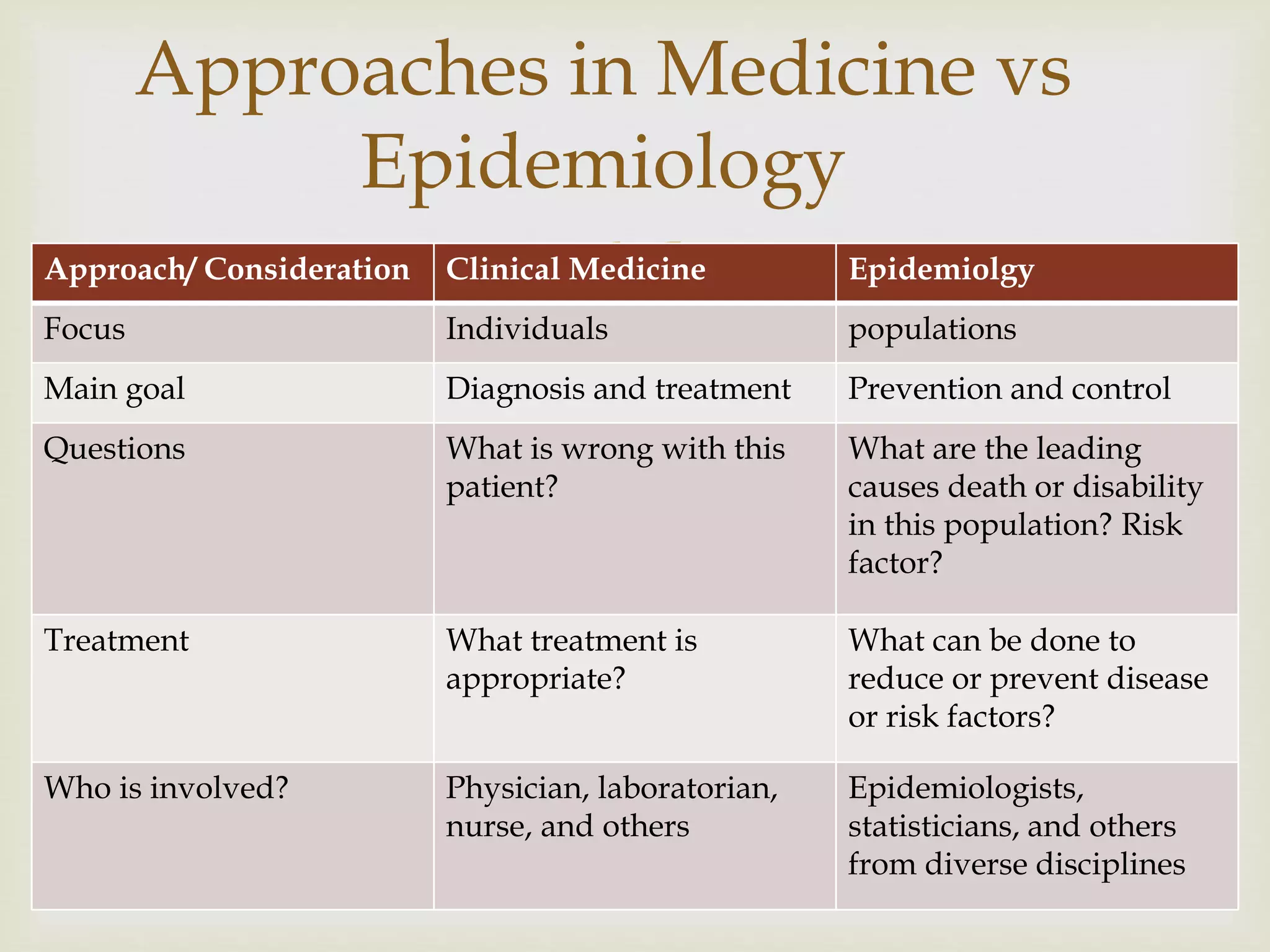
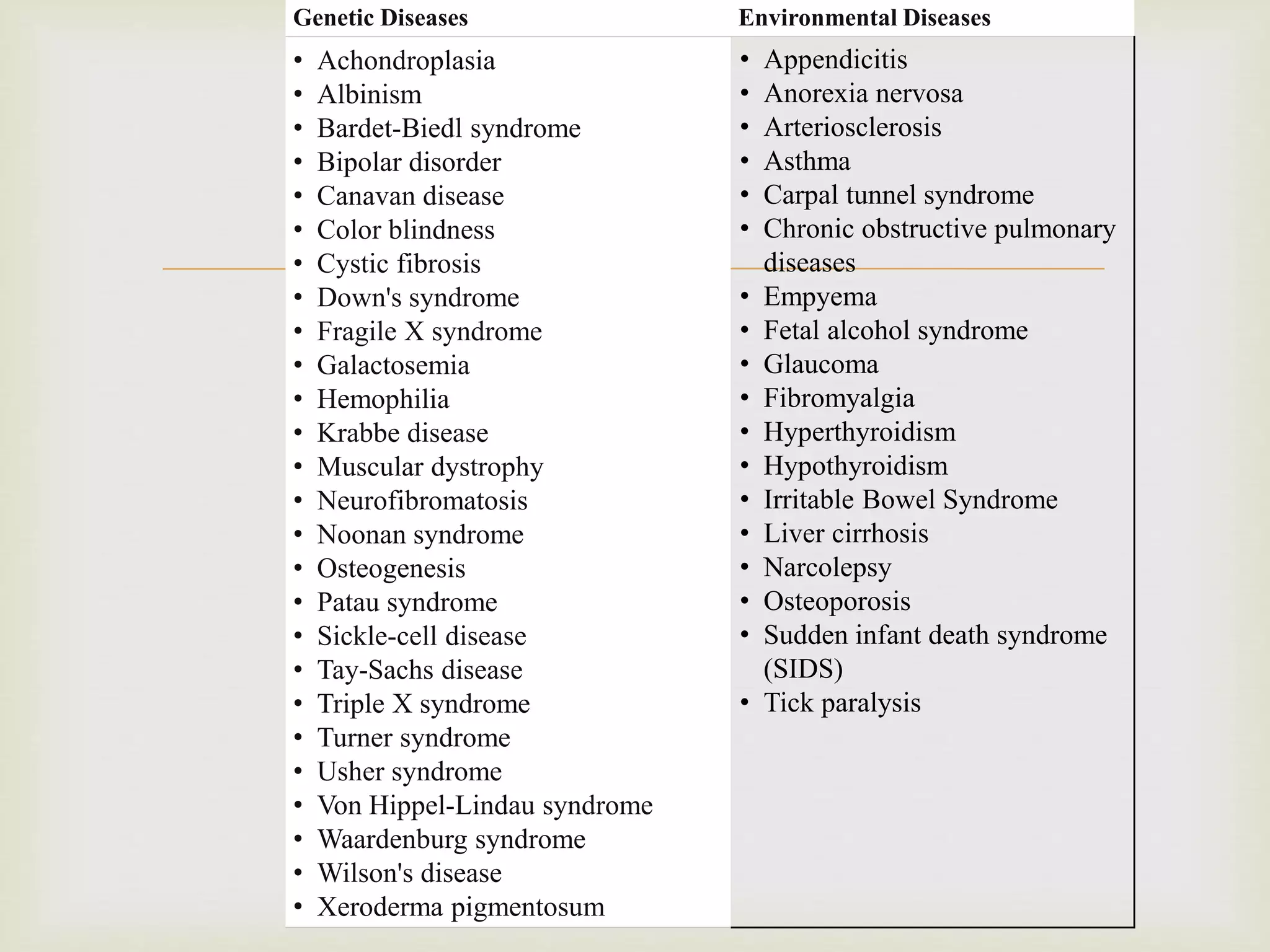
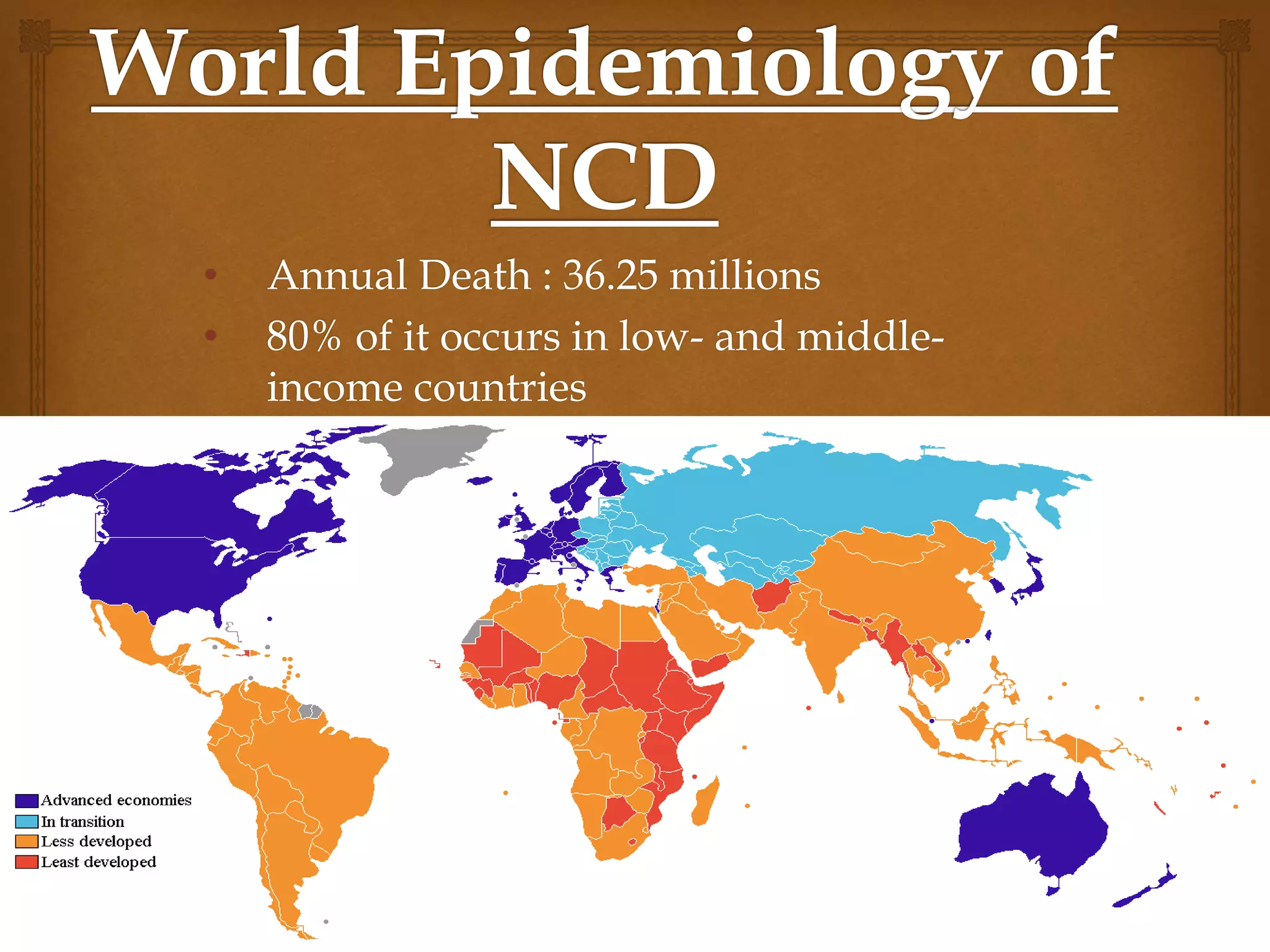
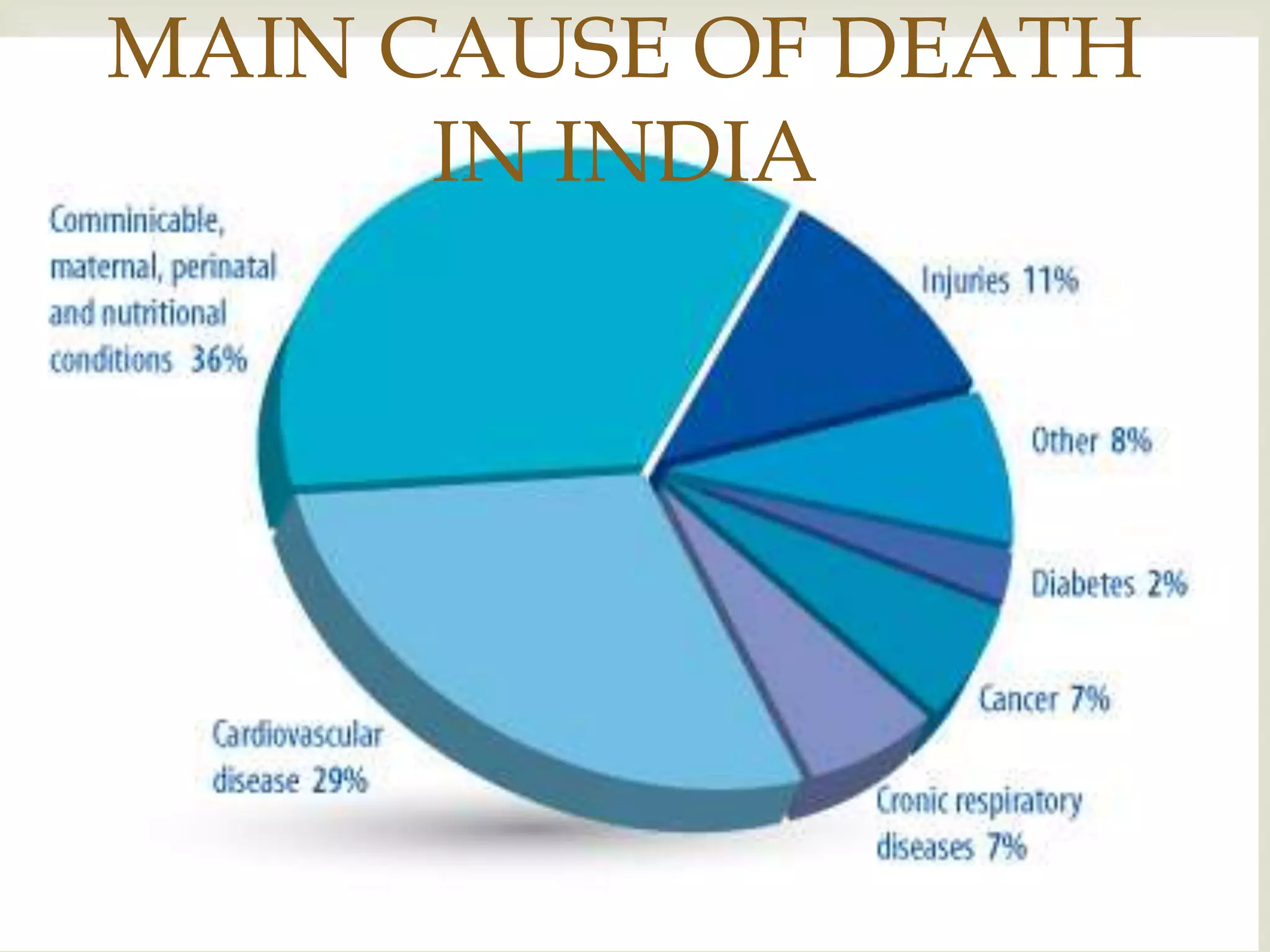
