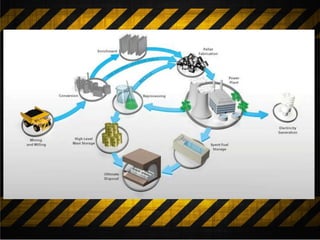
Nuclear waste is categorized as high, intermediate, or low-level waste and is produced from nuclear power plants, weapons, and other sources. High-level waste contains 95% of radiation and is disposed of through deep geological storage. Procedures to remove intermediate and low-level wastes include near-surface disposal and methods using bacteria or sulfide sponges that can absorb radioactive materials. While disposal is commonly used, new techniques showing promise in more quickly removing radiation include the Notre Dame Thorium Borate and sulfide sponges.