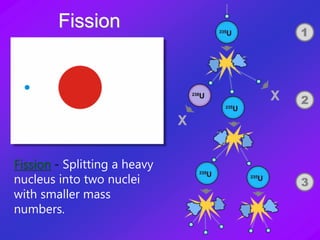
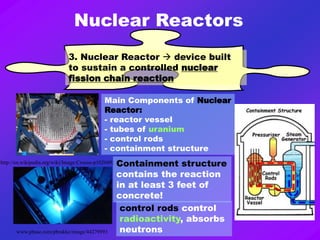
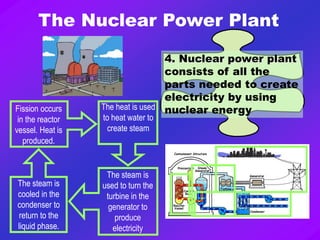
Nuclear power plants produce electricity through a process called nuclear fission. Uranium-235 is used as fuel and splits into parts when hit by neutrons, releasing energy. This energy heats water to produce steam that spins turbines to generate electricity. While nuclear power has benefits like being efficient and producing low emissions, it also has risks like radioactive waste storage and potential disasters. Three major nuclear disasters include the incidents at Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and Fukushima.