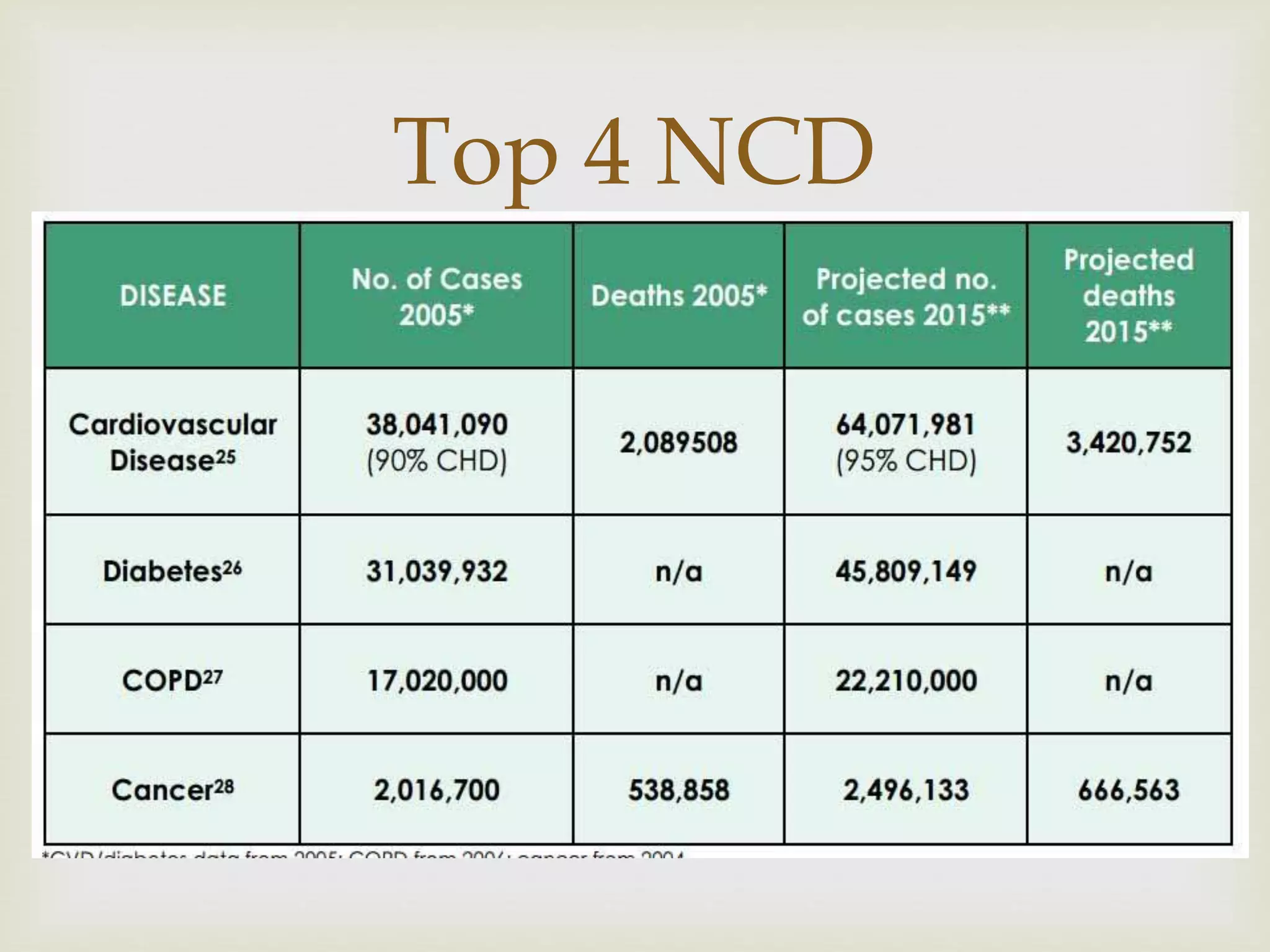
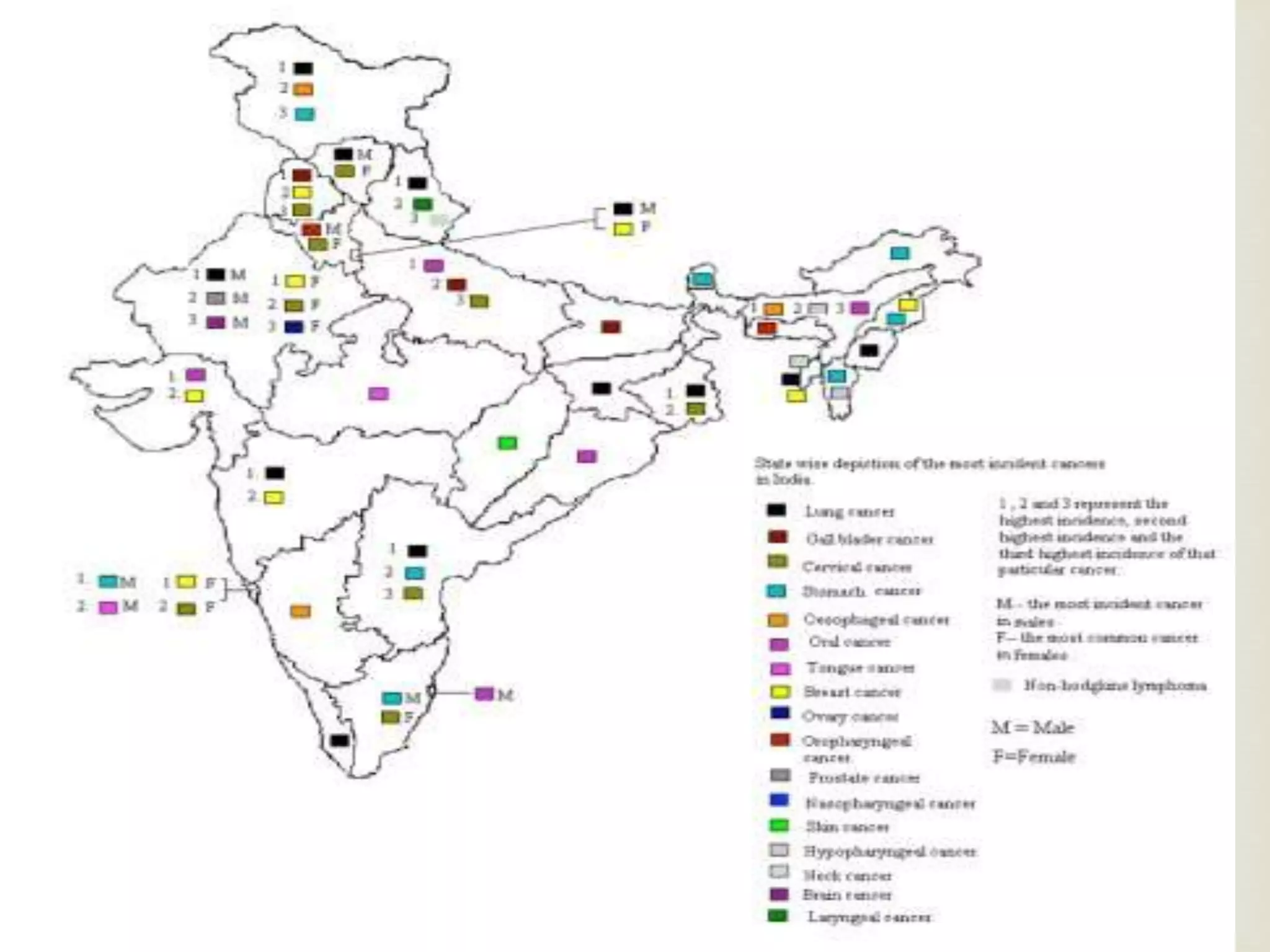
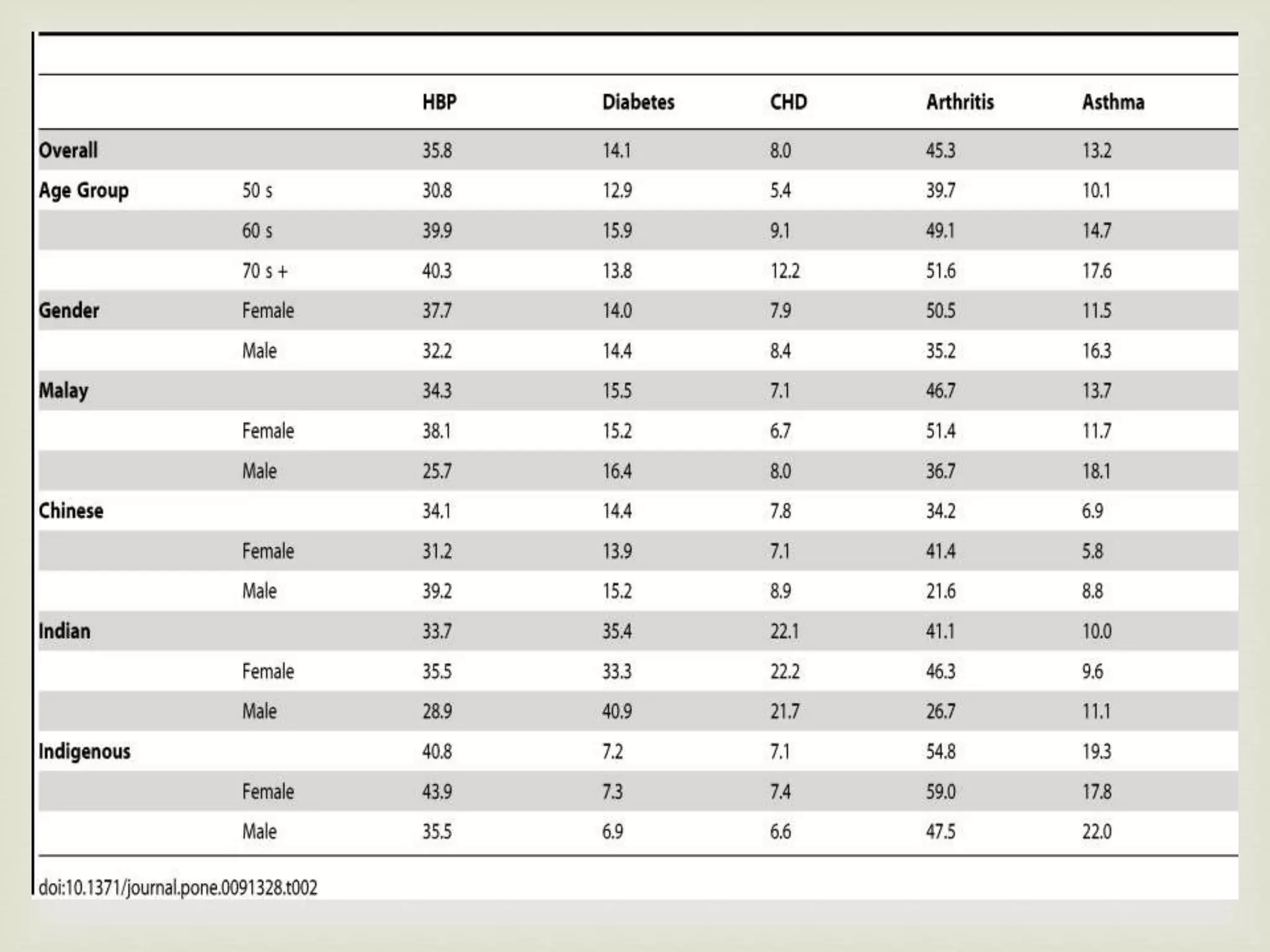
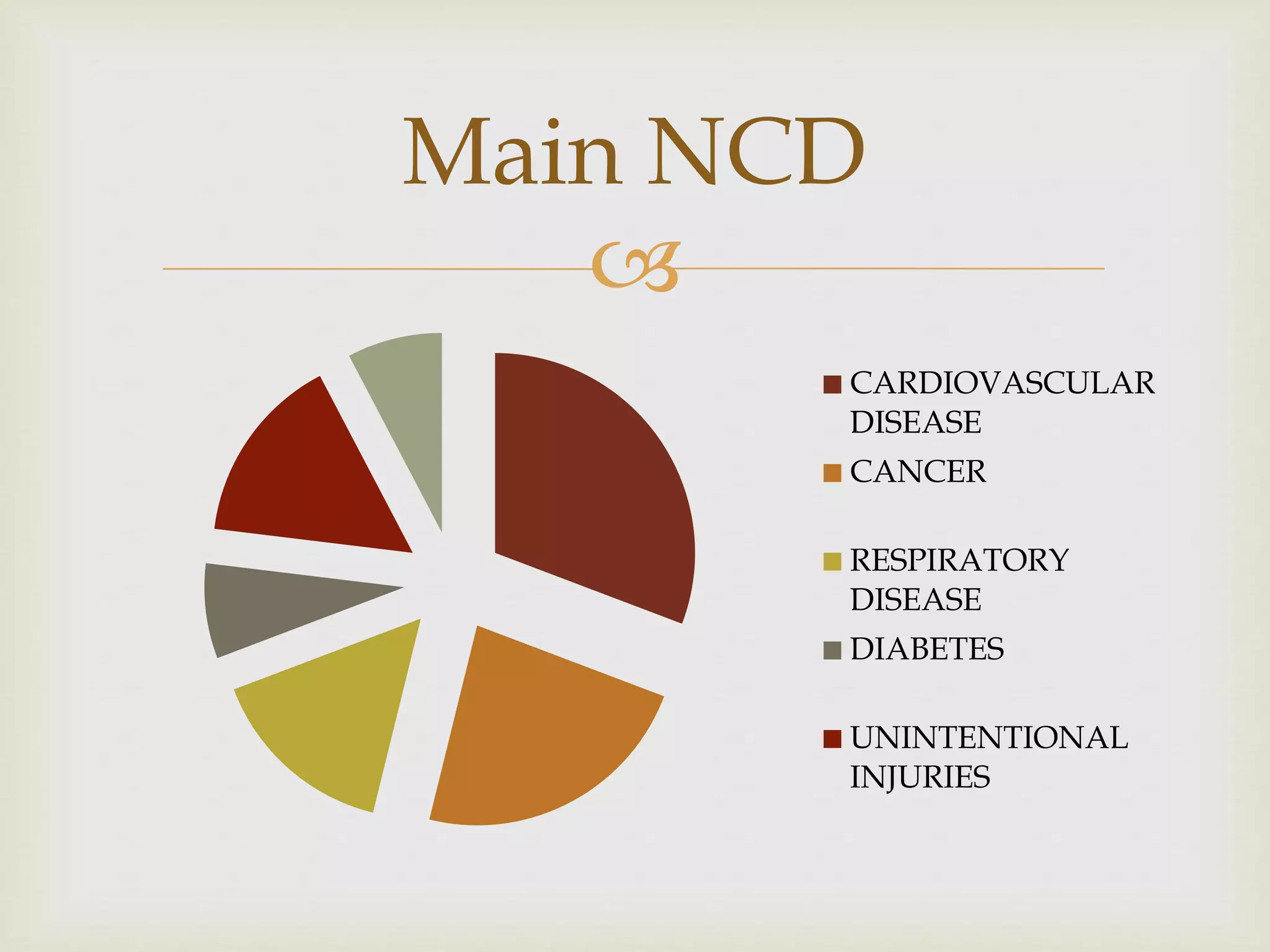
