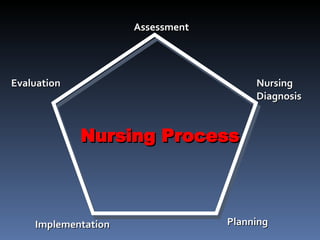
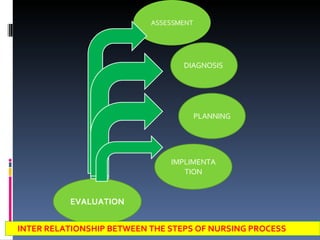
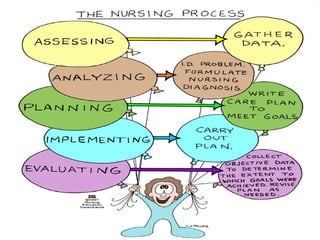
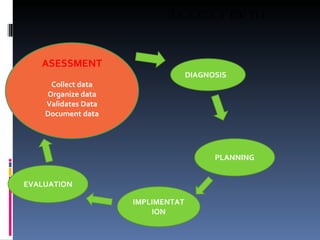
The nursing process is a systematic problem-solving approach used by nurses to provide care. It involves five steps: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Assessment involves continuously collecting and organizing data through various methods like observation, interviews, and physical exams. This data is then validated and documented before moving to the diagnosis step to identify any health problems or needs.