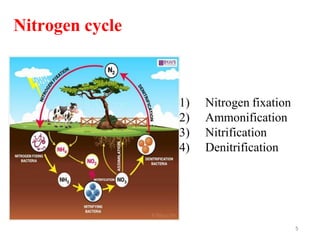
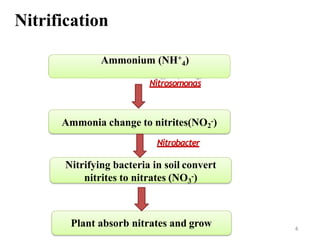
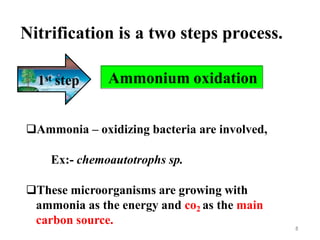
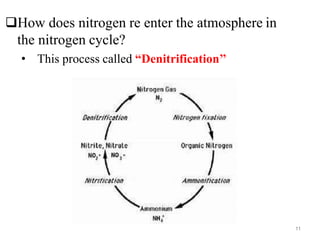
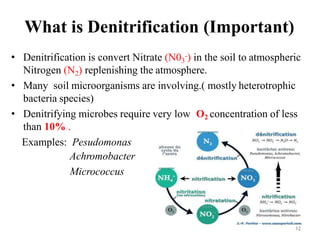
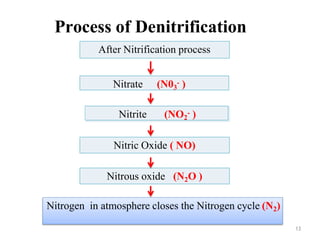
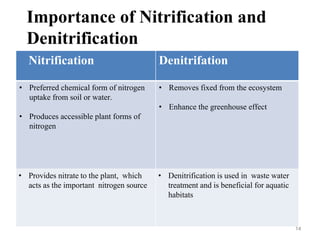
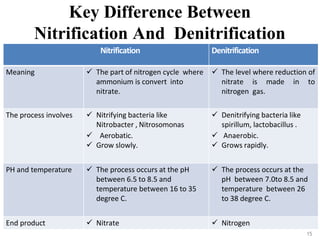
The document outlines the key processes of nitrification and denitrification in the nitrogen cycle, highlighting their importance and differences. Nitrification converts ammonium into nitrate, which is essential for plant growth, while denitrification reduces nitrate back to atmospheric nitrogen, playing a crucial role in maintaining nitrogen balance. Overall, both processes are vital for ecological health and agricultural productivity.