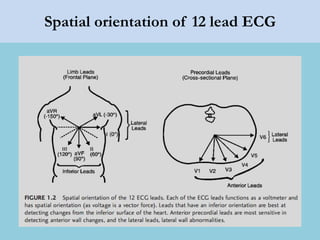
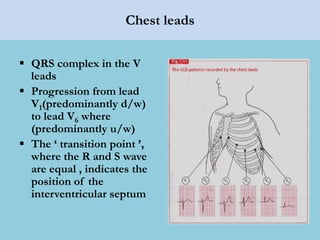
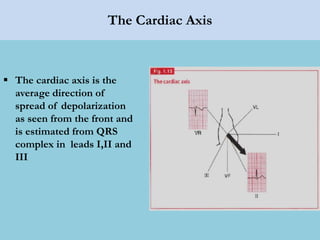
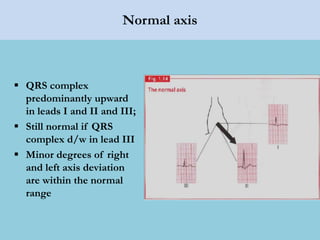
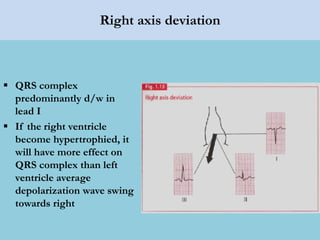
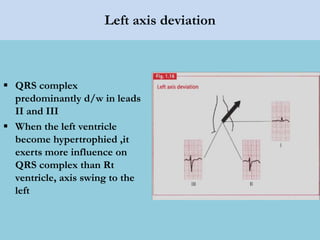
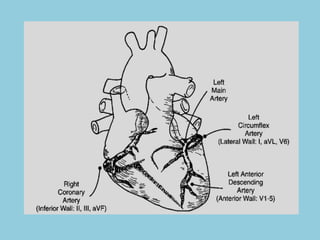
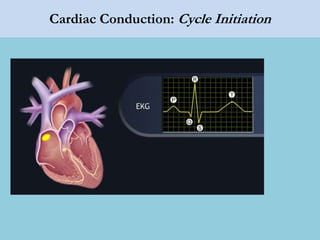
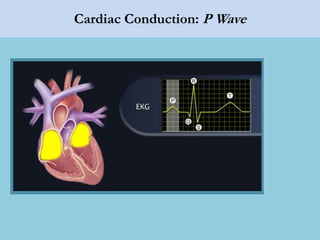
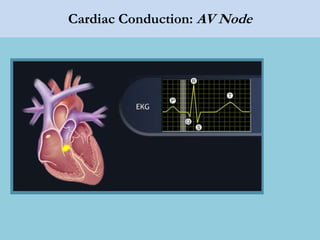
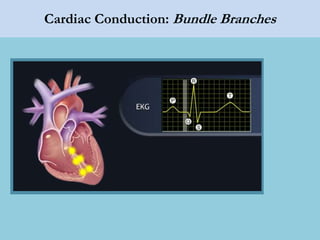
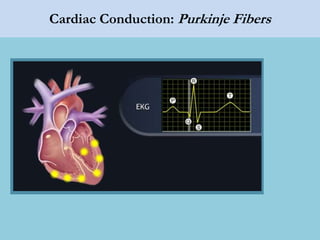
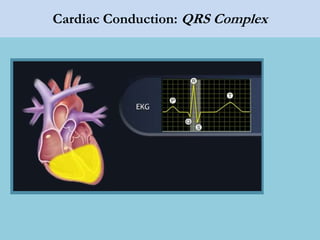
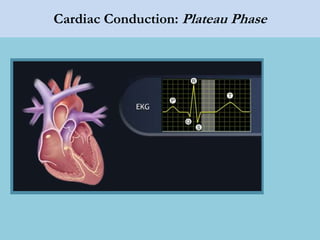
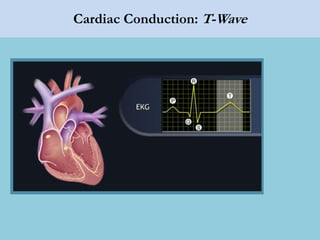
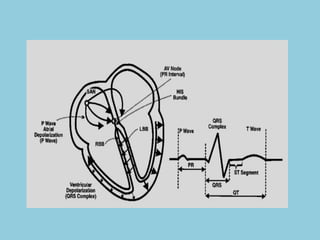
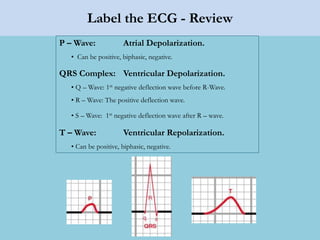
