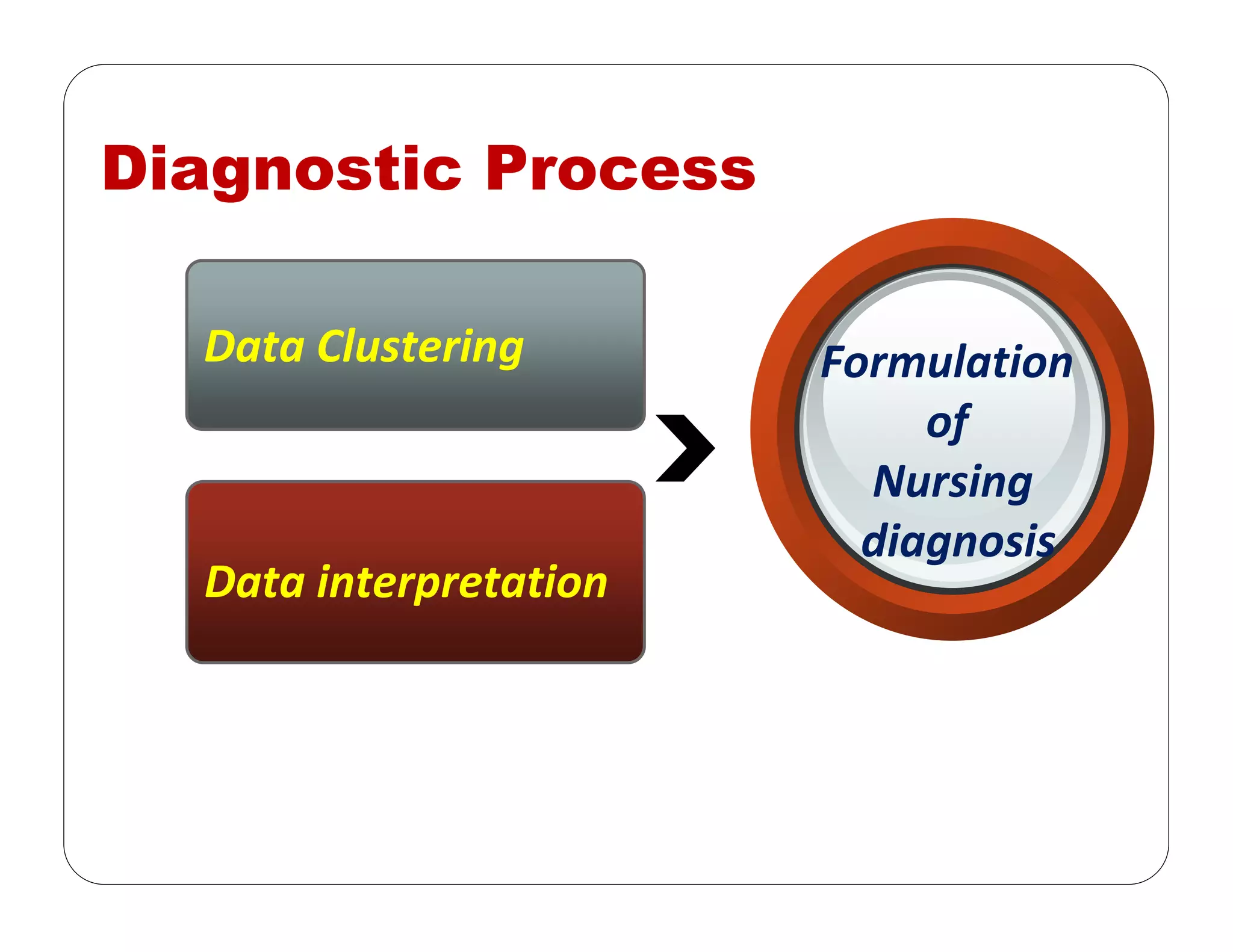
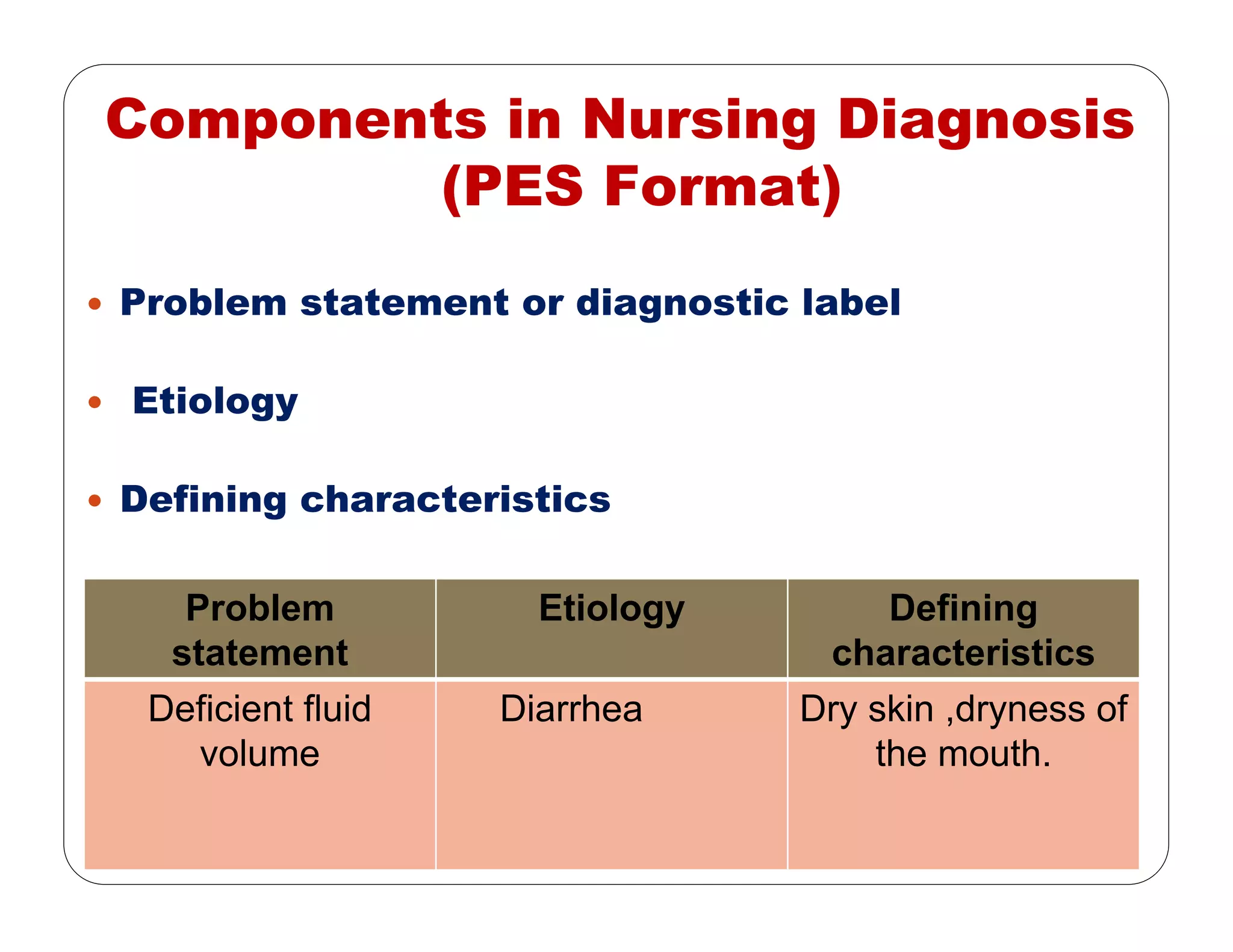
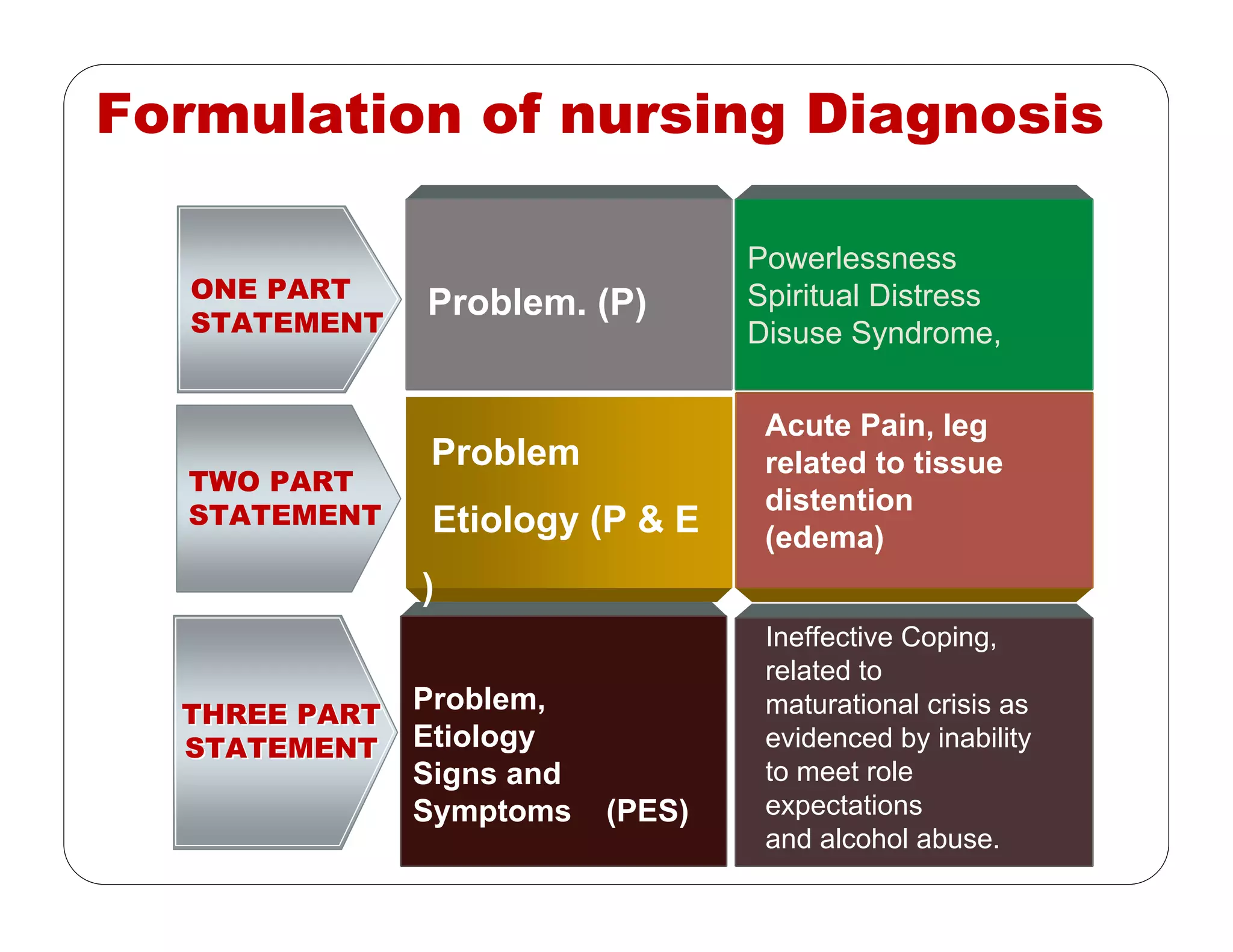
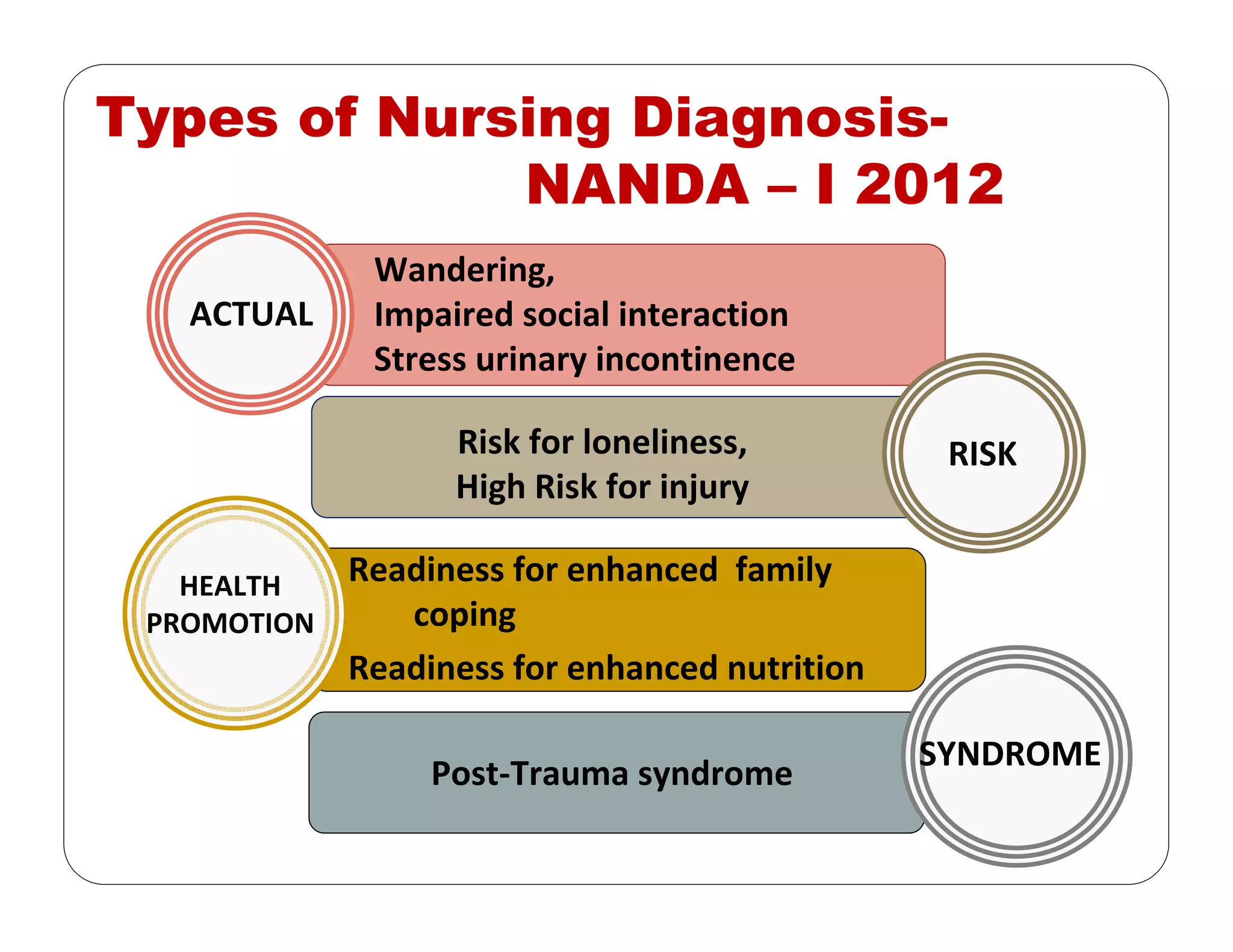
