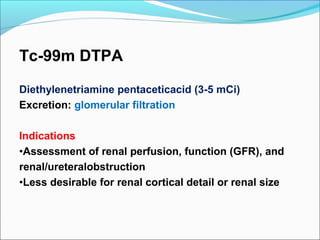
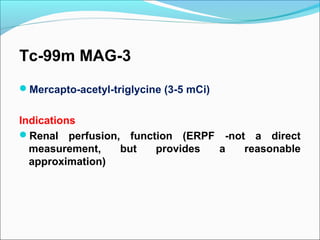
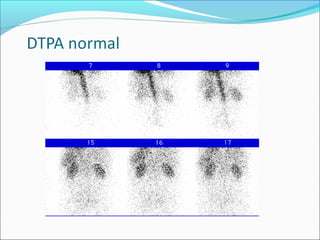
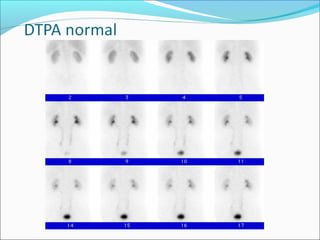
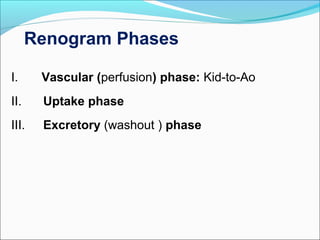
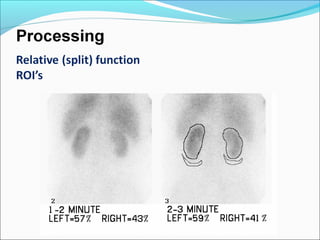
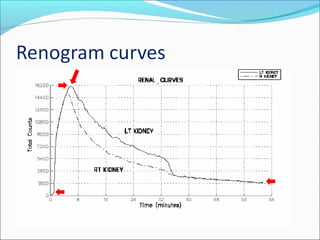
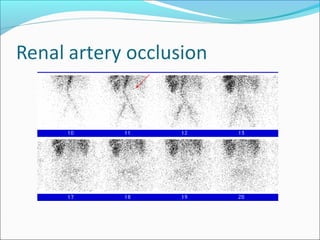
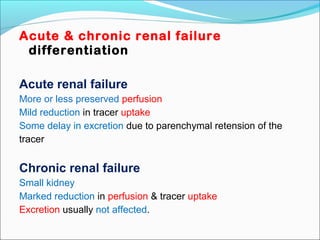
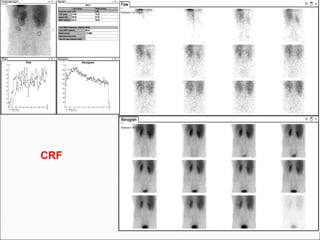
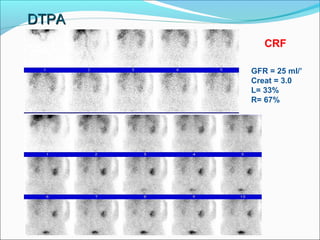
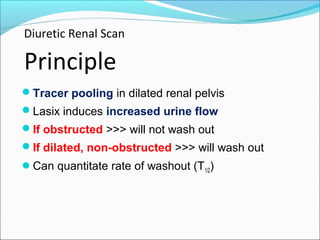
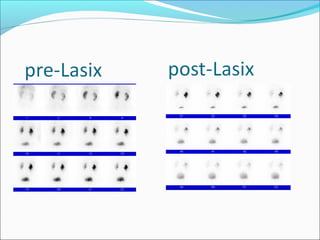
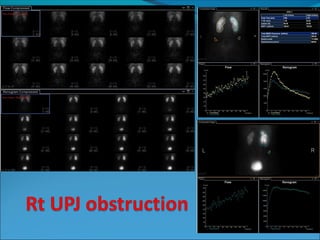
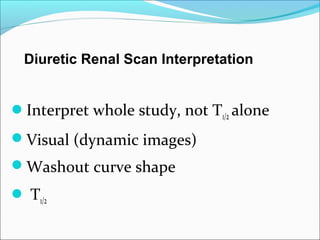
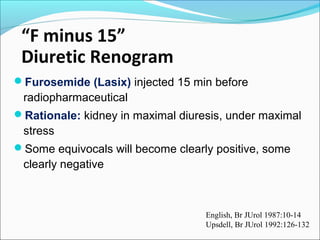
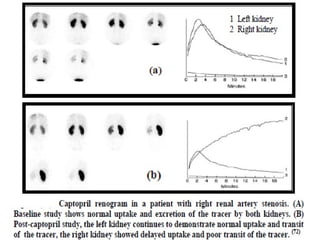
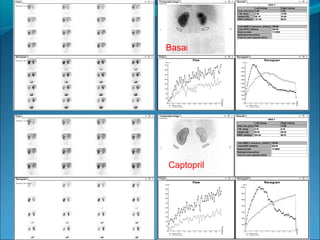