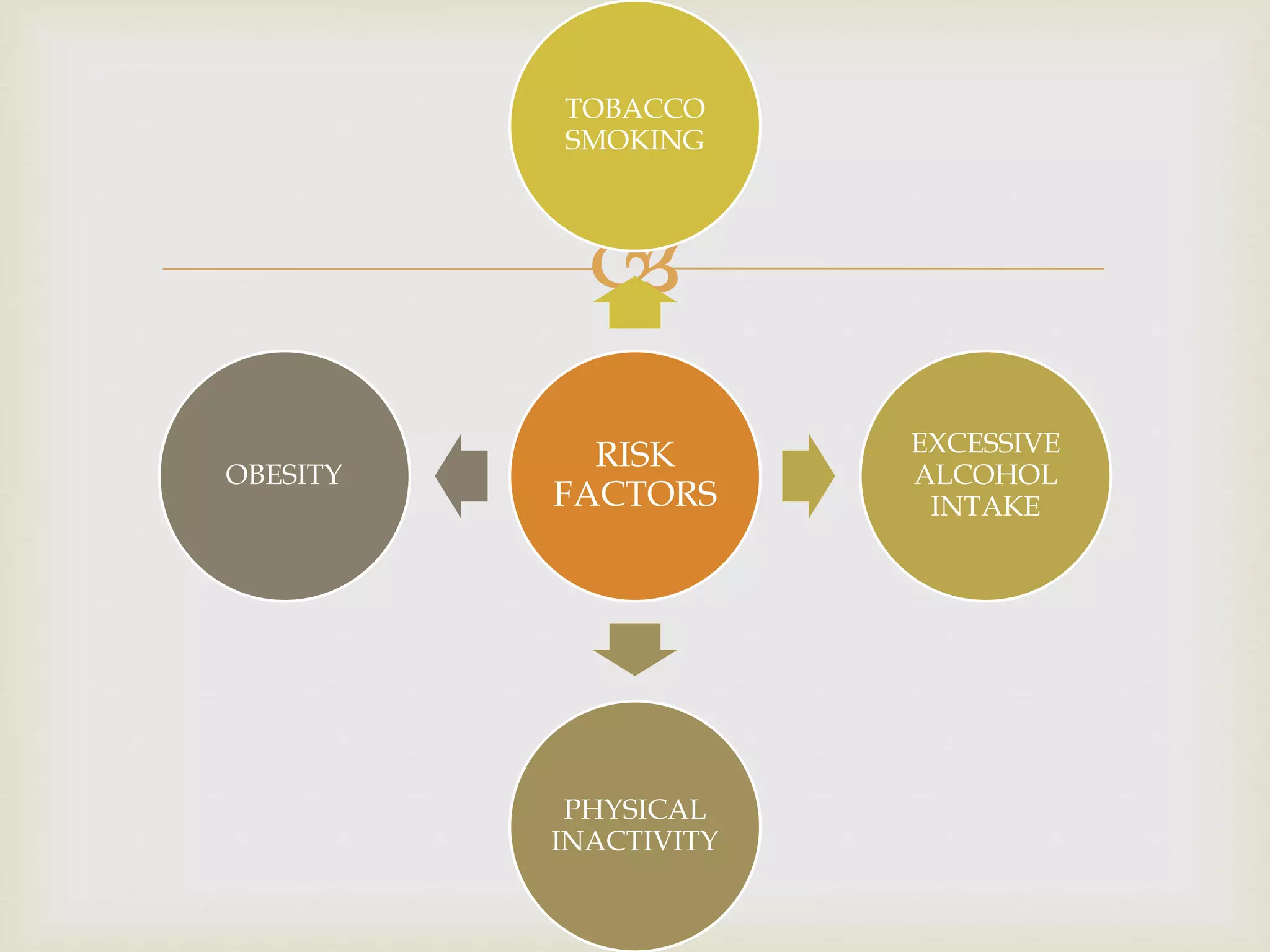
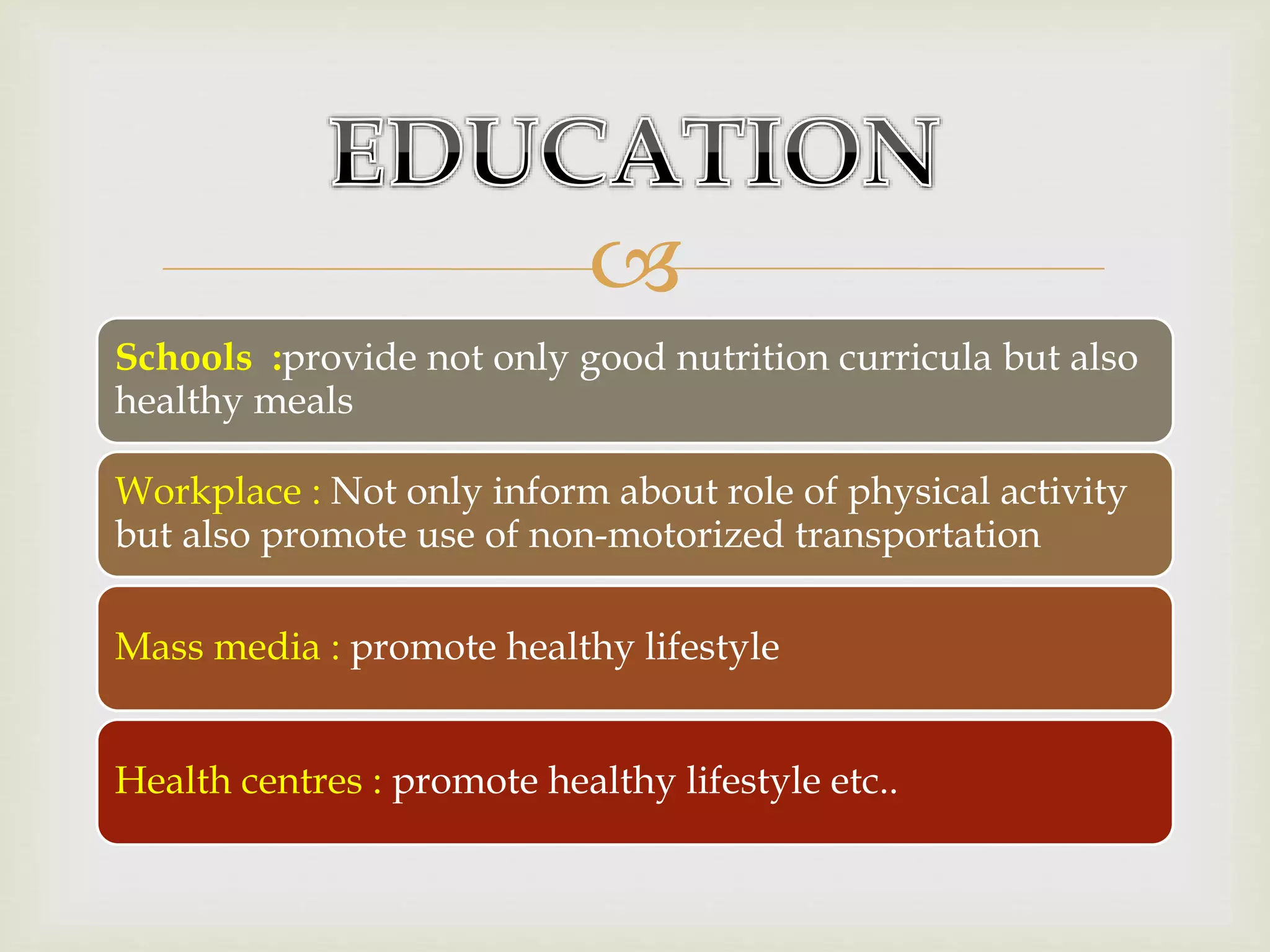
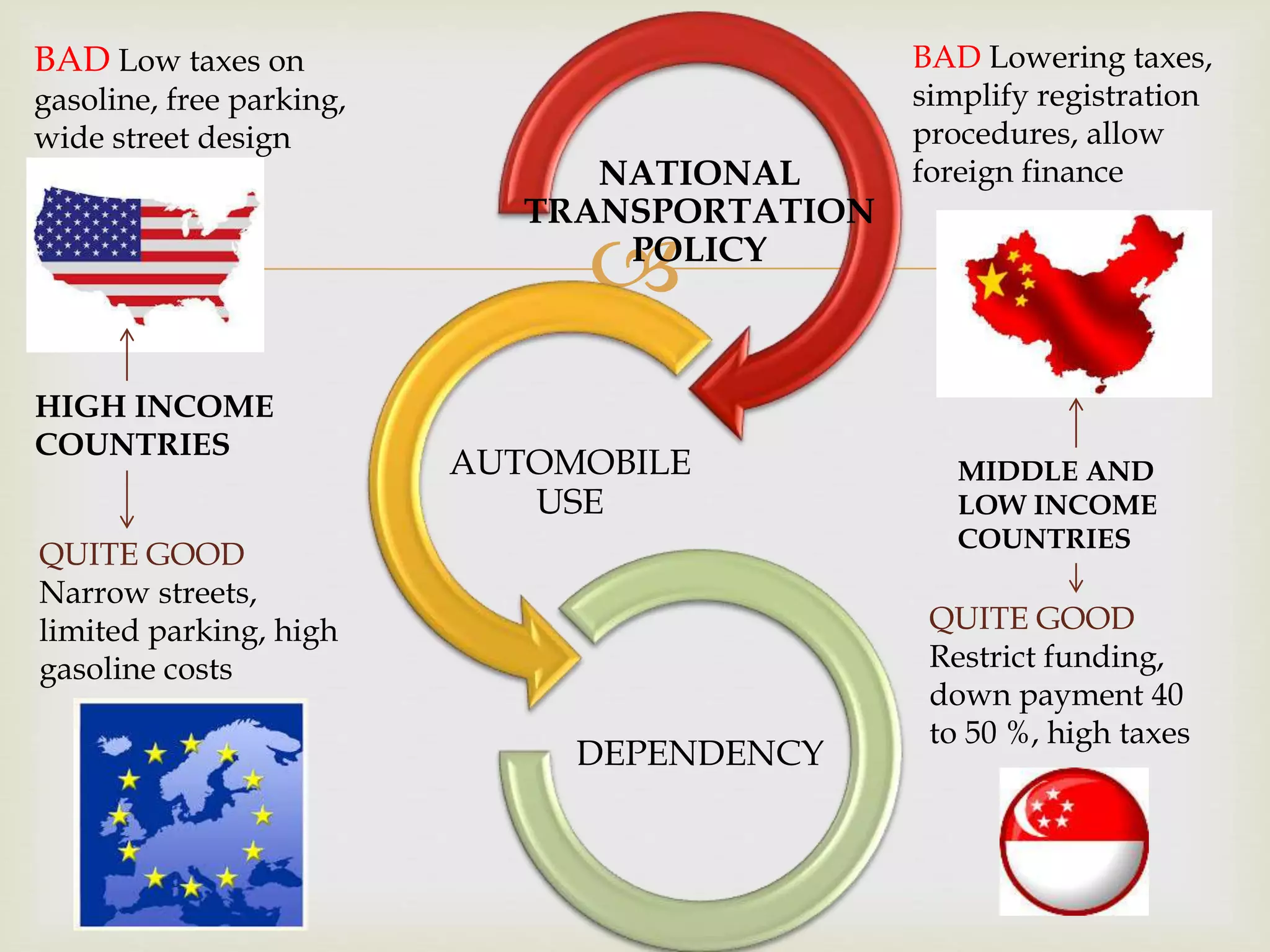
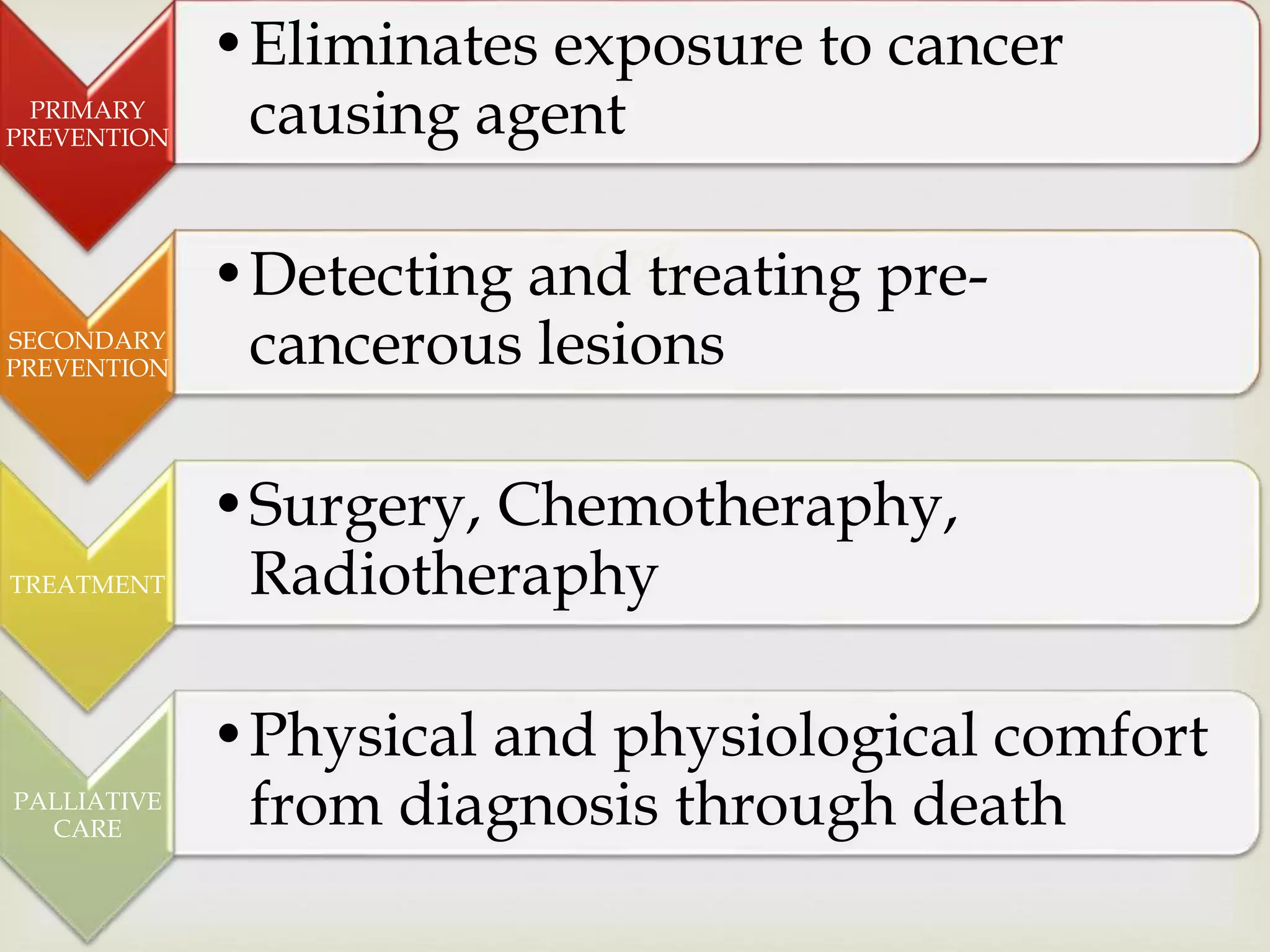