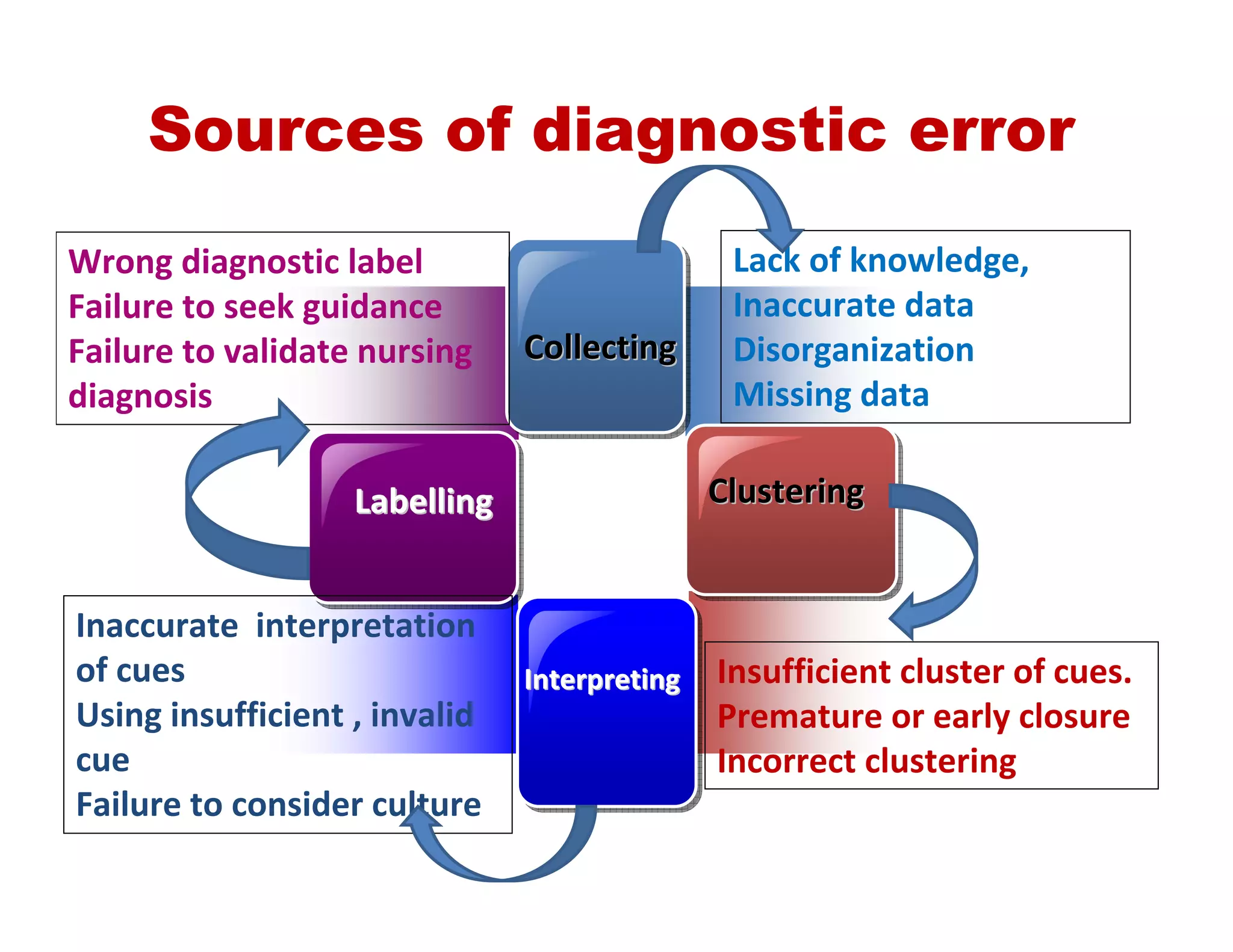
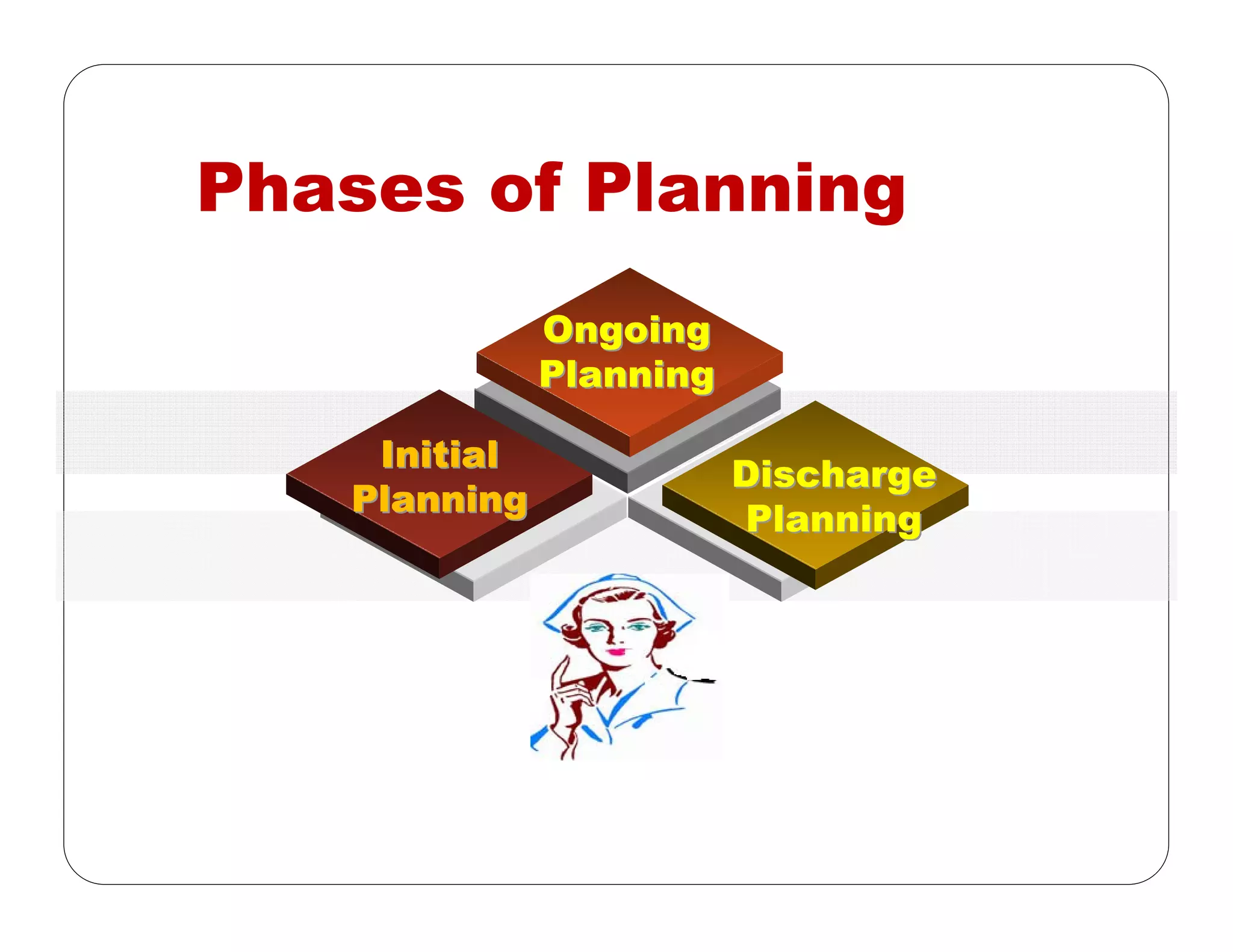
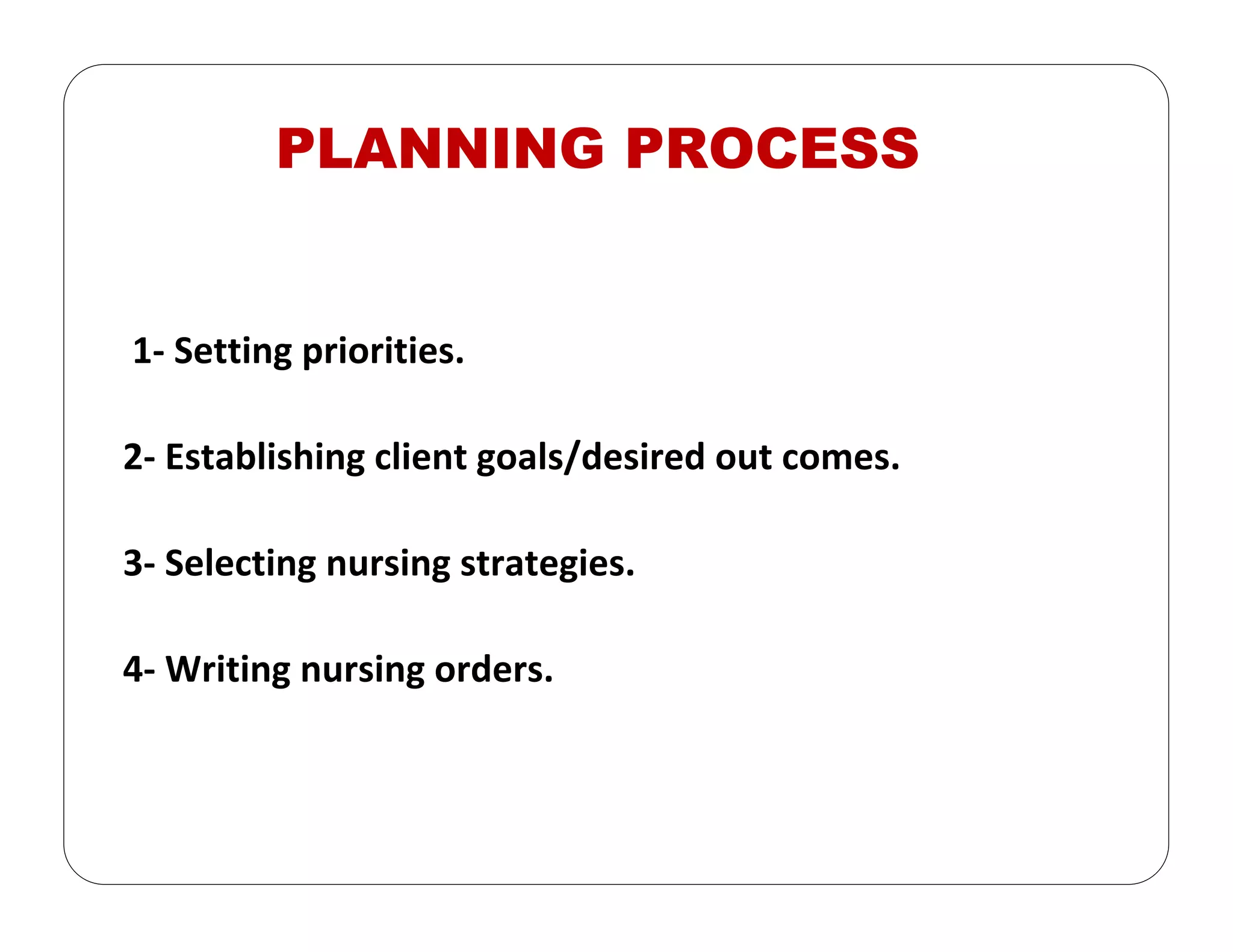
