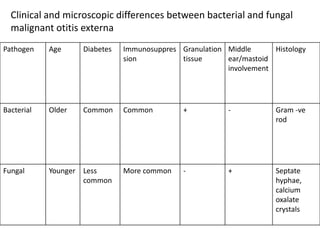
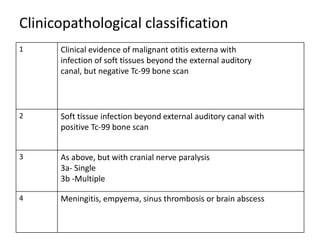
Malignant otitis externa is an aggressive infection of the soft tissues of the external ear that can spread to involve the skull base. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the causative organism in 95% of cases. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus and immunosuppression. Clinically, patients experience long-standing ear pain and drainage. The infection can spread to involve cranial nerves and potentially spread to the brain. Diagnosis involves clinical examination, biopsy, and imaging tests like CT, MRI, and bone scans. Treatment involves long-term intravenous and oral antibiotics, sometimes with the addition of surgery to debride infected tissues and hyperbaric oxygen therapy.