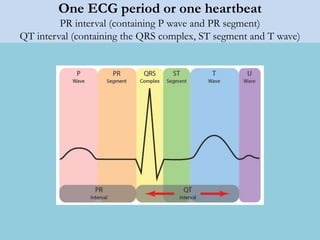
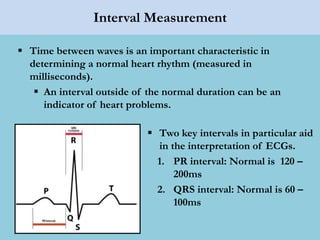
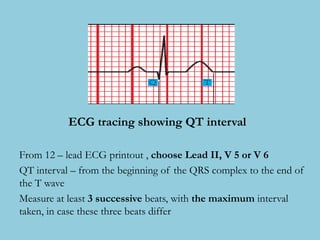
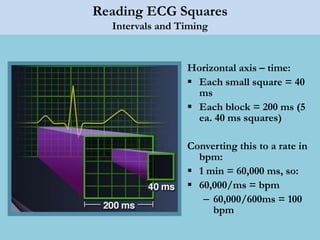
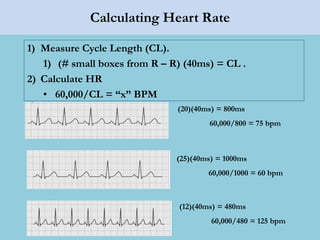
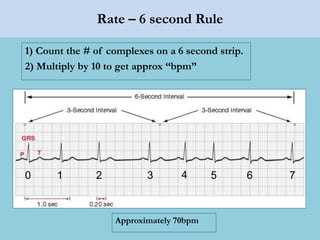
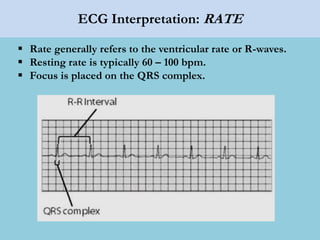
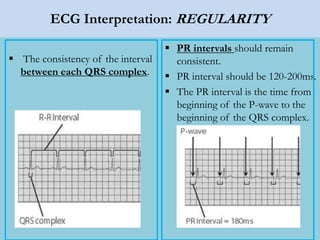
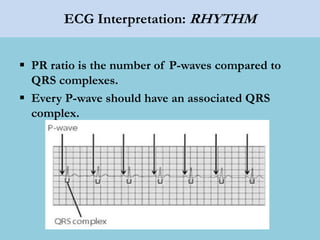
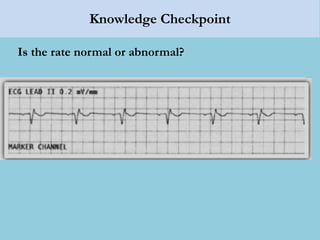
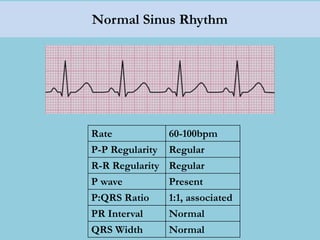
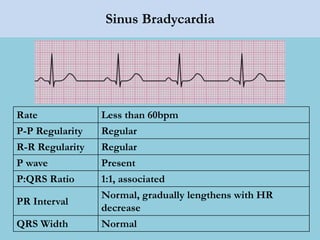
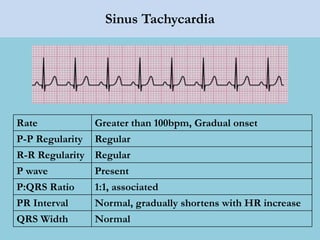
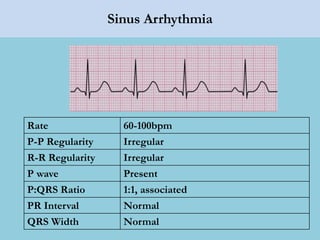
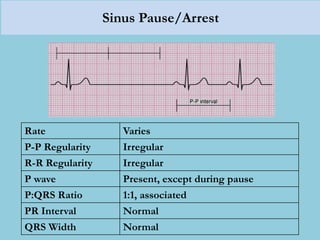
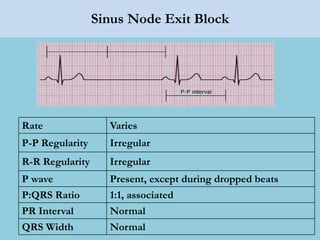
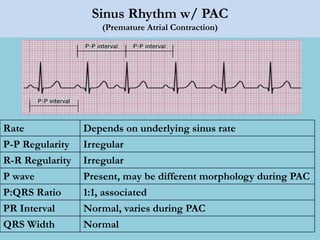
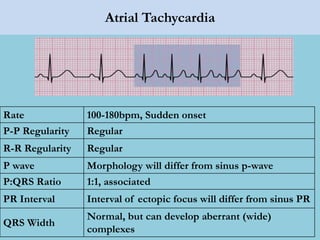