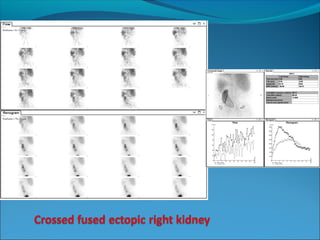
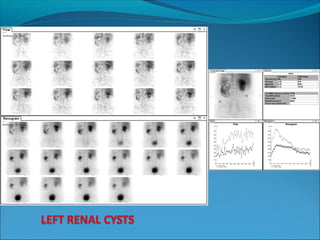
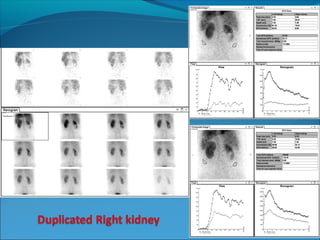
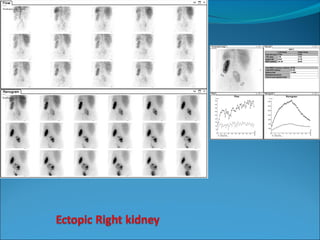
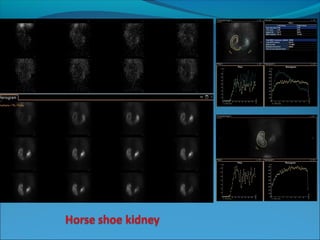
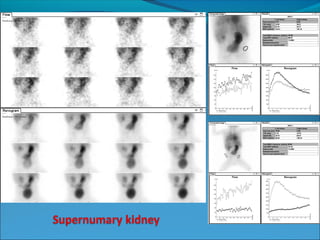
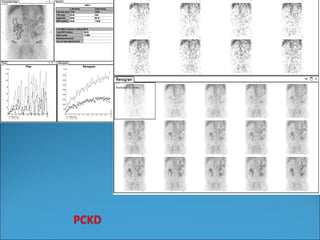
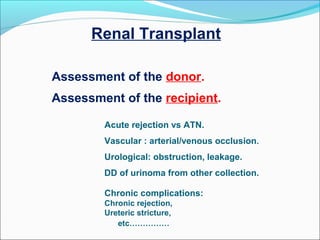
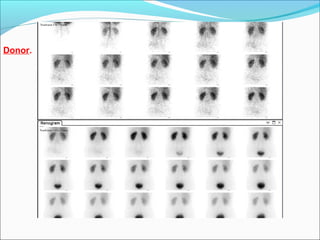
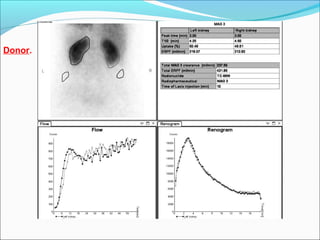
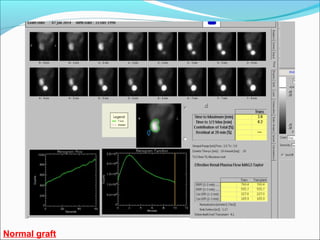
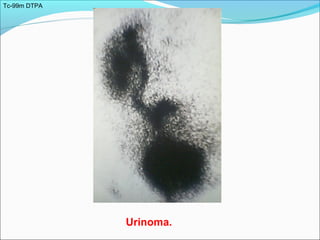
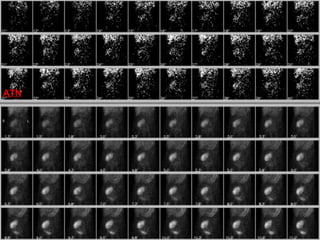
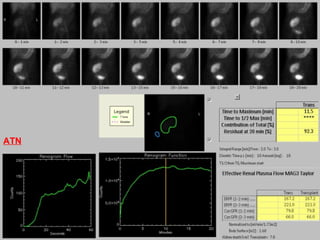
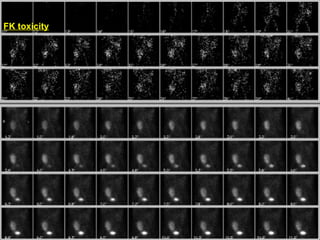
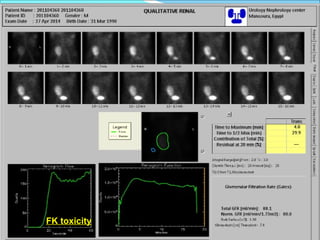
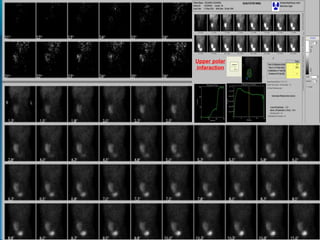
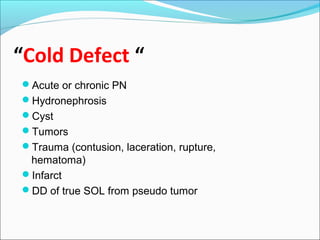
