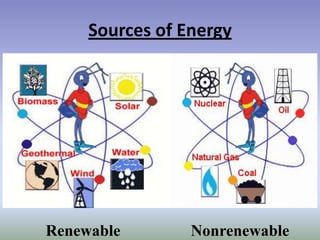
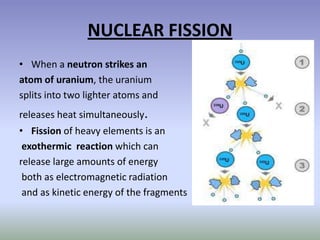
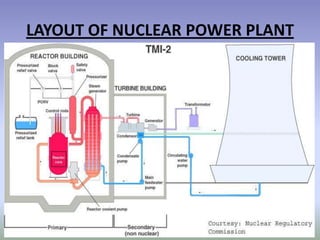
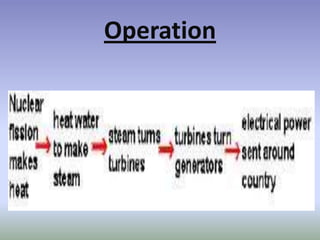
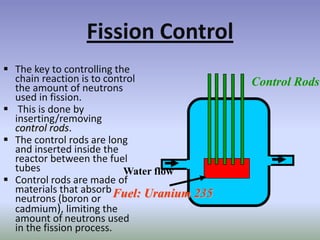
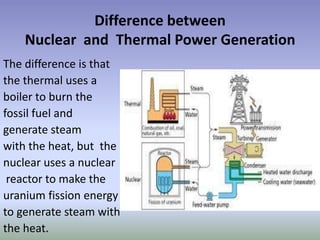
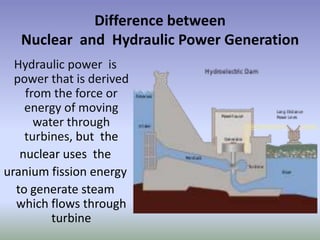
Nuclear energy comes from splitting atoms in a process called nuclear fission. Nuclear power plants use uranium, a radioactive element, to create electricity through controlled nuclear fission chain reactions. The key to controlling the chain reaction is to control the number of neutrons used in fission using control rods. Nuclear power plants have advantages over other power sources like high energy density and low emissions, but also have disadvantages like high costs and radioactive waste disposal challenges.