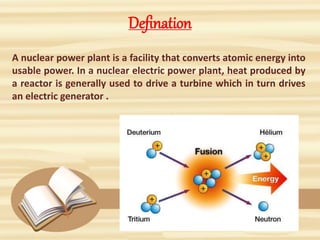
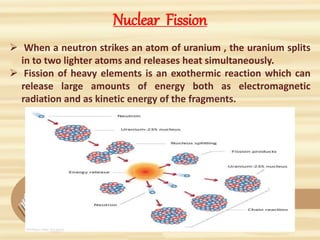
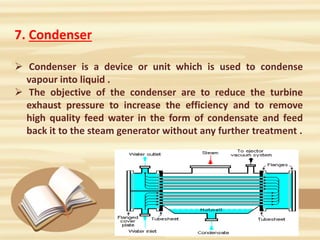
1. A nuclear power plant uses nuclear fission to generate heat and convert it to usable energy. Uranium atoms are split in the nuclear reactor, producing heat to boil water into steam.
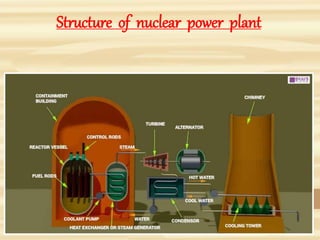
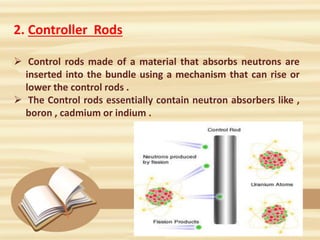
2. The steam turns turbines that generate electricity. Control rods regulate the fission rate. Steam generators, turbines, pumps, condensers, and cooling towers complete the steam/water cycle.
3. Nuclear power has low carbon emissions but produces radioactive waste disposal challenges. It also poses risks from accidents, though plants aim for maximum safety. Fuel resources like uranium are finite as well.