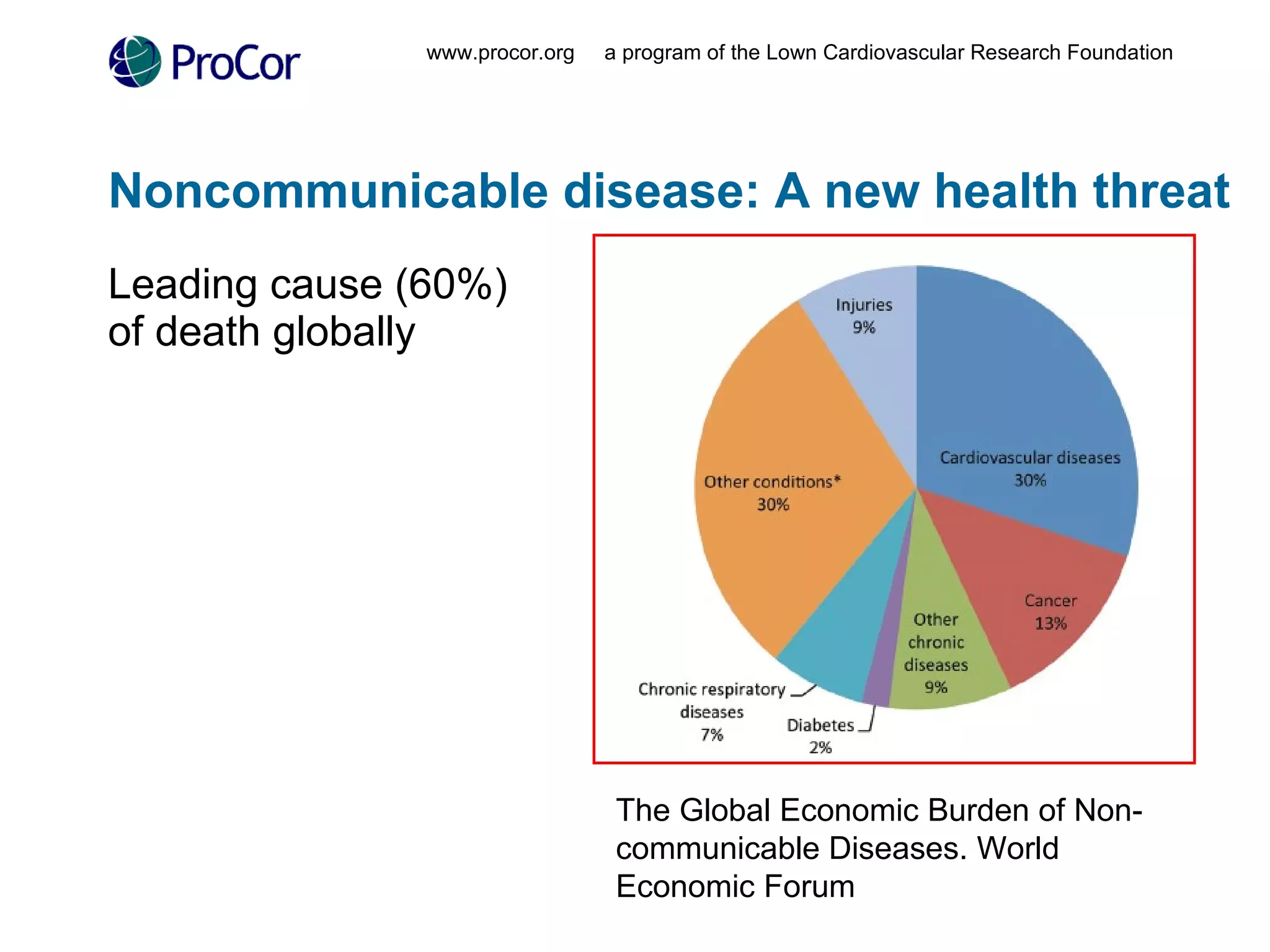
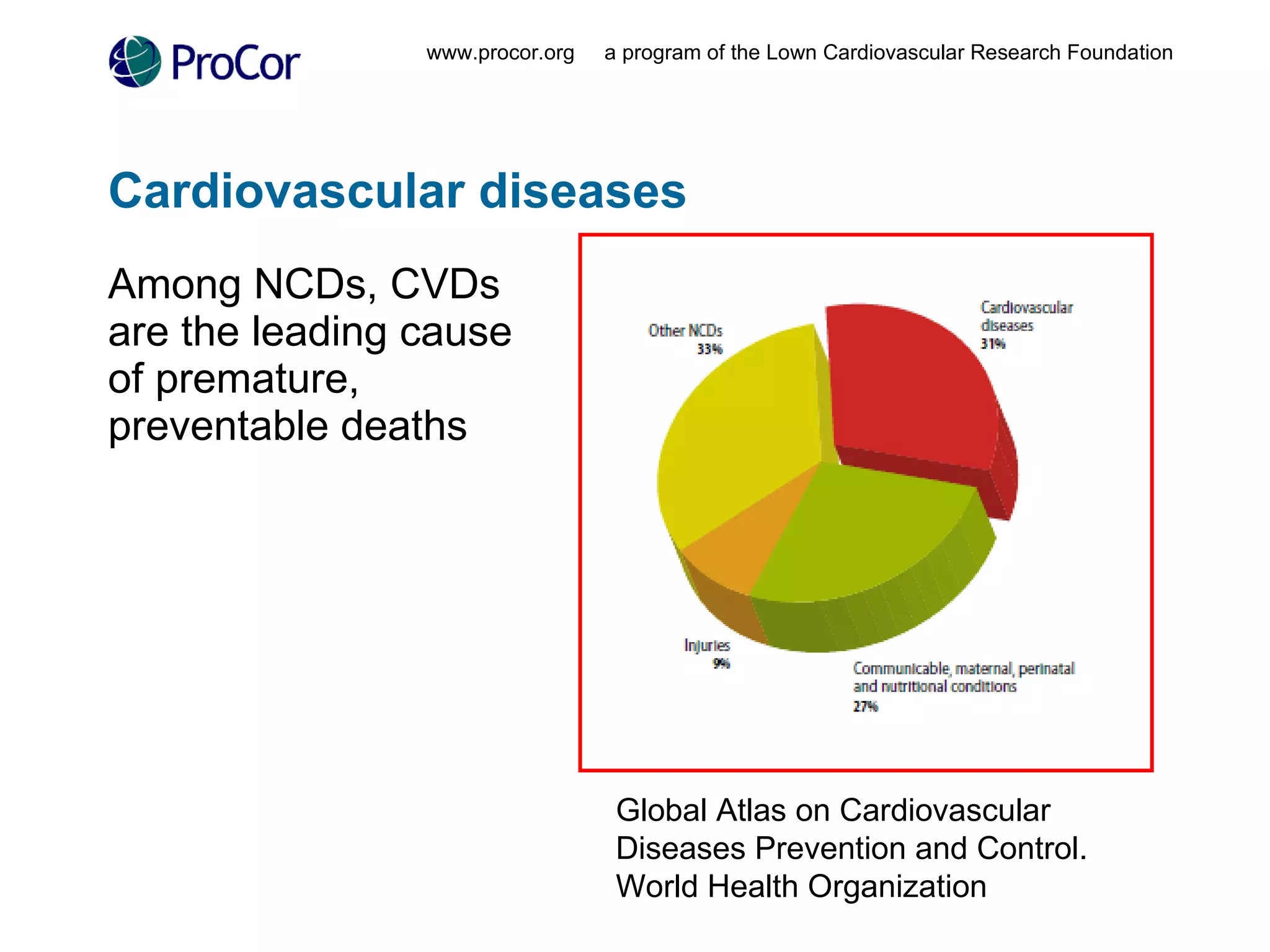
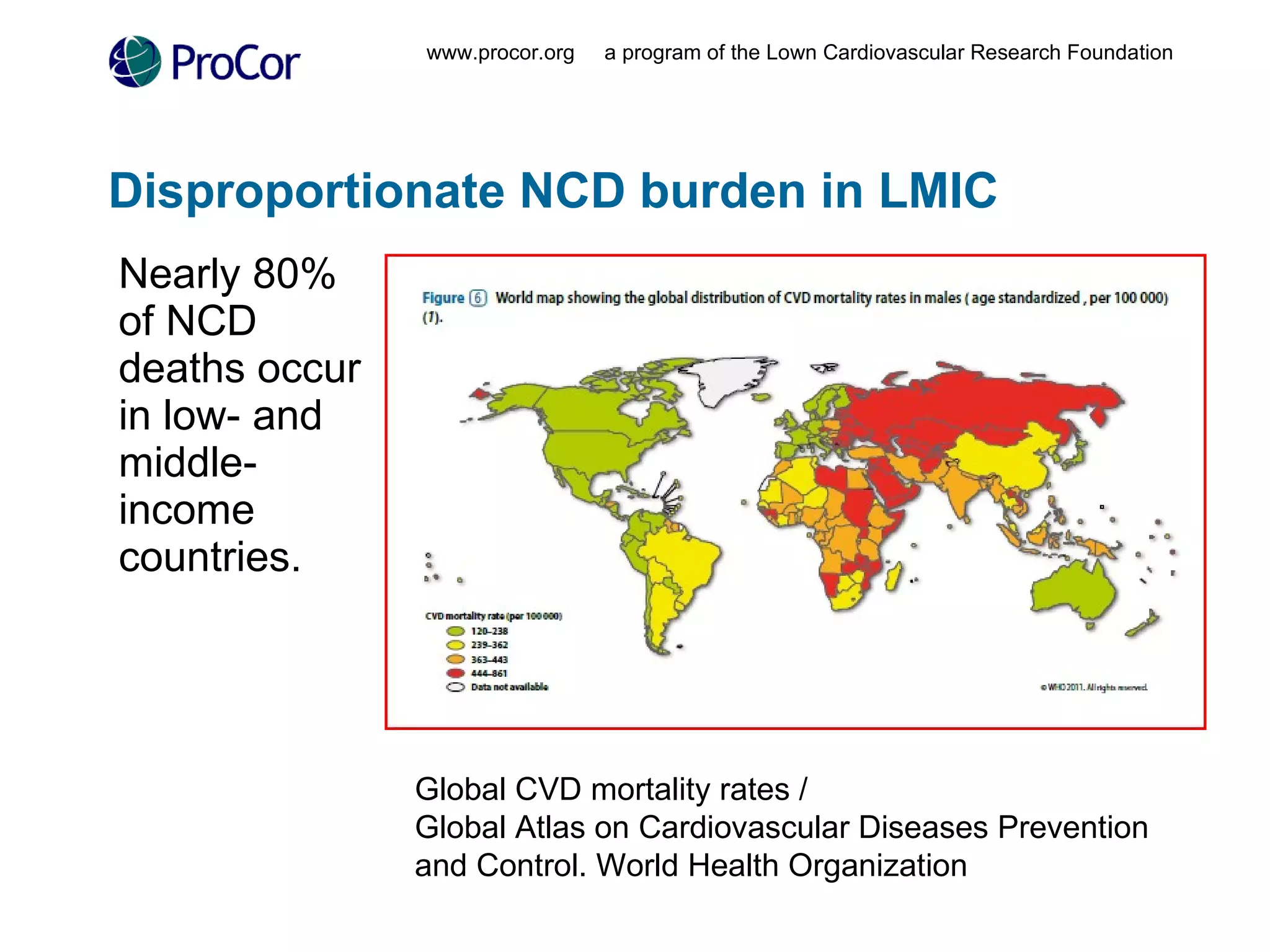
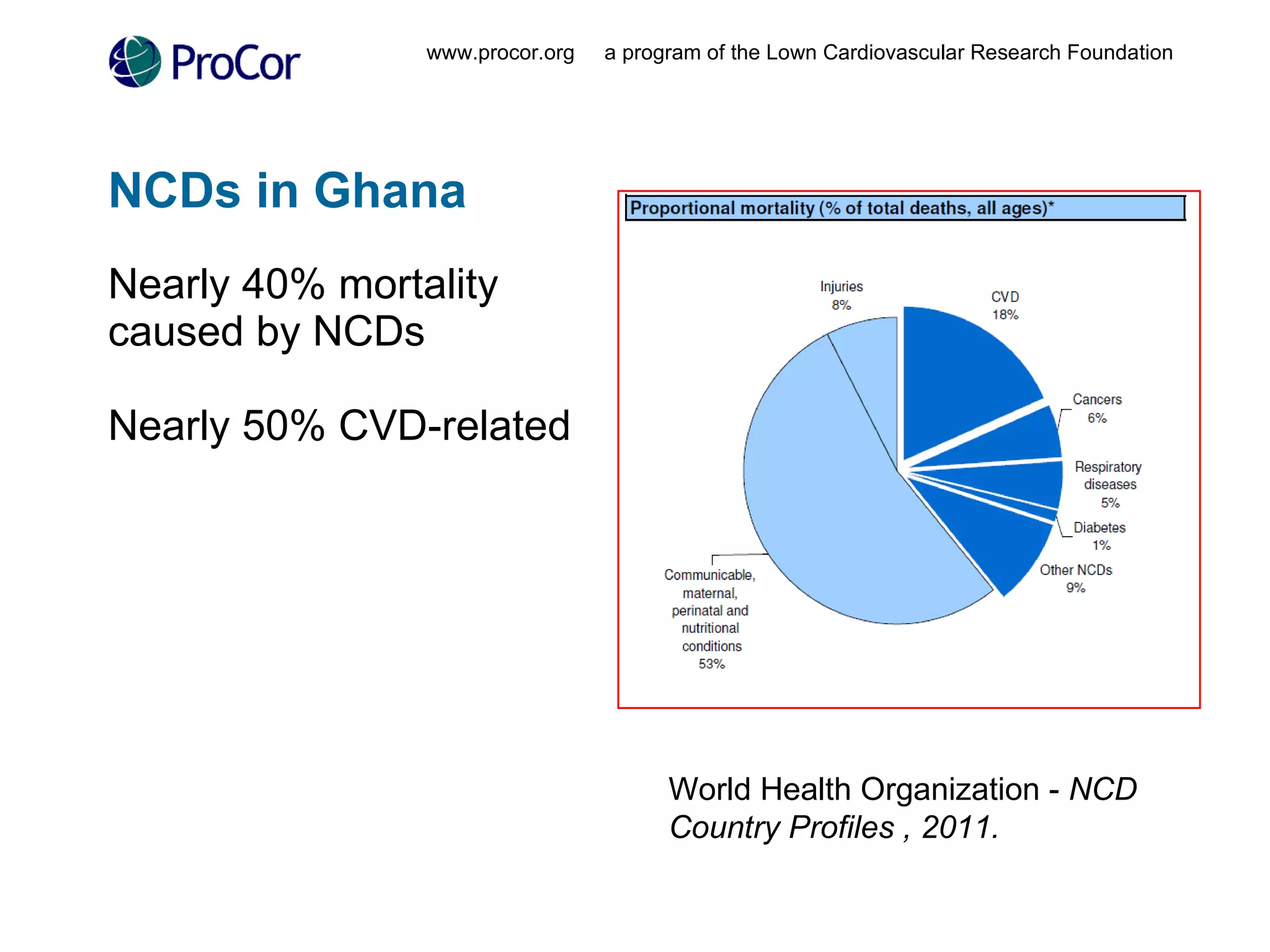
The document discusses noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) like cardiovascular disease which cause a large burden in developing countries. It outlines a study conducted in Ghana that found health workers have high awareness of NCDs but face barriers to accessing up-to-date information like cost and unreliable internet connectivity. The study recommends addressing these issues by providing local, open-access research and knowledge sharing to help prevent NCDs.


















![Support prevention. Share knowledge. Subscribe to ProCor. www.procor.org [email_address] Benn Grover Editor, ProCor Lown Cardiovascular Research Foundation 21 Longwood Avenue Brookline, MA 02446 www.procor.org [email_address] www.procor.org a program of the Lown Cardiovascular Research Foundation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/collinskokuro-111102101756-phpapp01/75/Open-access-publishing-and-noncommunicable-disease-prevention-26-2048.jpg)