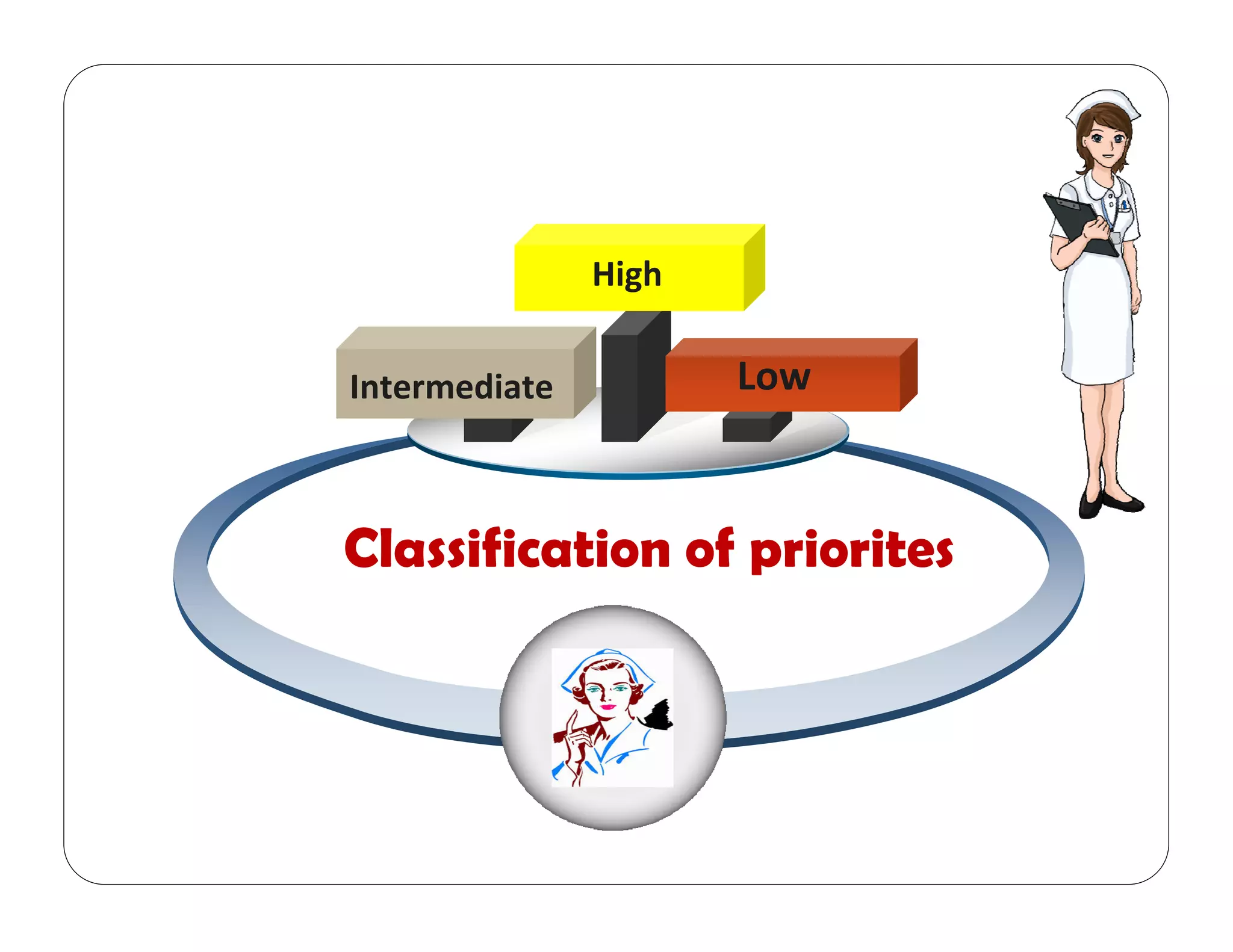
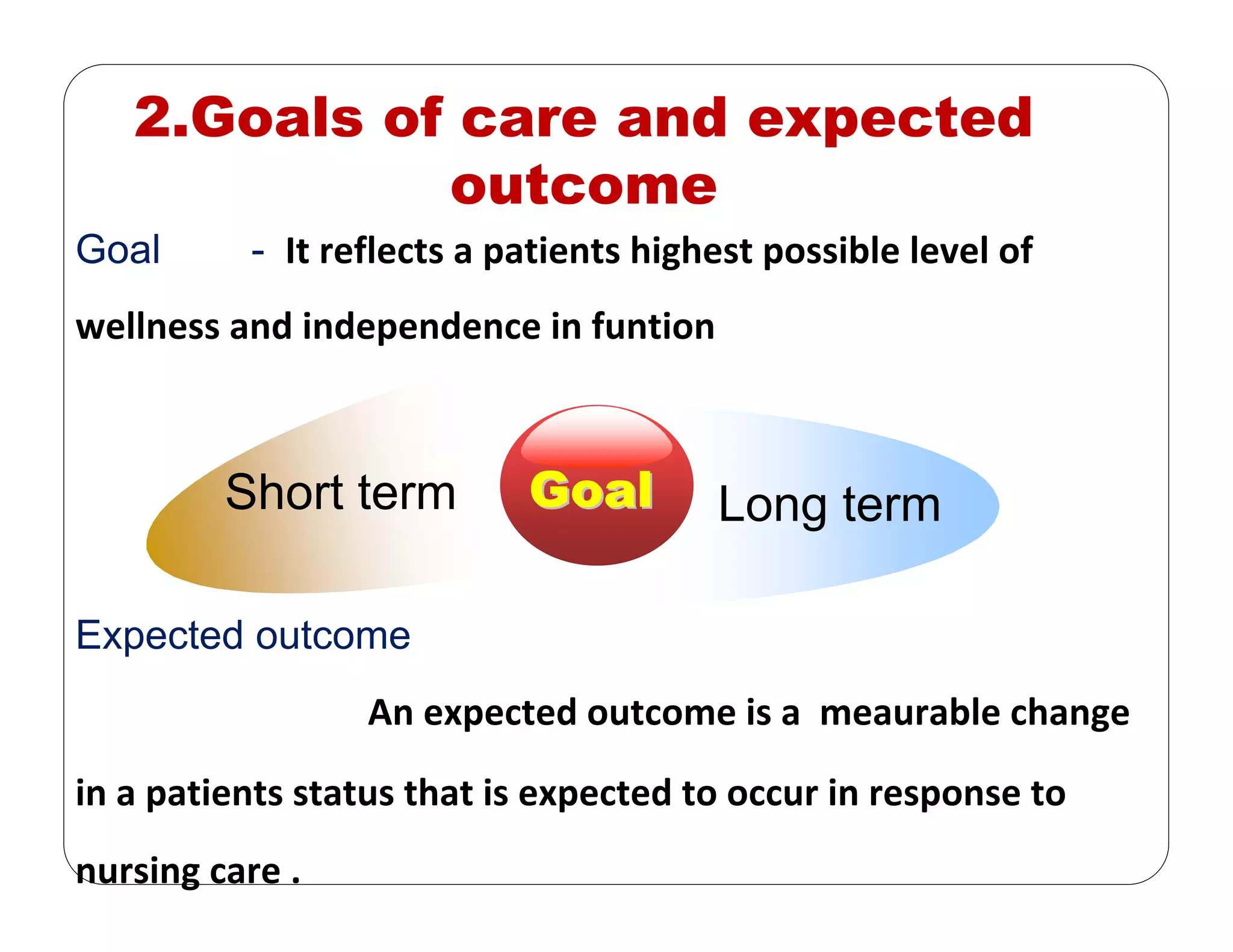
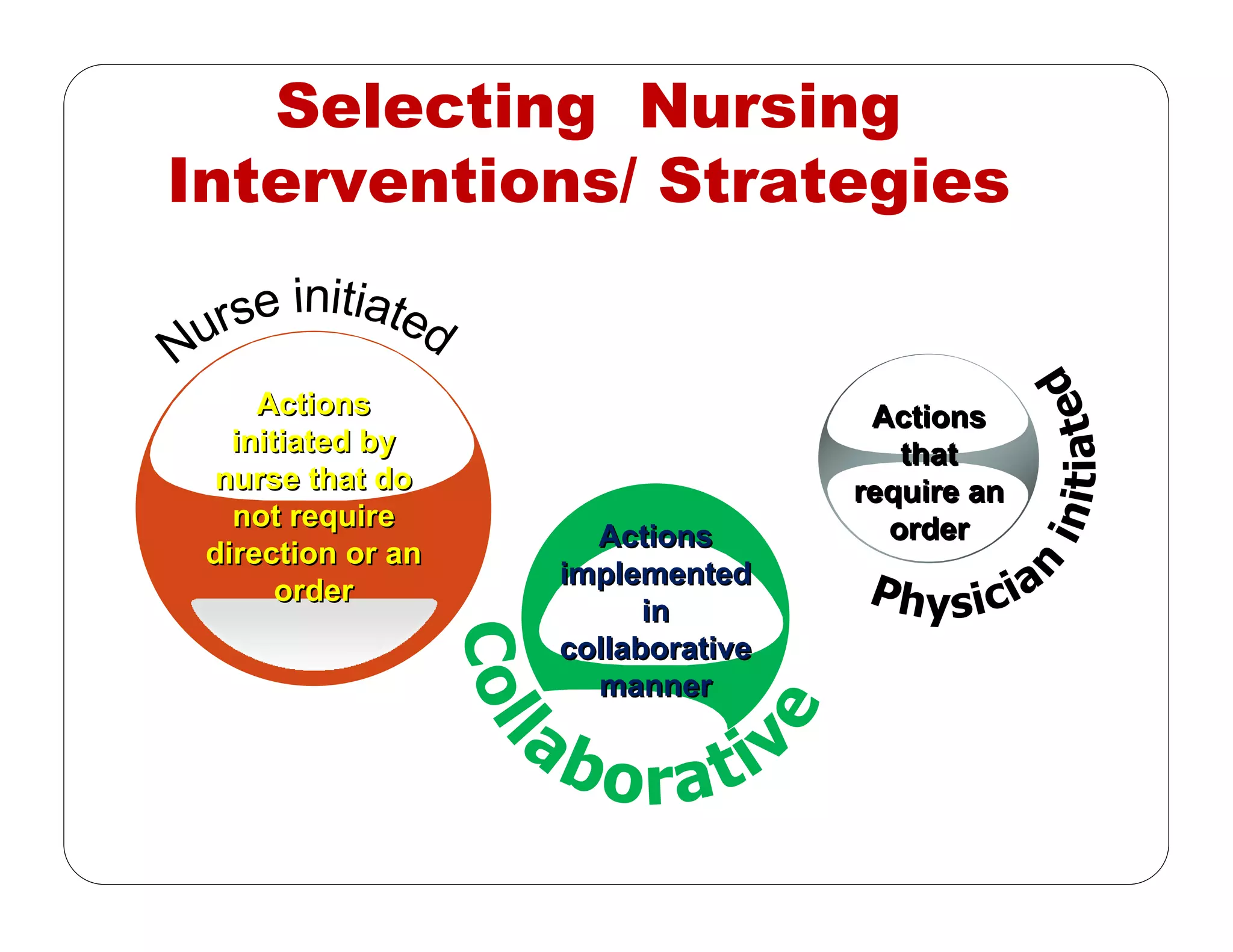
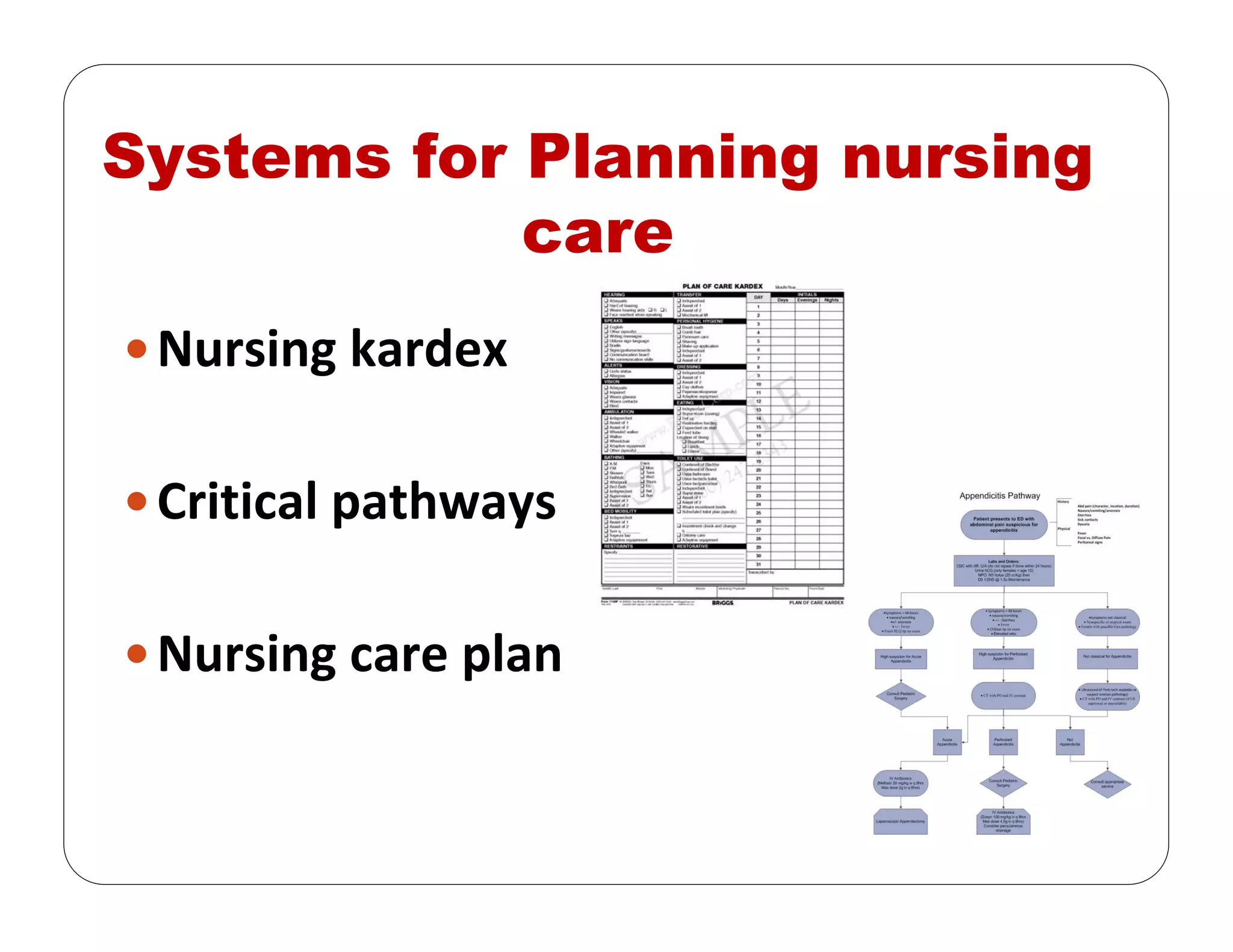