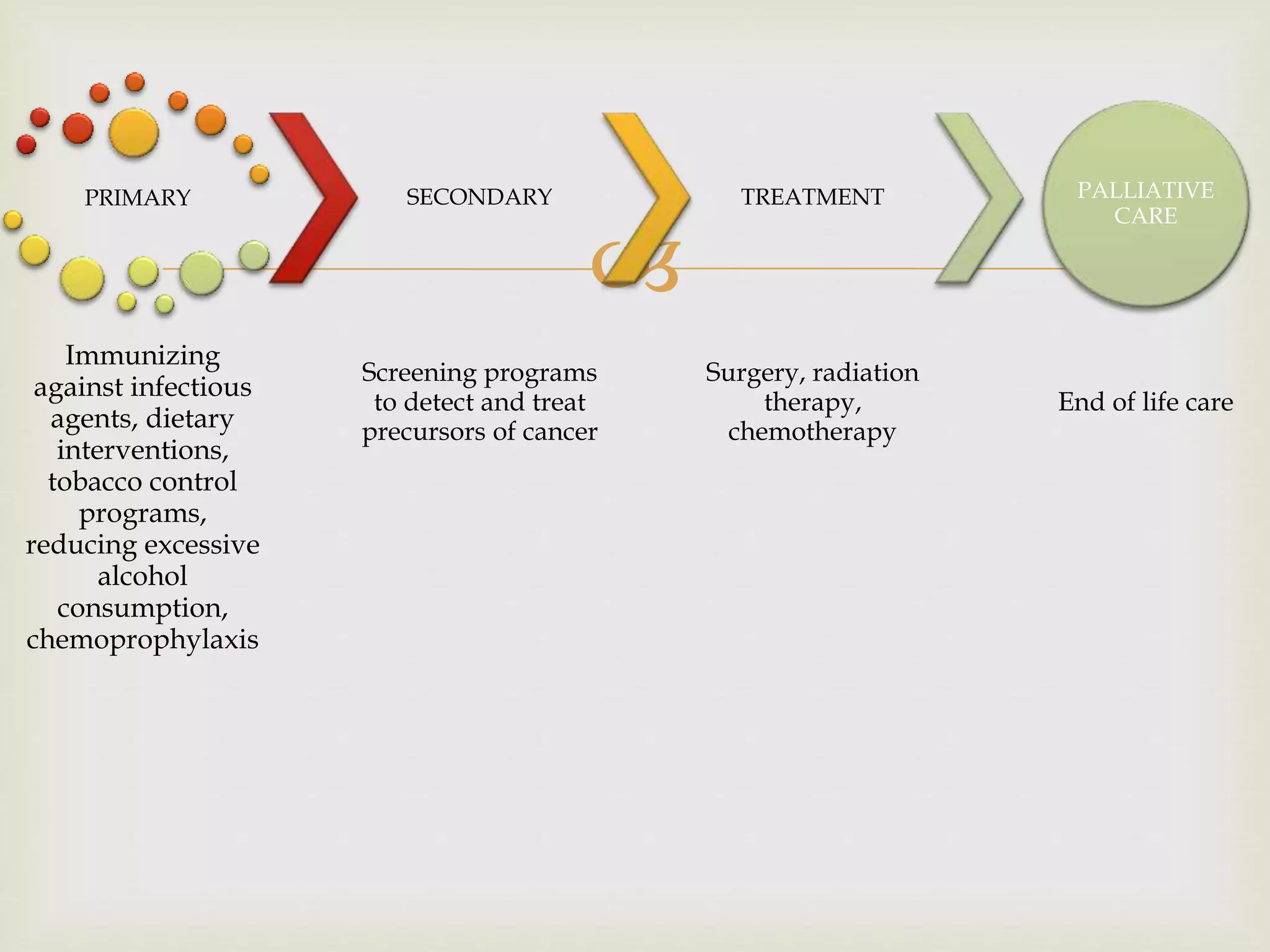
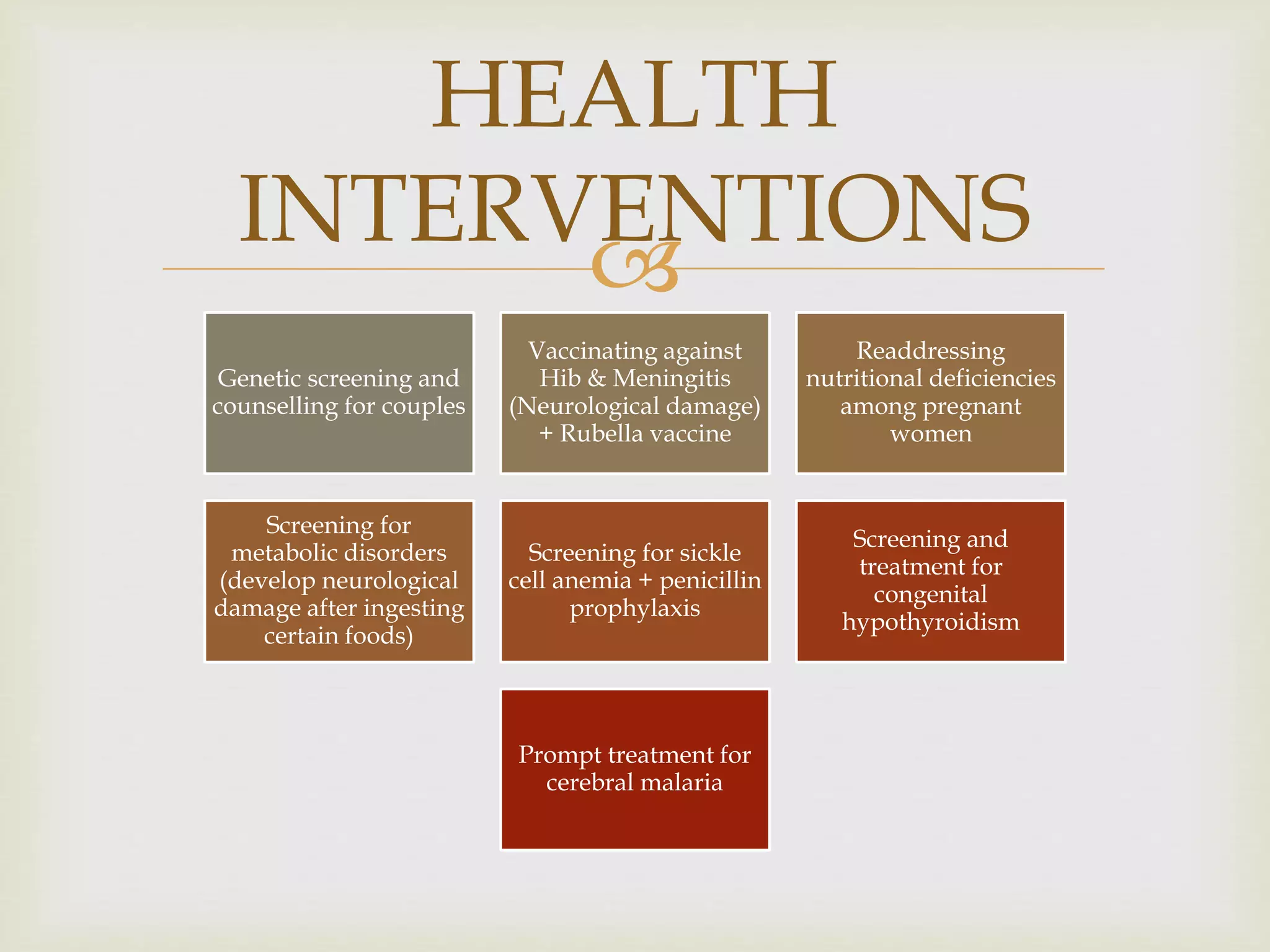
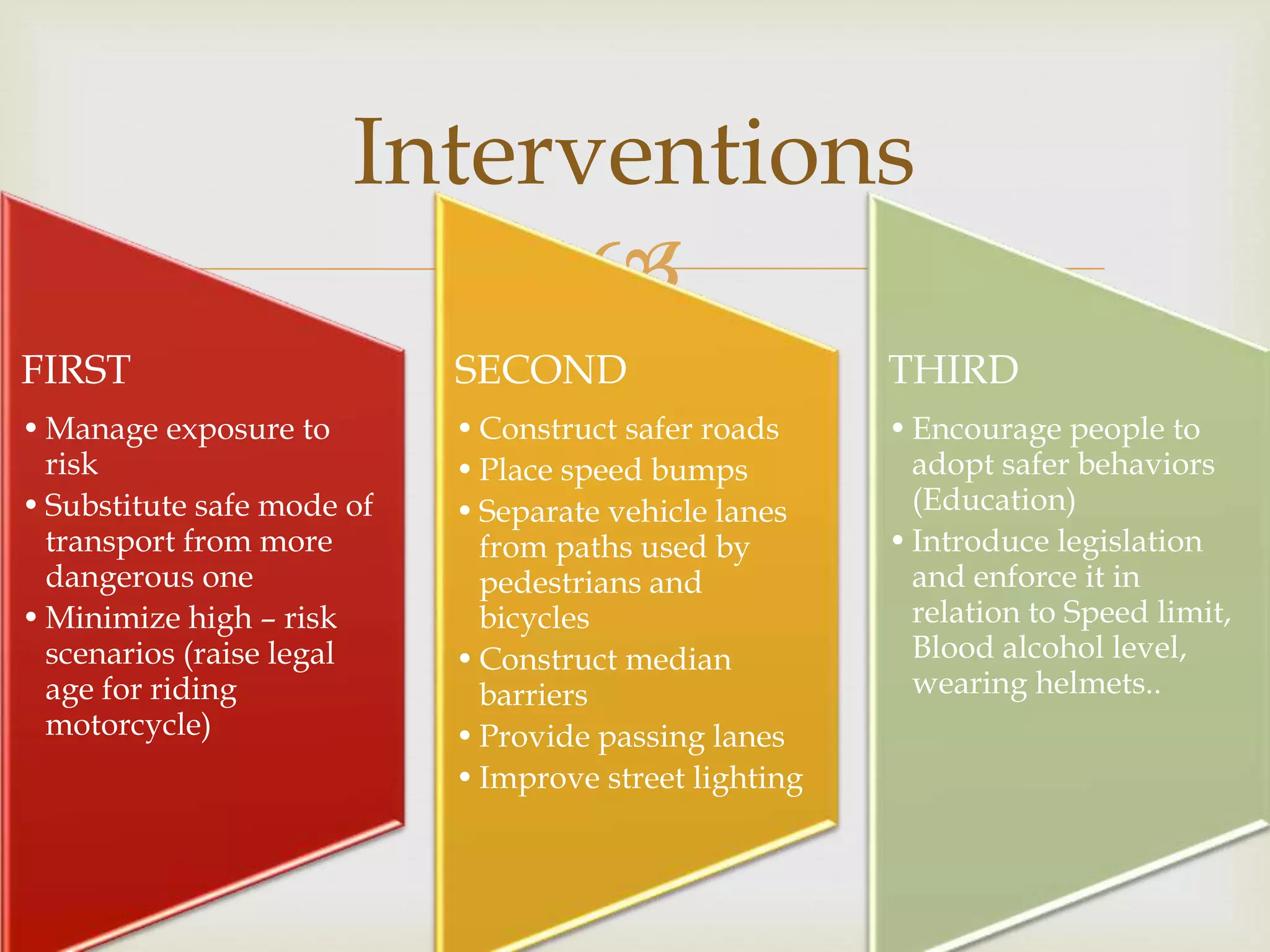
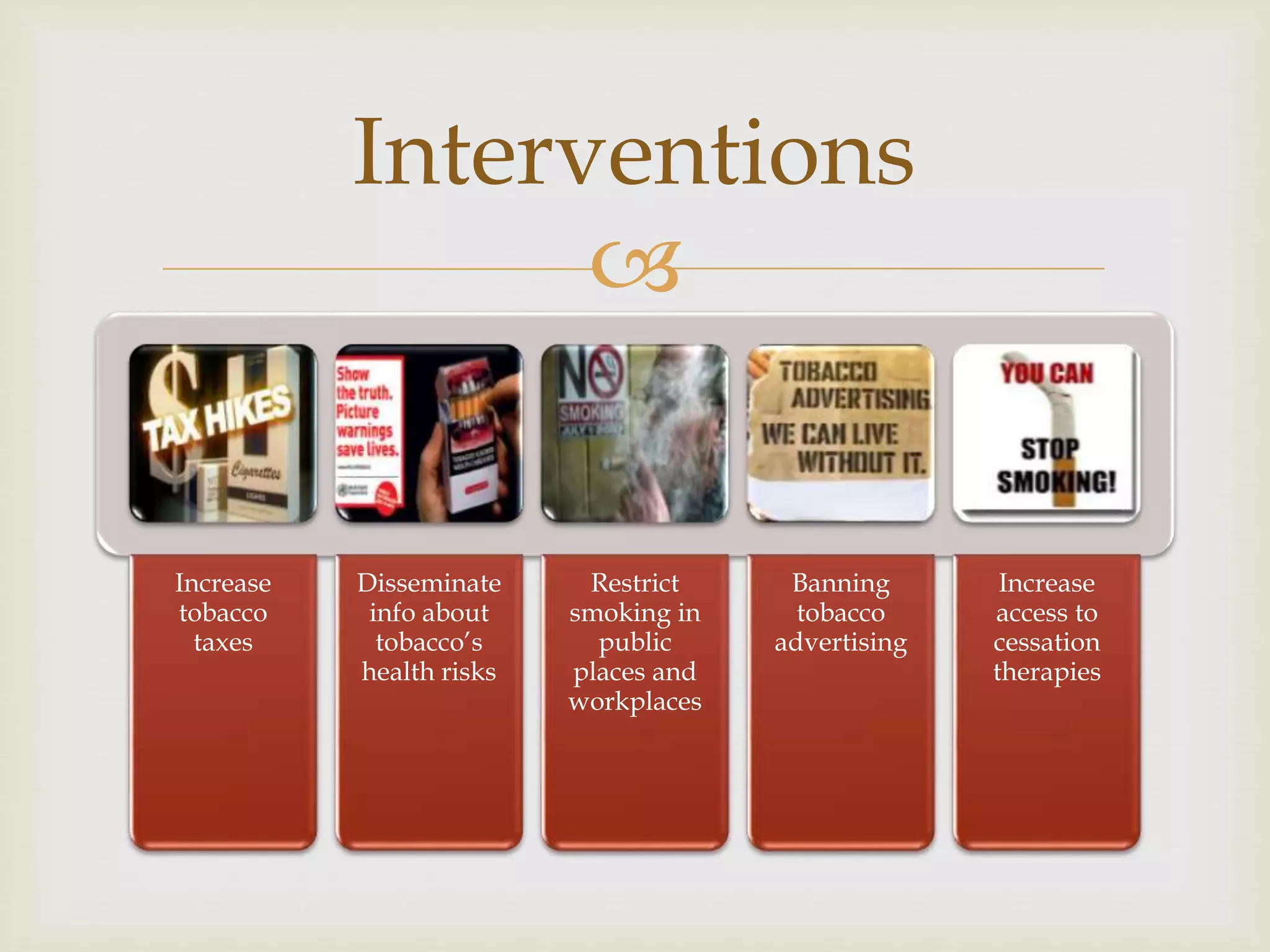