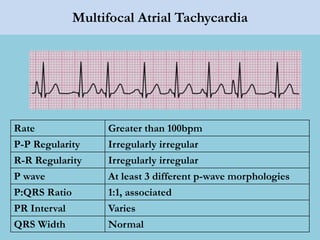
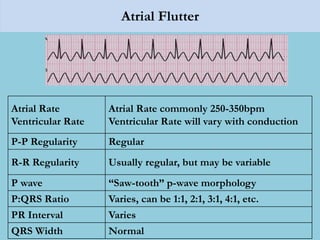
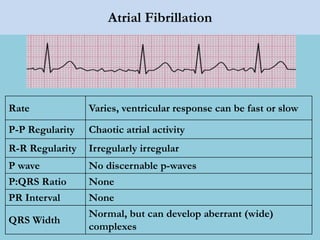
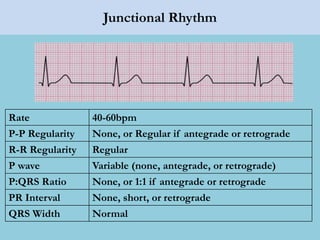
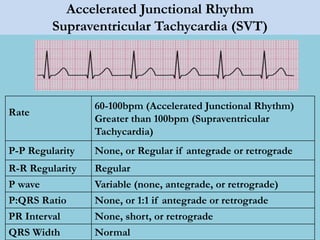
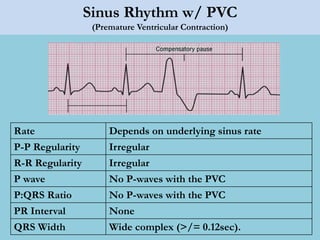
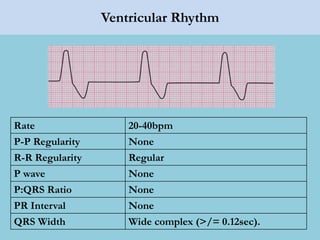
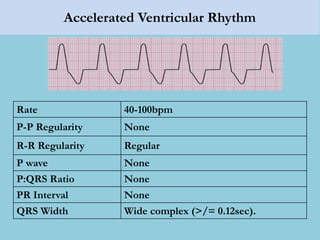
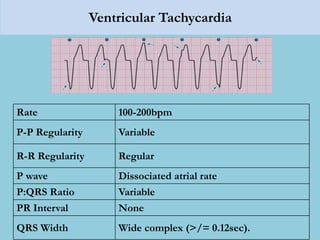
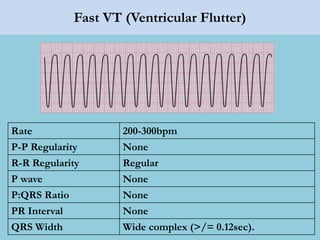
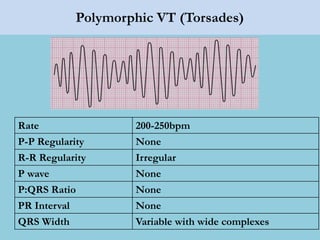
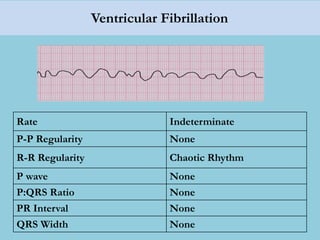
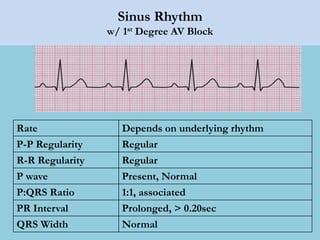
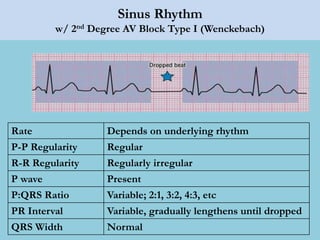
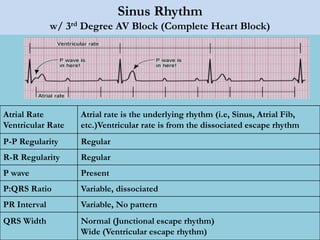
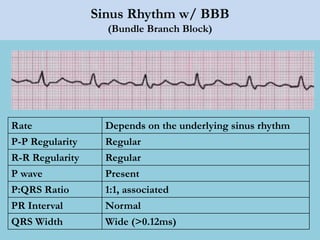
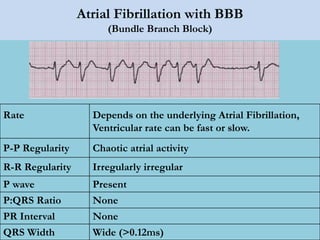