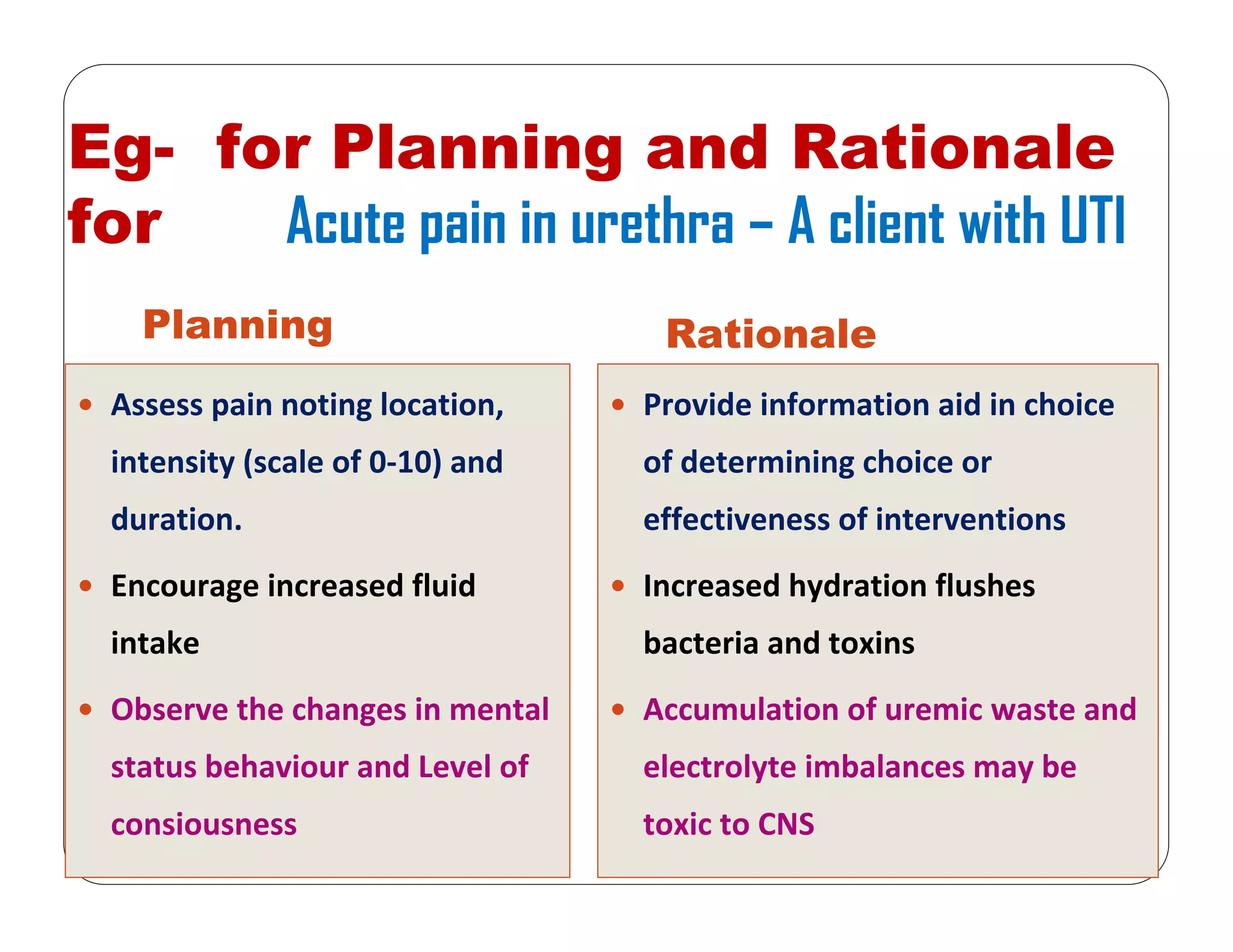
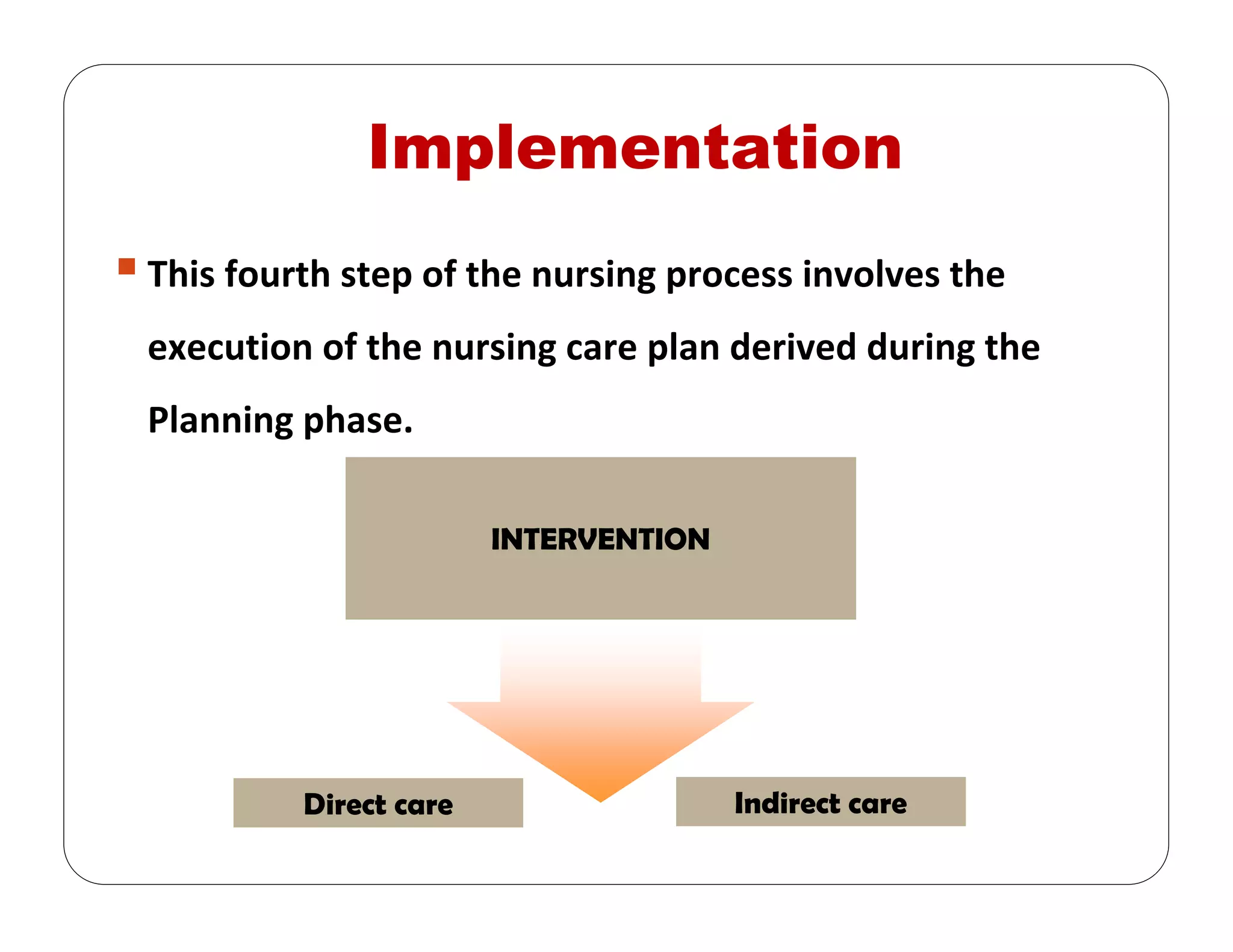
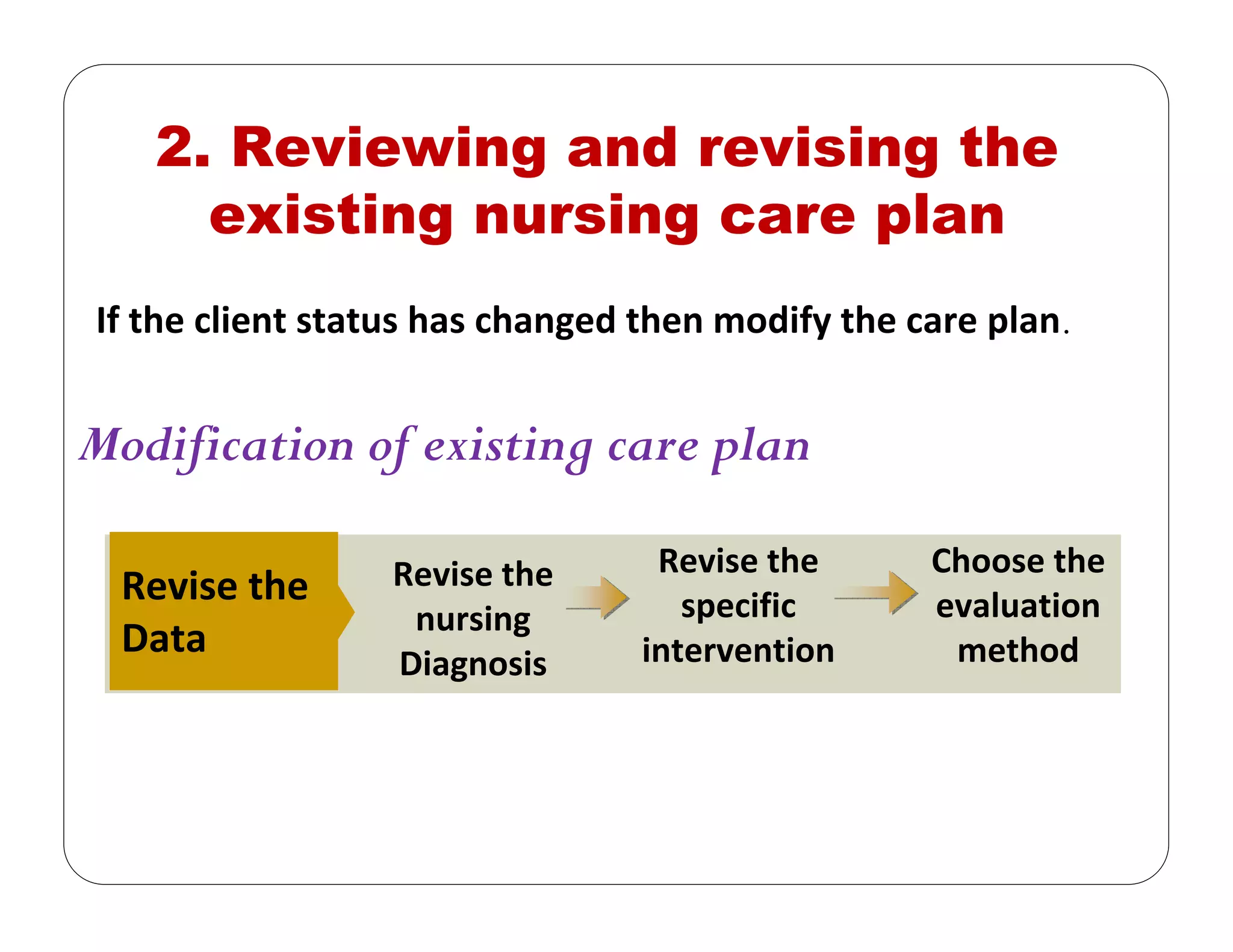
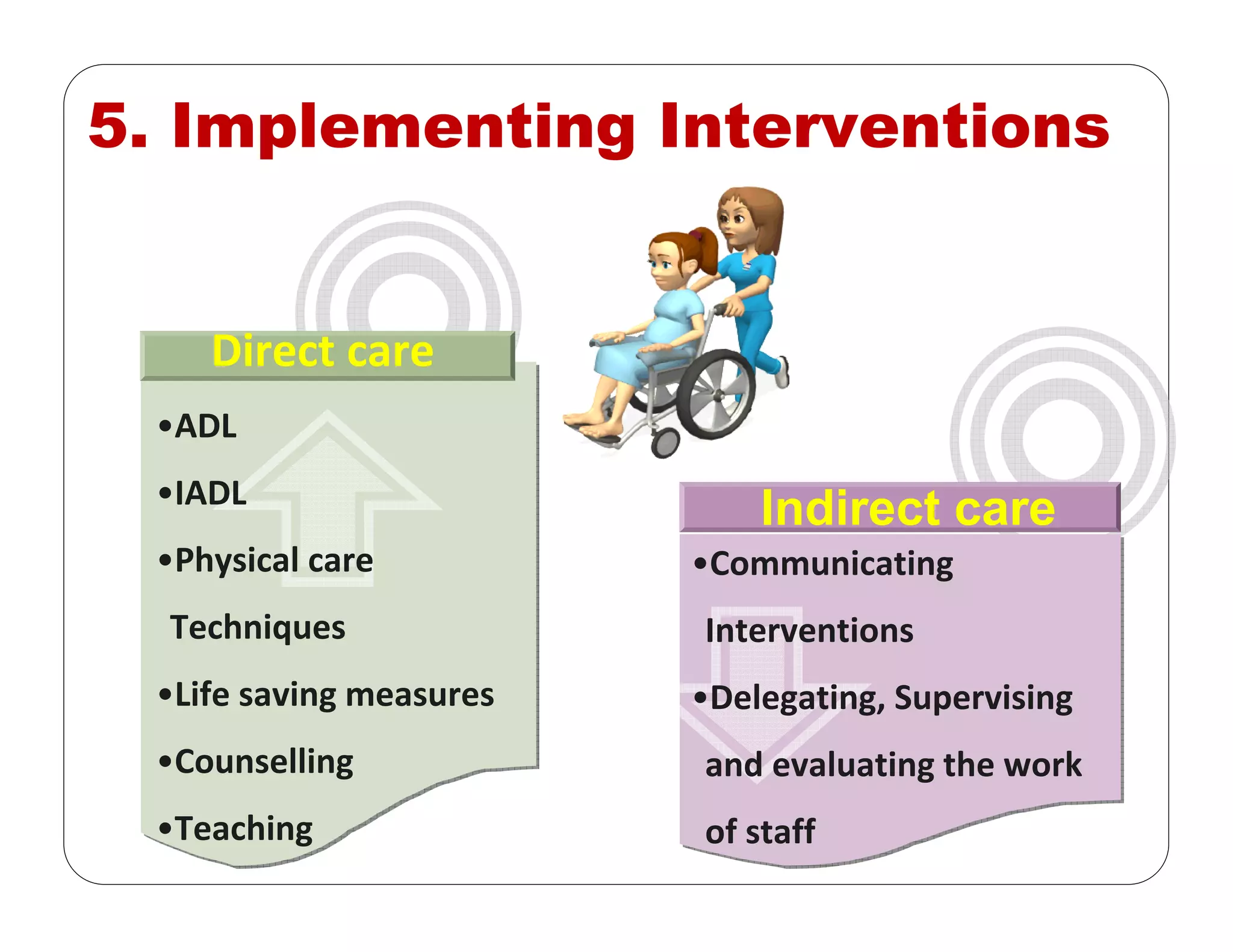
