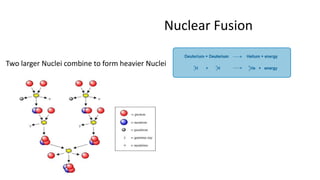
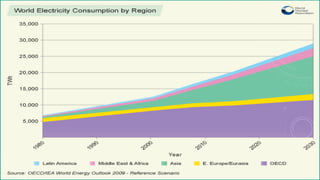
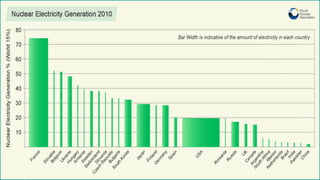
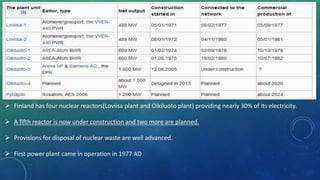
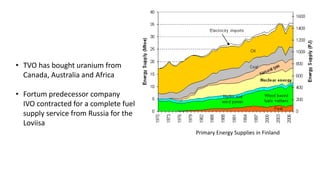
Nuclear energy is produced through two main reactions: nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. Nuclear fission involves splitting heavier nuclei into larger nuclei by shooting neutrons at them, while nuclear fusion involves combining two larger nuclei to form heavier nuclei. Nuclear power plants use these reactions to generate extreme heat and produce steam that spins turbines to generate electricity. Finland obtains about 30% of its electricity from four nuclear reactors, with plans to build more, and manages nuclear waste through long-term storage and planned deep geological disposal.