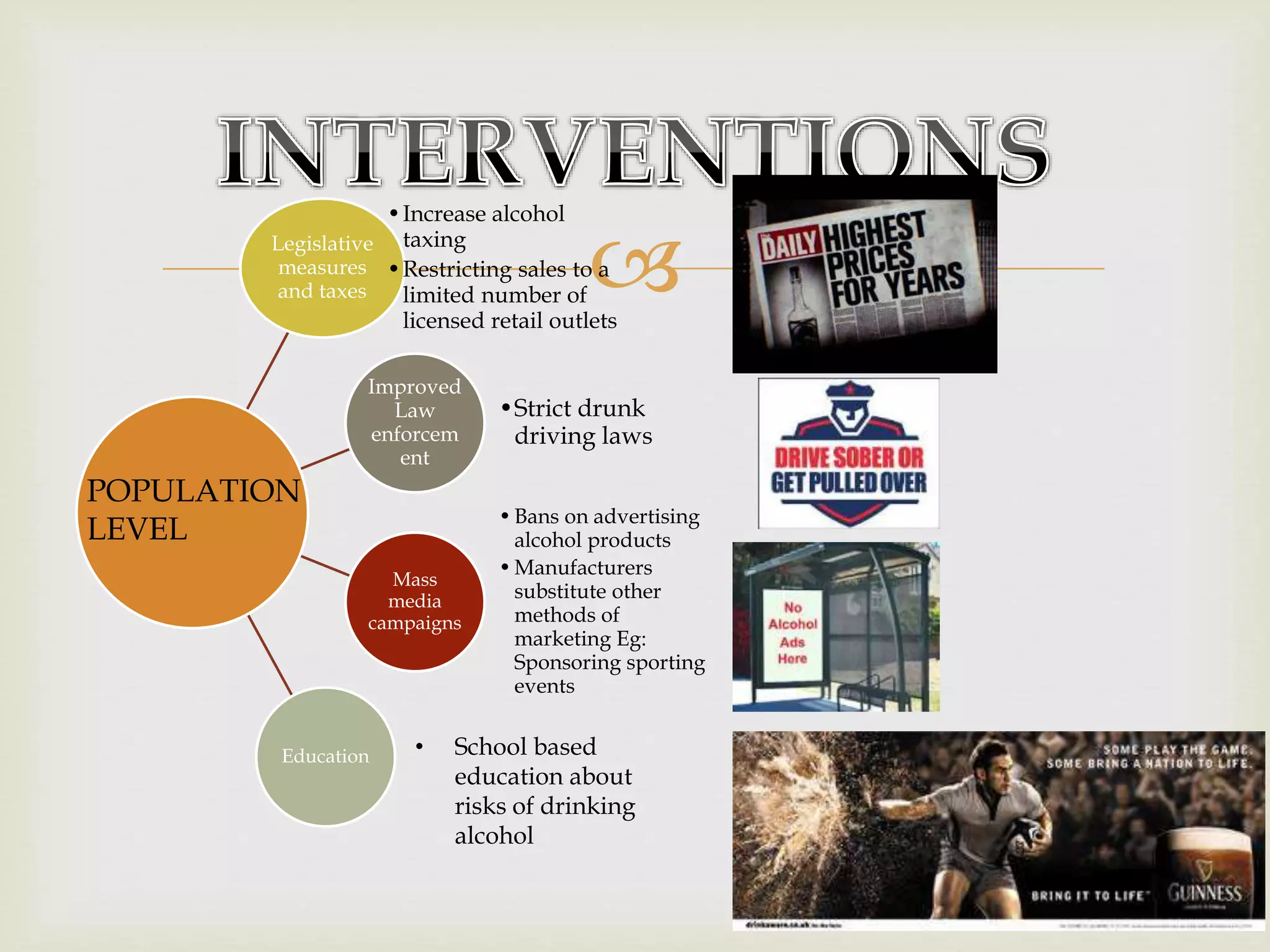
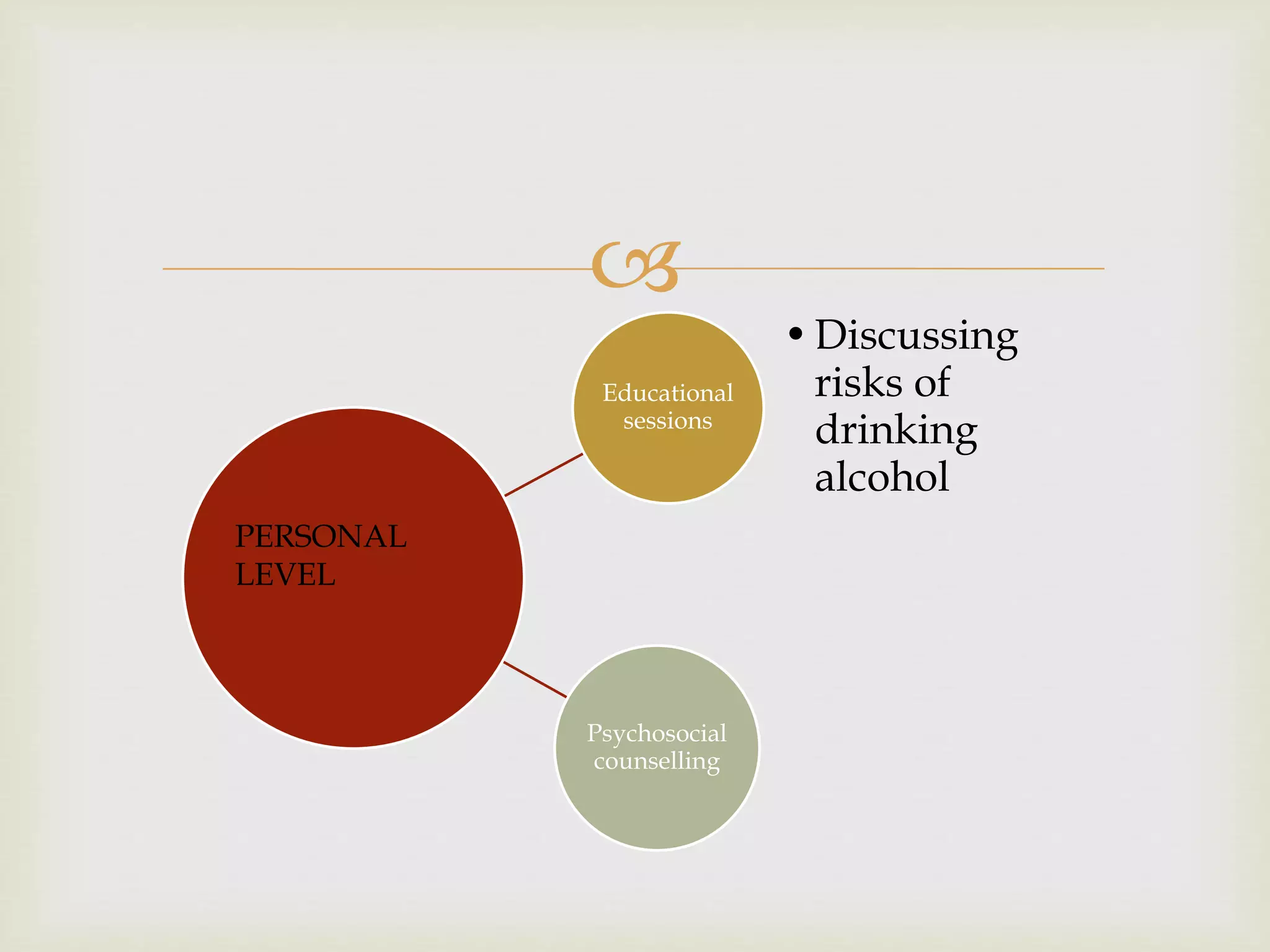
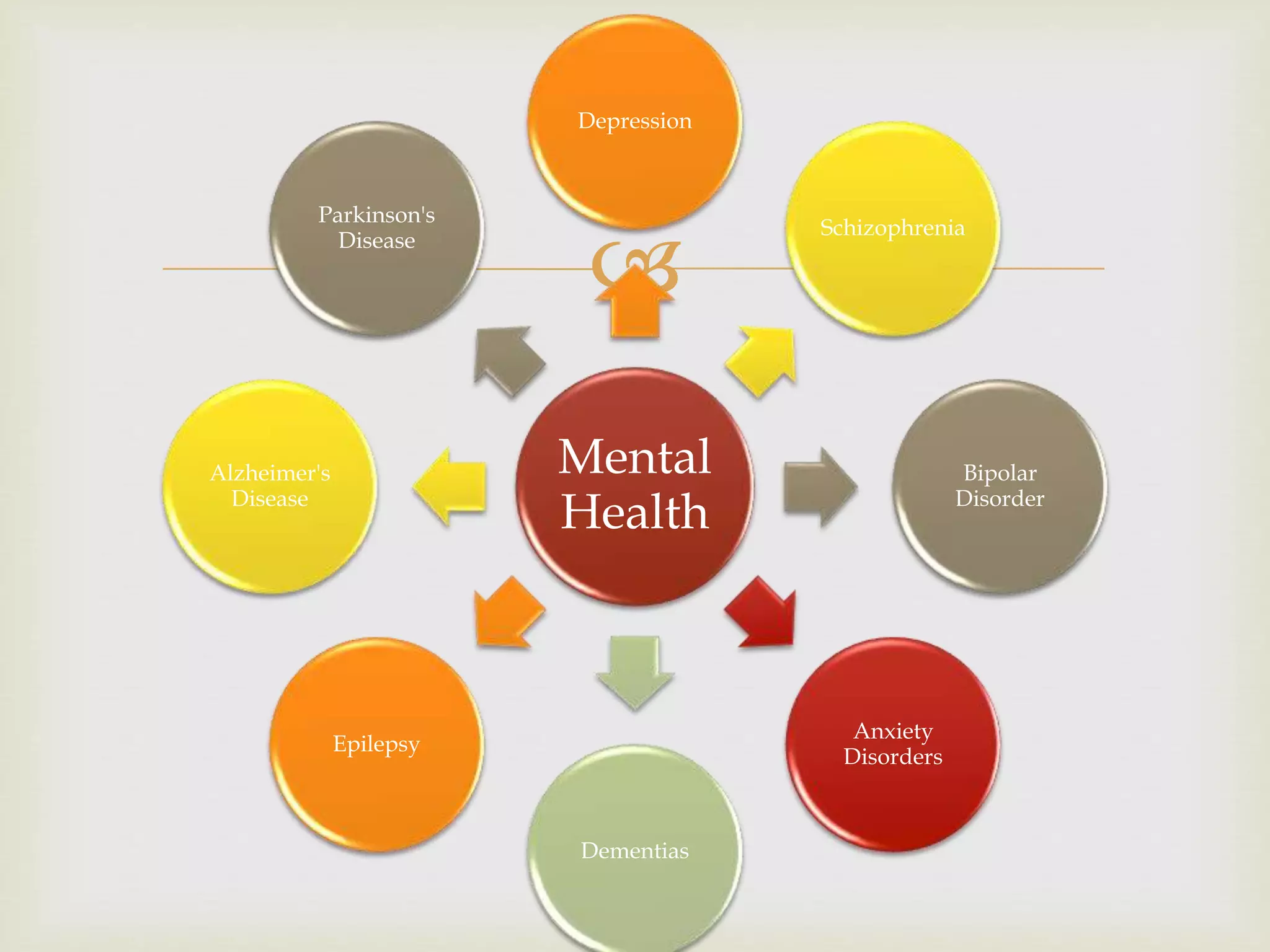
The document provides an overview of epidemiology, focusing on the distribution and determinants of health-related states in specific populations. It outlines the importance of both descriptive and analytic epidemiology in identifying health trends and risk factors, while discussing non-communicable diseases and their causes, particularly in the context of various countries. Additionally, the document emphasizes the need for prevention, intervention strategies, and policies to address the challenges posed by such diseases.