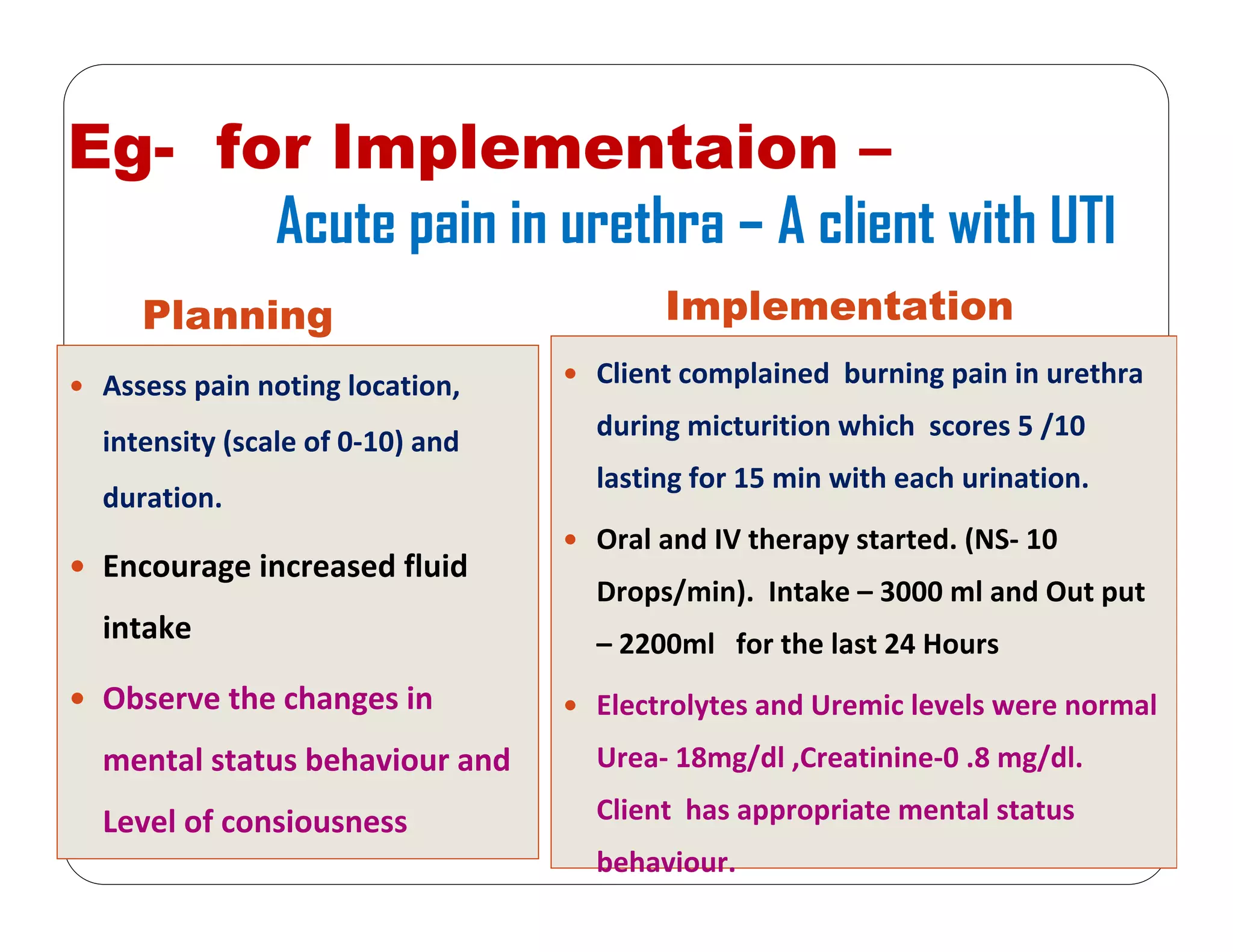
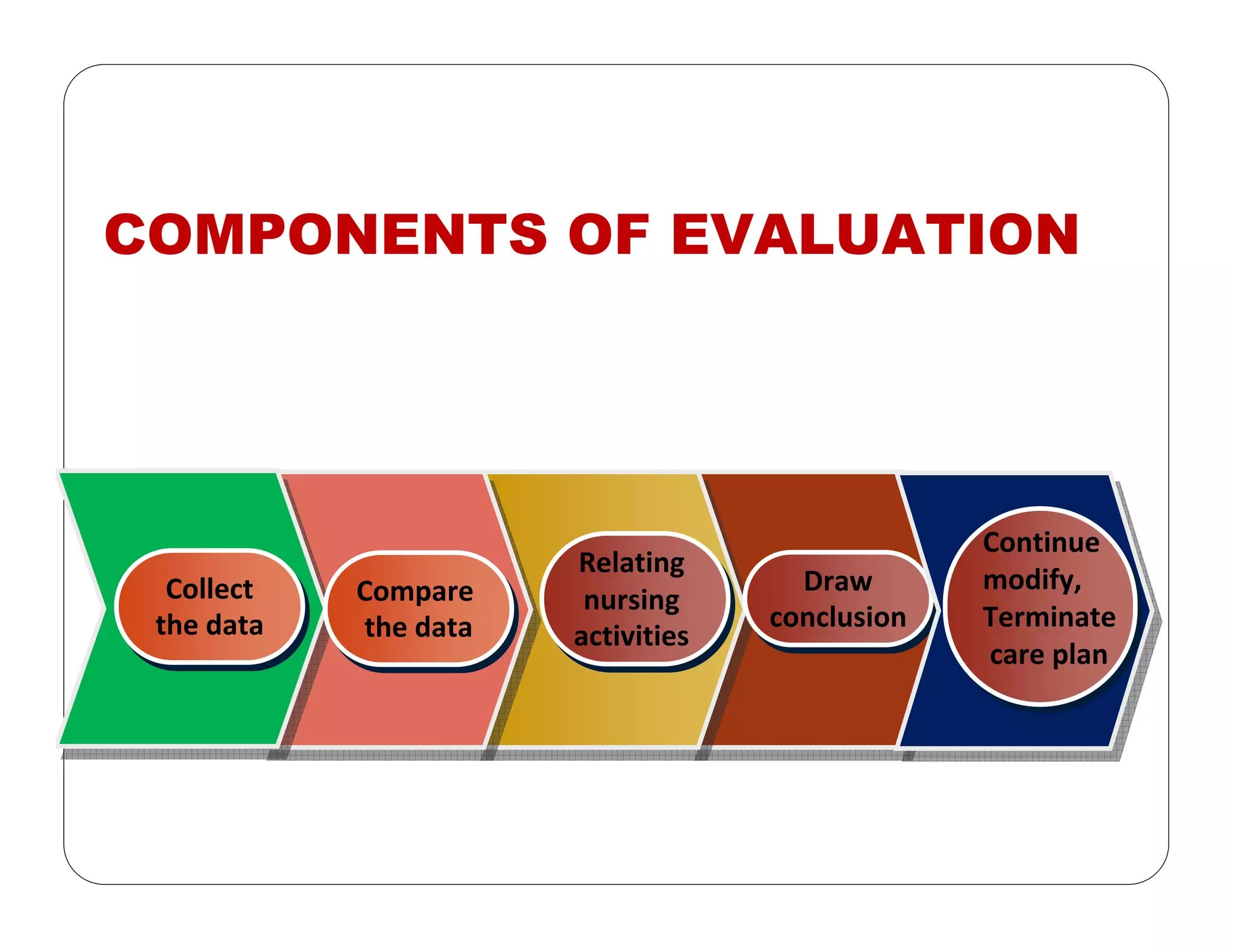
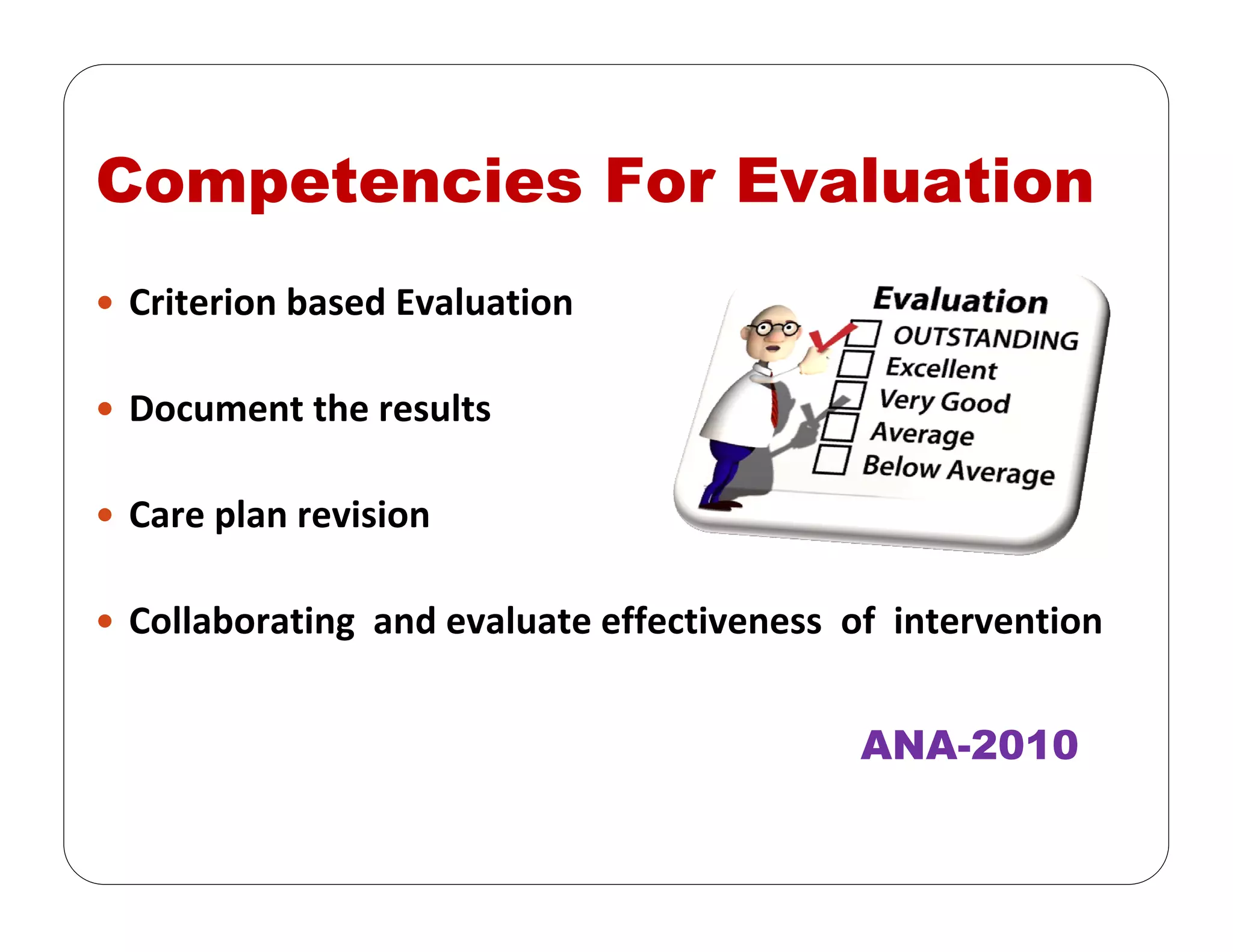
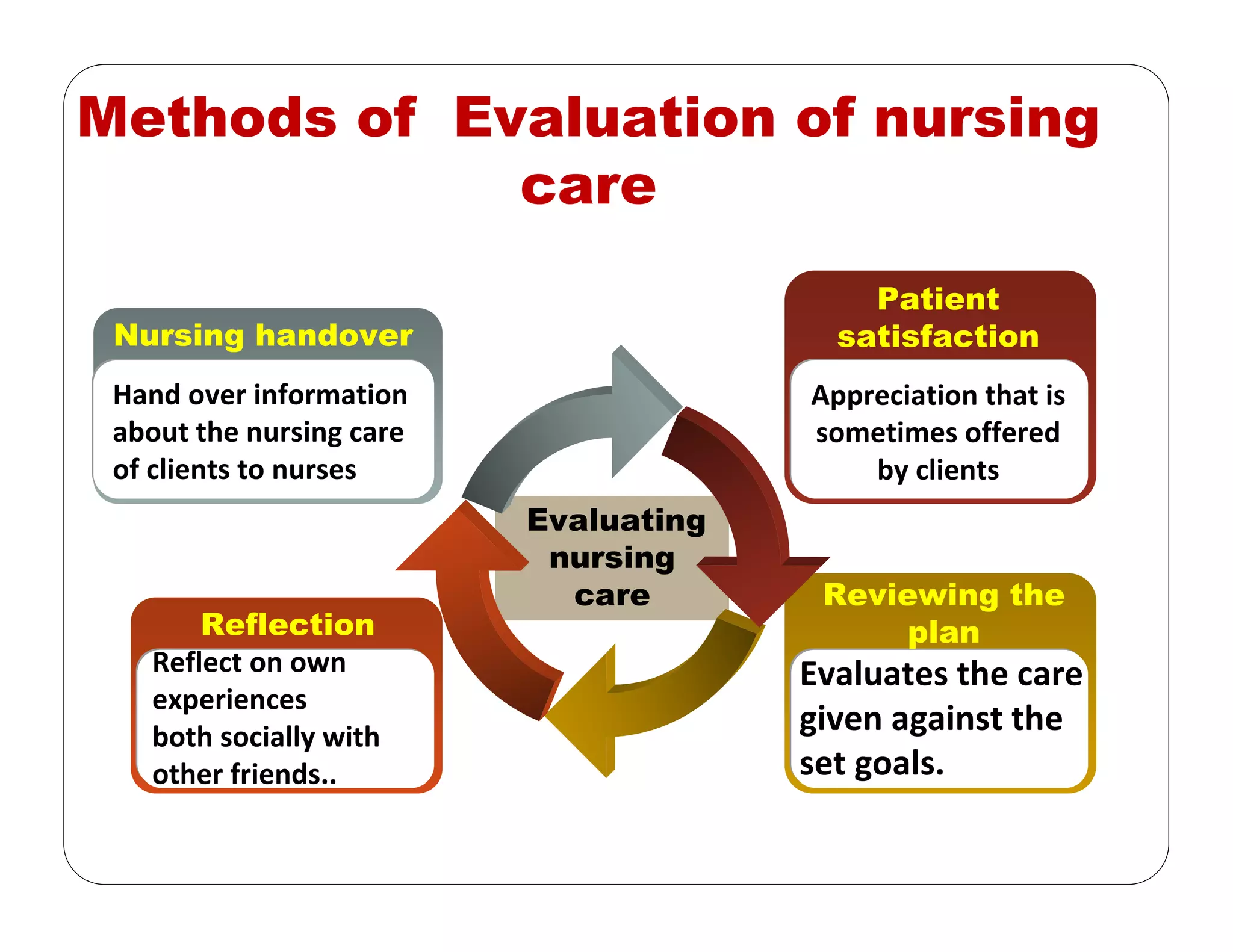
This document outlines the nursing process, emphasizing the importance of assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation in nursing care. It details various types and methods of nursing assessments, the diagnostic process for identifying patient needs, and the planning and execution of nursing interventions. Additionally, it highlights the significance of documenting and evaluating care to ensure effective patient outcomes.