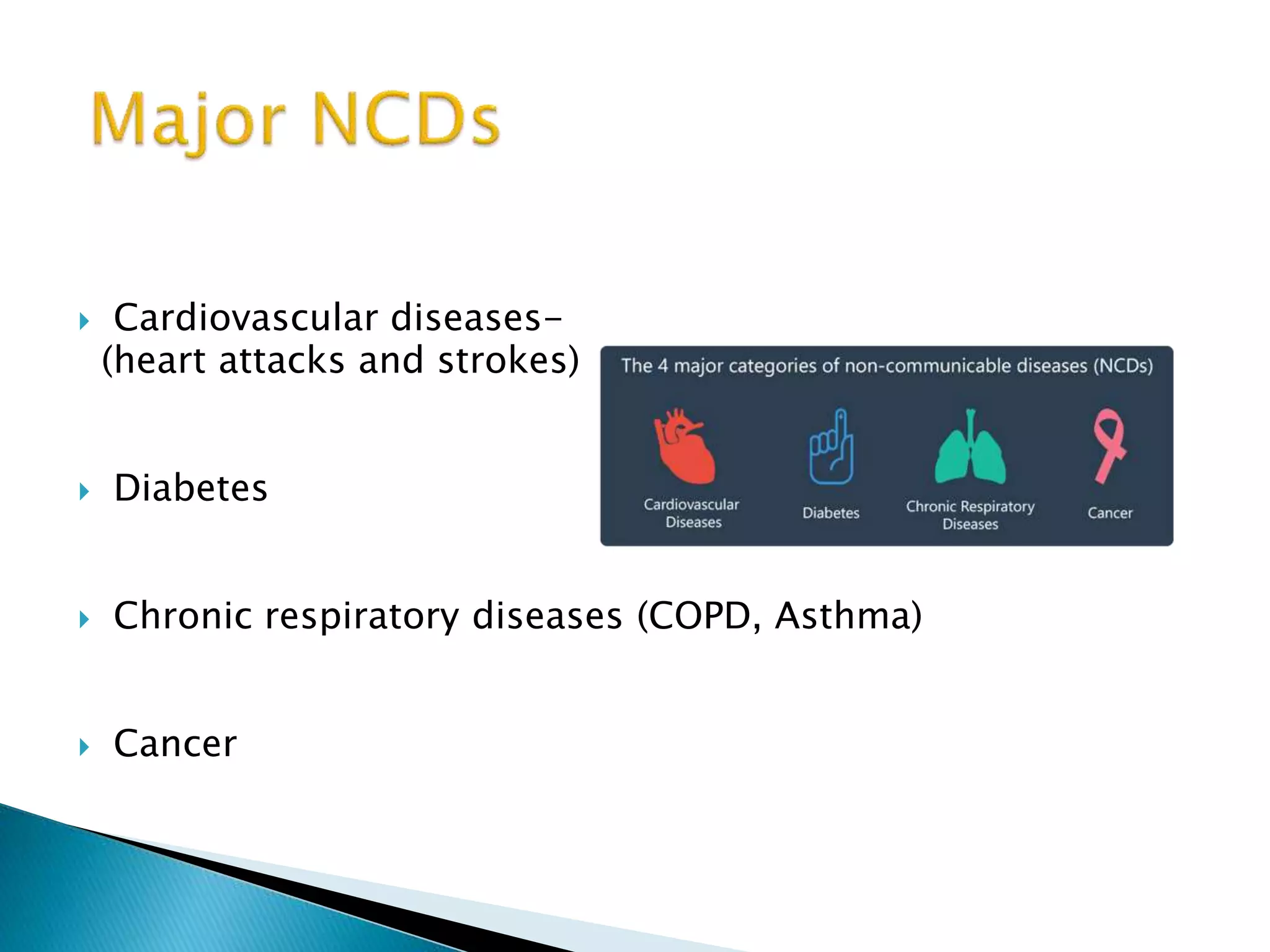
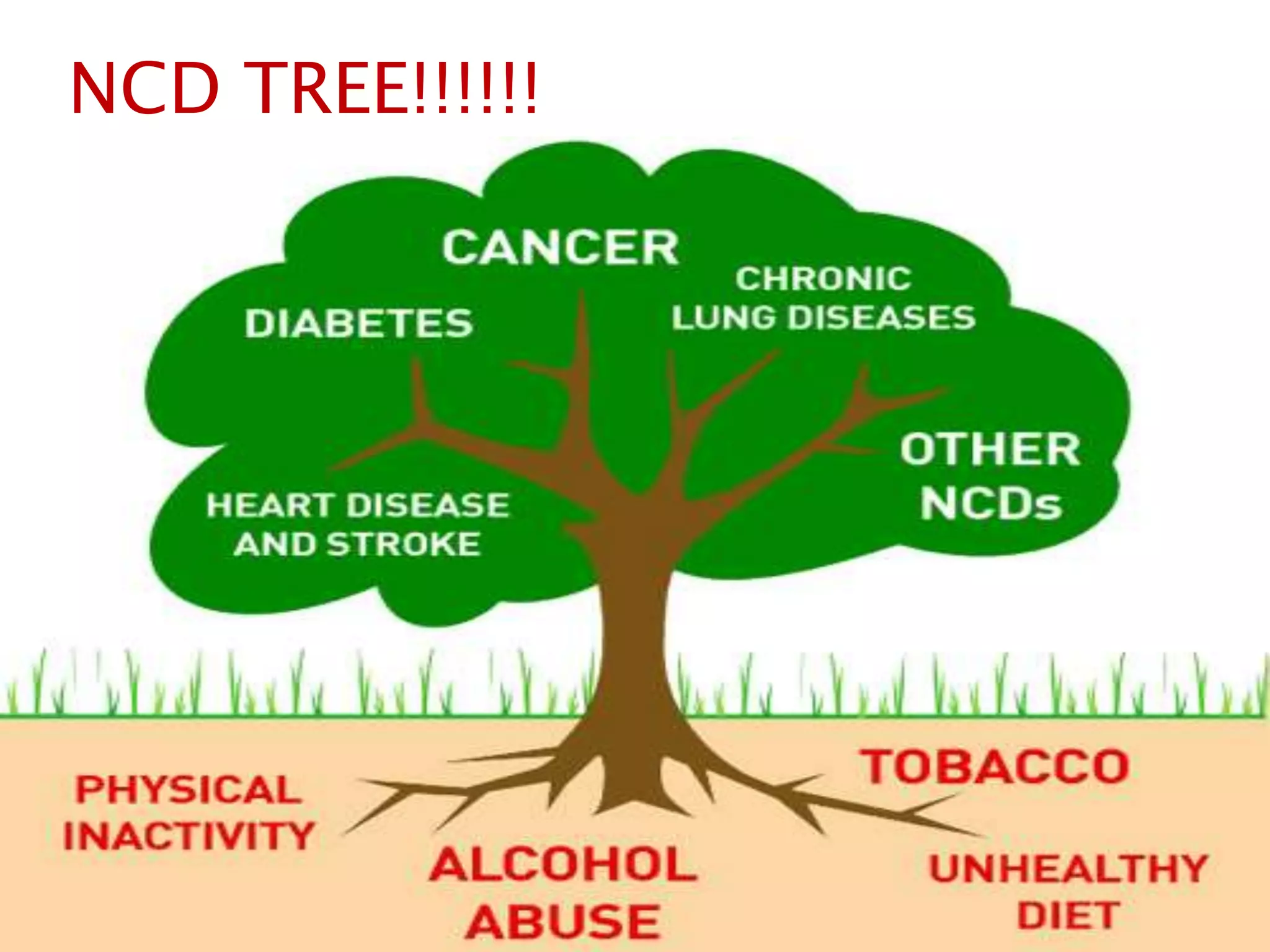
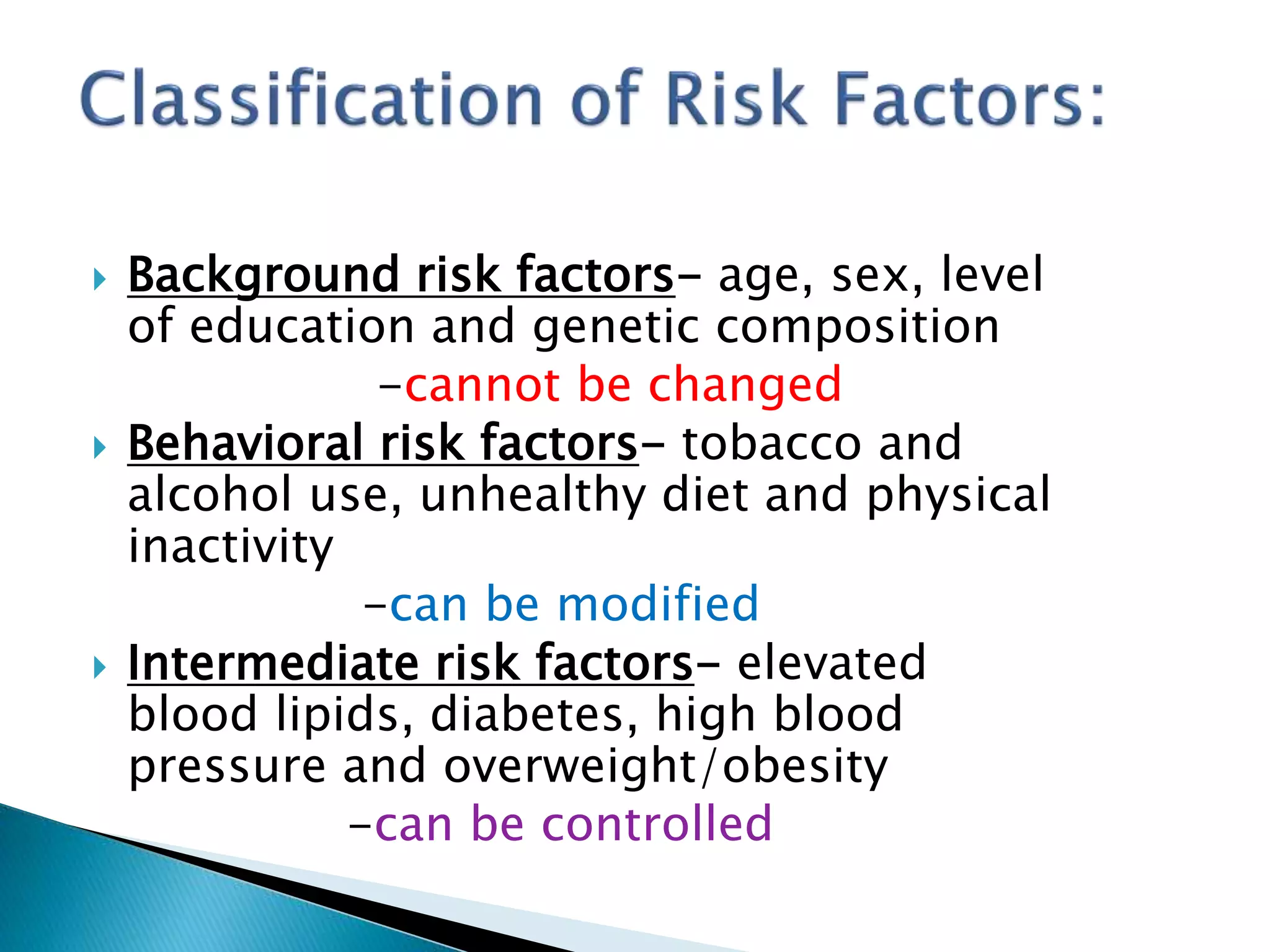
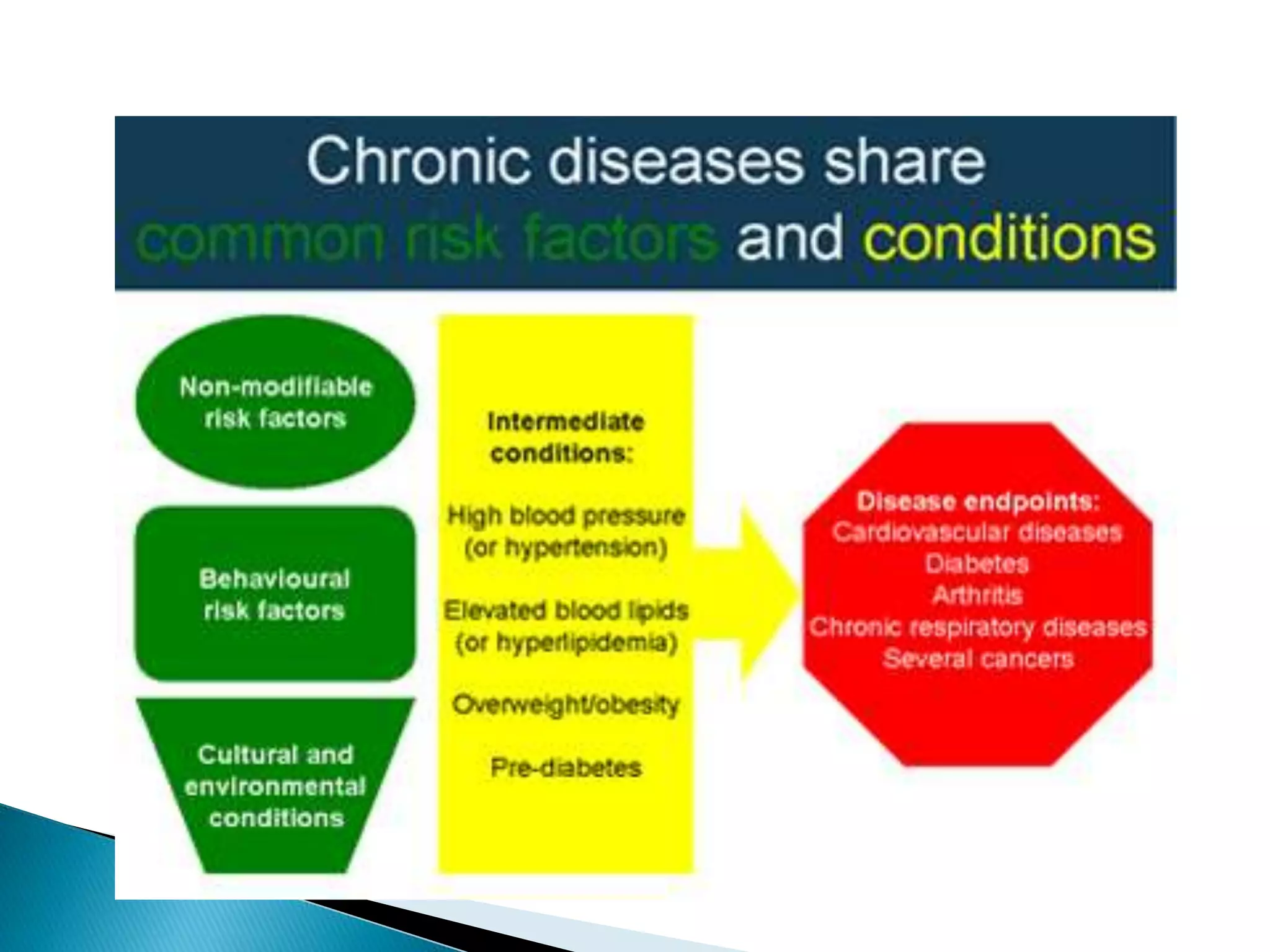
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are a leading cause of mortality globally, responsible for over 36 million deaths annually, particularly affecting low- and middle-income countries. Major risk factors include unhealthy diets, tobacco use, and physical inactivity, with strategies like enhanced surveillance, prevention programs, and health policy development required to address these issues effectively. Bangladesh has made progress in NCD management through various health initiatives, but further emphasis on program monitoring and national data collection is crucial for improving outcomes.