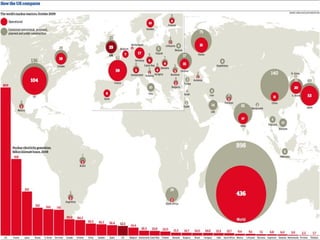
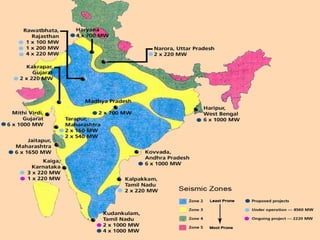
Nuclear energy originates from splitting uranium atoms through fission. This process is used in nuclear power plants to generate heat and produce steam to power turbines for electricity generation. Nuclear energy was first discovered in 1934 and was later used in nuclear weapons. It provides a concentrated source of energy but also has disadvantages like high costs, nuclear waste, and risks of nuclear weapons proliferation and accidents.