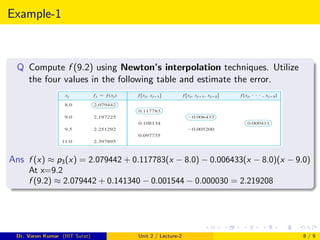
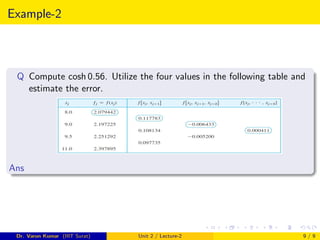
1. Newton's divided difference interpolation is a method for interpolating or finding function values between given data points. It involves constructing polynomials that pass through the given points.
2. The method works by first constructing lower degree Newton polynomials that fit the existing data points, then adding higher degree terms to fit additional points. These terms involve divided differences of the function values at the data points.
3. The general Newton interpolation formula expresses the interpolating polynomial as a sum of terms, with each term being a product of divided differences and factors corresponding to the distances between the interpolated point and data points.



![Continued–
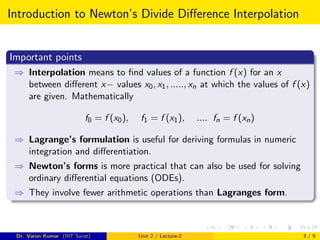
⇒ Using (3), let x = xn
an =
fn − pn−1(xn−1)
(xn − x0)(xn − x1)....(xn − xn−1)
⇒ We write ak instead of an and show that ak equals to the kth divided
difference, recursively.
a1 = f [x0, x1] =
f1 − f0
x1 − x0
a2 = f [x0, x1, x2] =
f [x1, x2] − f [x0, x1]
x2 − x0
ak = f [x0, ...., xk] =
f [x1, x2, .., xk] − f [x0, ..xk−1]
xk − x0
Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat) Unit 2 / Lecture-2 5 / 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmup-2-210818121530/85/Newton-s-Divide-and-Difference-Interpolation-5-320.jpg)
![Continued–
⇒ If n = 1, then pn−1(xn) = p0(x1) = f0 because p0(x) is constant.
Hence from (3)
a1 =
f1 − p0(x1)
x1 − x0
=
f1 − f0
x1 − x0
= f [x0, x1]
⇒ Hence Newton’s interpolation for the first degree
p1(x) = f0 + (x − x0)f [x0, x1]
⇒ If n = 2, then pn−1(xn) = p1(x2). Hence from (3)
a2 =
f2 − p1(x2)
(x2 − x1)(x2 − x0)
=
f2 − f0 − (x2 − x0)f [x0, x1]
(x2 − x1)(x2 − x0)
= f [x0, x1, x2]
Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat) Unit 2 / Lecture-2 6 / 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmup-2-210818121530/85/Newton-s-Divide-and-Difference-Interpolation-6-320.jpg)
![Continued–
⇒ We thus obtain the second Newton’s polynomial
p2(x) = f0 + (x − x0)f [x0, x1] + (x − x0)(x − x1)f [x0, x1, x2]
⇒ For n = k, we can write
pk(x) = pk−1(x) + (x − x0)(x − x1)....(x − xk−1)f [x0....xk]
⇒ The more generalized Newton’s divide and difference
interpolation formula can be expressed as
f (x)= f0 + (x − x0)f [x0, x1] + (x − x0)(x − x1)f [x0, x1, x2] + ...+
= (x − x0)(x − x1)....(x − xn−1)f [x0, ..., xn]
Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat) Unit 2 / Lecture-2 7 / 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmup-2-210818121530/85/Newton-s-Divide-and-Difference-Interpolation-7-320.jpg)