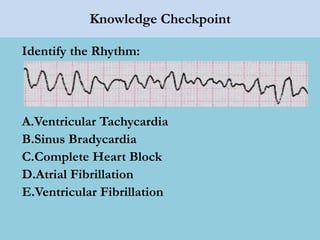
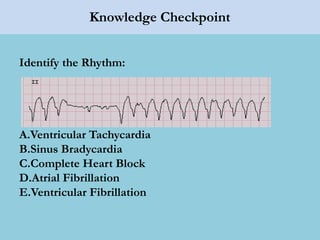
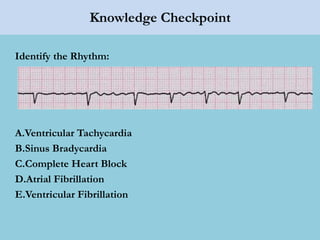
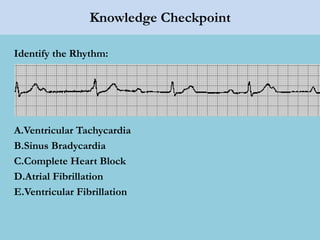
This document provides an overview of basic ECG interpretation. It begins by describing the spatial orientation of the 12 lead ECG and how it relates to different areas of the heart. It then discusses normal cardiac conduction, including the roles of the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers. Key intervals like the PR and QT intervals are also explained. Common rhythms are then summarized, focusing on identifying features like rate, regularity, and relationship between P waves and QRS complexes to determine if a rhythm is normal or abnormal.