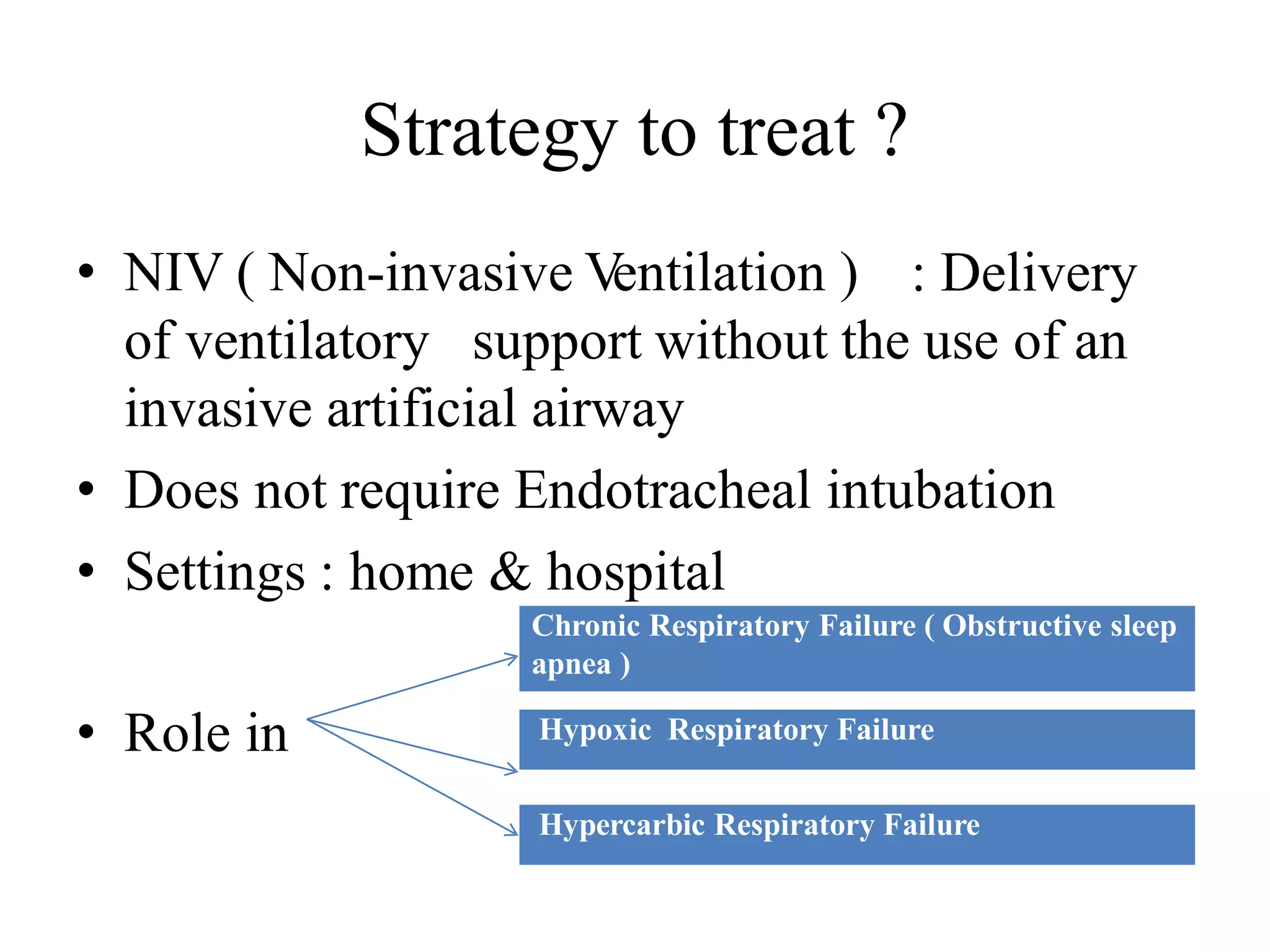
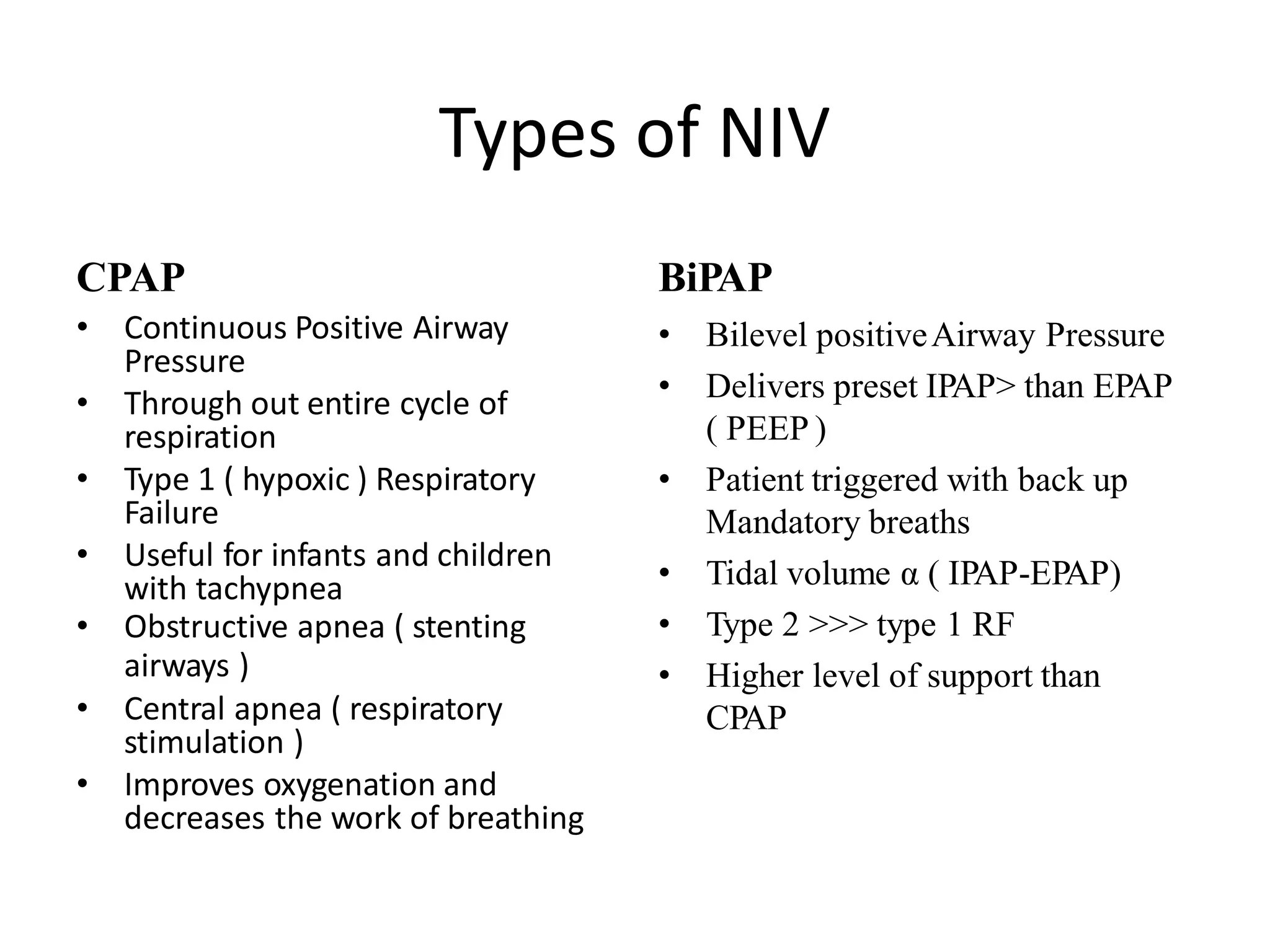
Non Invasive Ventilation in Children (NIV-C) provides respiratory support without invasive intubation. It assists in airway distension and oxygenation at the alveolar level, reducing respiratory effort. NIV-C improves outcomes and decreases intubation needs in acute settings. Proper patient selection and interface are important. NIV includes CPAP and BiPAP. CPAP provides constant pressure while BiPAP uses two pressure levels. Close monitoring is needed initially to assess response and potential failure requiring intubation. NIV-C benefits include avoiding intubation risks while allowing communication. Proper technique and settings are essential for success.














![BiPAP
• It has been suggested to start with [IPAP ] 10-12 cm H20 ;[EPAP]
5-6 cmH2O with a gradual increase in pressure( IPAP by 2cm
H2O; EPAP by 1cm H2O) to maintain spo2 >=92% and
continuously evaluating patient’s respiratory function and oxygen
saturation.
Ref : 1) Covid 19 diagnosis and management update Carlotti APCP et al, CLINICS 2020; 75e 2353
2) Pediatric noninvasive ventilation. Cathy Haut; J Pediatr Intensive care 2015; United States](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/noninvasiveventilation-230512125909-9ce3151e/75/Non-invasive-ventilation-pdf-19-2048.jpg)



![HFNC
4) Patient tolerance
Pts often prefer use of HFNC to that of CPAP or BiPAP as tight fiting mask
can be uncomfortable for some pts , many pts. Experience claustrophobia
while using CPAP masks,--- HFNC avoids this by using nasal prongs ,HFNC
works well for patients in respiratory distress who cannot tolerate
CPAP/BiPAP , [ awake, proning , feeding]
Patient must have intact respiratory drive to benefit from HFNC.
Recommended for patients with mild acute respiratory failure.
(Adapted from HFNC: Mechanisms of action and adult and pediatric indications,
Lodeserto et al, San Antonio, USA)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/noninvasiveventilation-230512125909-9ce3151e/75/Non-invasive-ventilation-pdf-23-2048.jpg)














