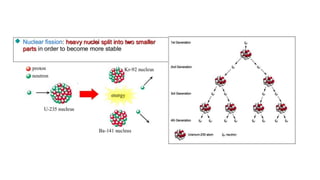
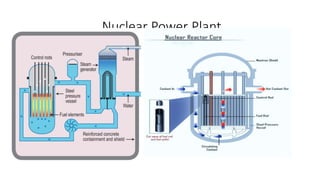
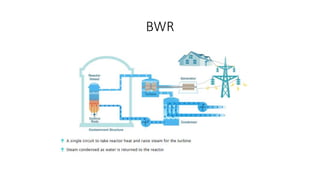
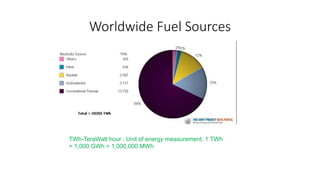
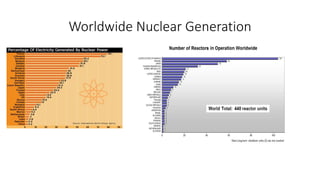
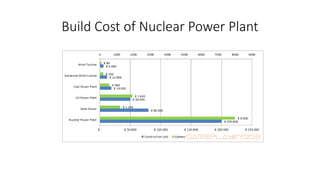
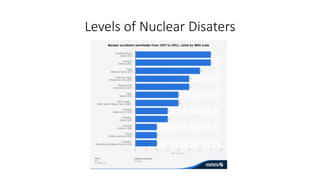
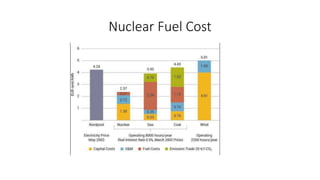
This document provides information about a nuclear power plant engineering course. It includes the group members, various topics to be covered such as nuclear fuel, chain reaction, power plant components, site selection, worldwide scenarios, and costs. It also discusses present scenarios in Bangladesh, facts, wastes, disasters, fuel costs, and advantages and disadvantages of nuclear power. Reference websites are also included at the end.