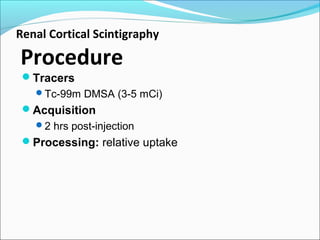
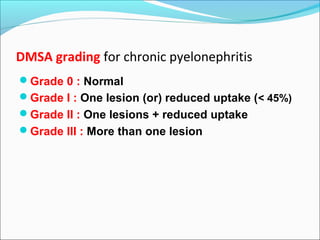
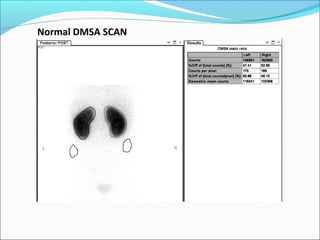
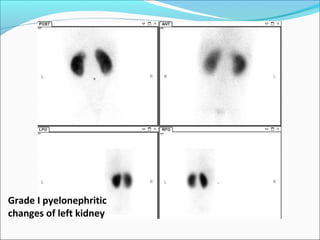
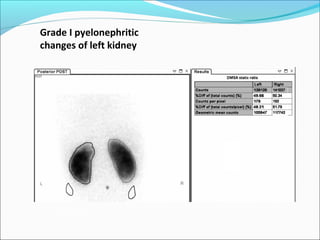
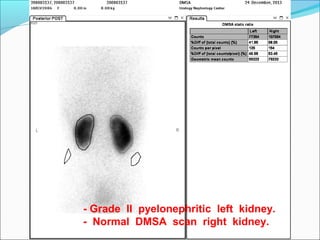
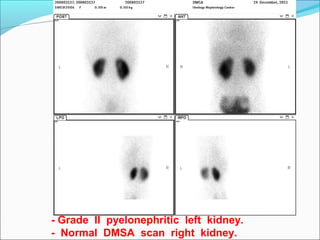
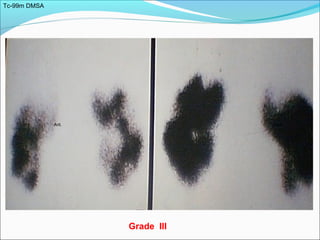
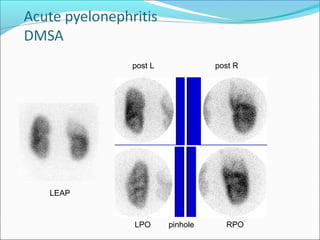
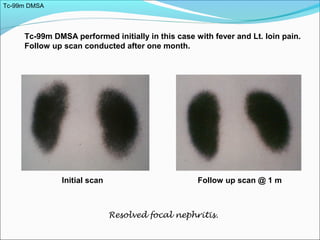
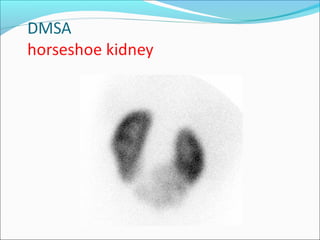
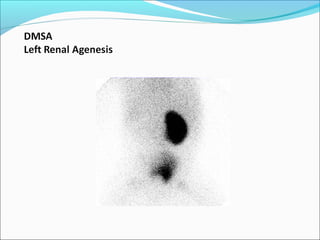
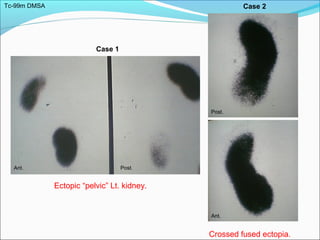
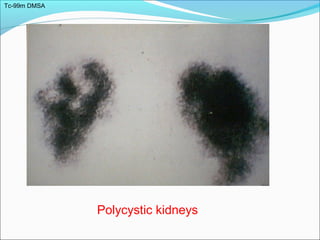
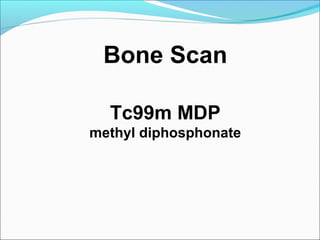
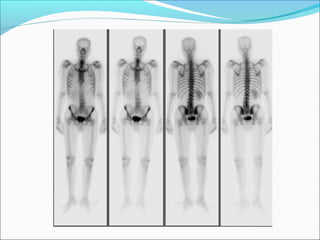
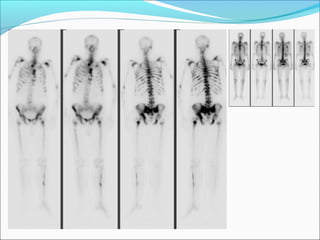
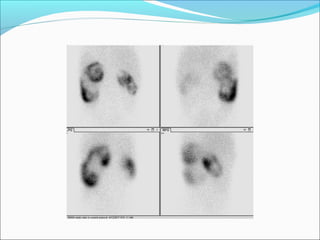
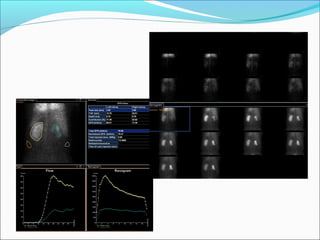
