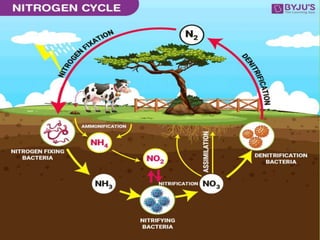
Nitrogen is essential for living organisms but is inert in its atmospheric form. The nitrogen cycle transforms nitrogen between its gas, organic, and inorganic forms through biological and environmental processes. These include nitrogen fixation by bacteria, ammonification by decomposers, nitrification by bacteria, and denitrification by other bacteria. The cycle is crucial for providing nitrogen to plants and recycling waste nitrogen back into usable forms and the atmosphere.