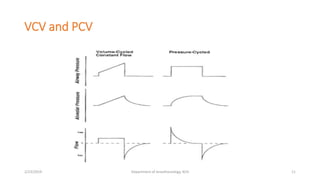
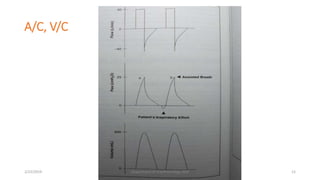
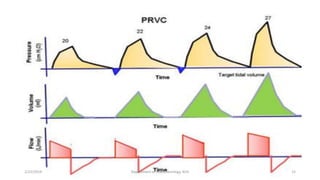
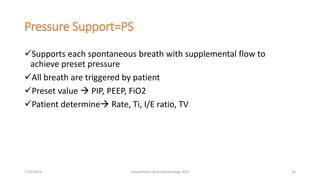
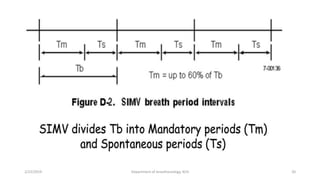
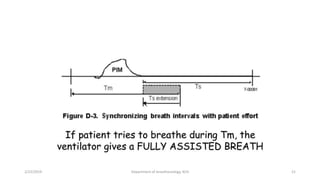
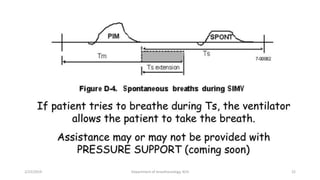
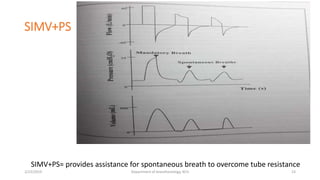
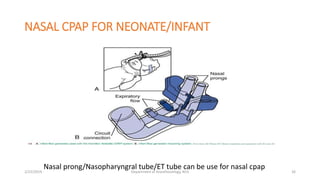
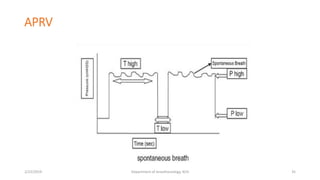
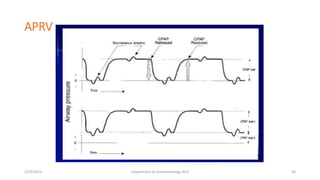
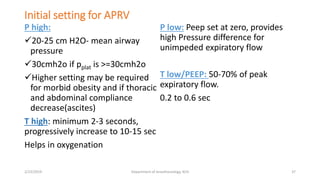
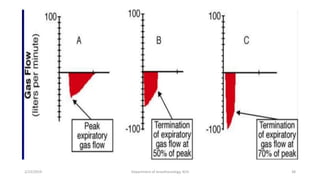
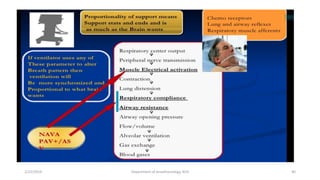
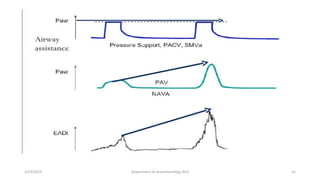
The document discusses mechanical ventilation, including its indications, goals, assessment, classifications of modes, and descriptions of various modes like VCV, PCV, PRVC, PS, SIMV, CPAP, APRV, and NAVA. The objectives are to discuss indications for mechanical ventilation and different modes that can be used. Proper assessment of patients and setting of appropriate modes and parameters are emphasized to minimize lung injury while providing adequate ventilation and oxygenation.