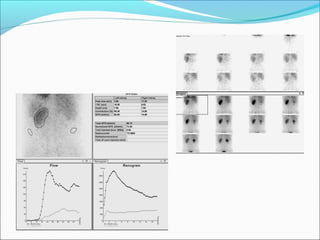
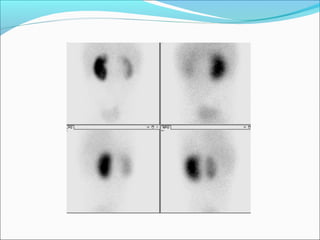
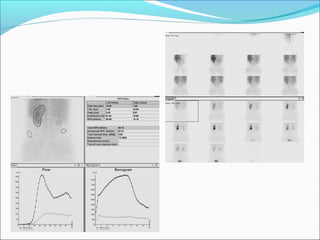
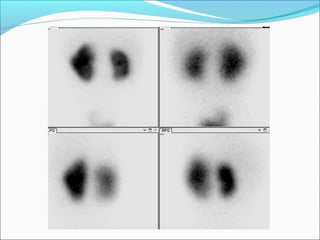
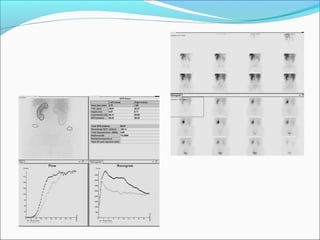
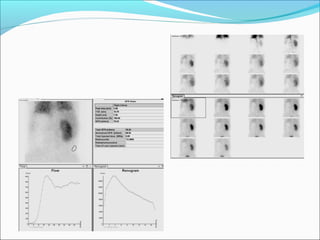
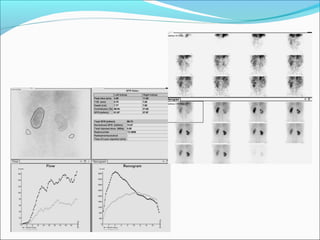
This document discusses the use of radio-nuclides in nephro-urology. It describes various radiotracers including Tc99m DTPA and Tc99m MAG3 that are commonly used for renal scintigraphy to evaluate renal function and obstruction. Specific indications and interpretations for renal perfusion scans, Lasix renal scans, renal transplant scans, and DMSA scans are provided. The basic principles of acquiring and interpreting renograms are also summarized.