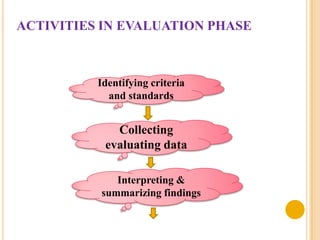
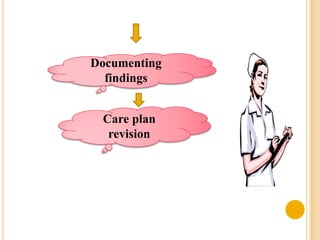
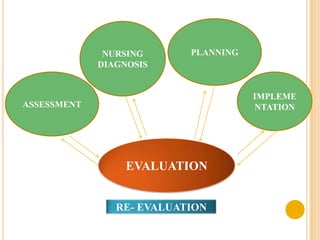
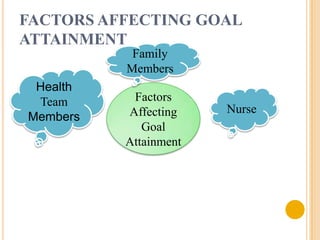
The document discusses the evaluation phase of the nursing process. It defines evaluation as comparing a patient's responses to predetermined goals and outcomes. The nurse evaluates whether expected outcomes were met, not just if interventions were done. Key aspects of evaluation include collecting and interpreting data, comparing outcomes to goals, documenting findings, and revising the care plan if needed. The evaluation determines if care was effective and ensures continuous good patient outcomes.