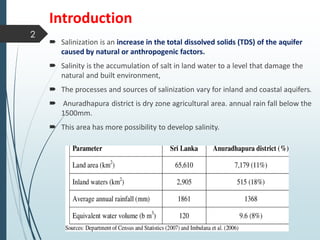
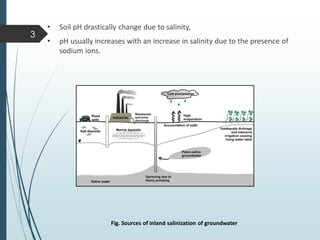
In Anuradhapura, a dry zone agricultural area with annual rainfall below 1500mm, inland salinity is a growing concern caused by factors such as excessive groundwater pumping and poor irrigation practices. Salinization negatively affects soil properties and plant growth, leading to reduced agricultural productivity. Measures to combat salinity include maintaining vegetation cover, using gypsum or fertilizers, and planting salt-tolerant crops.