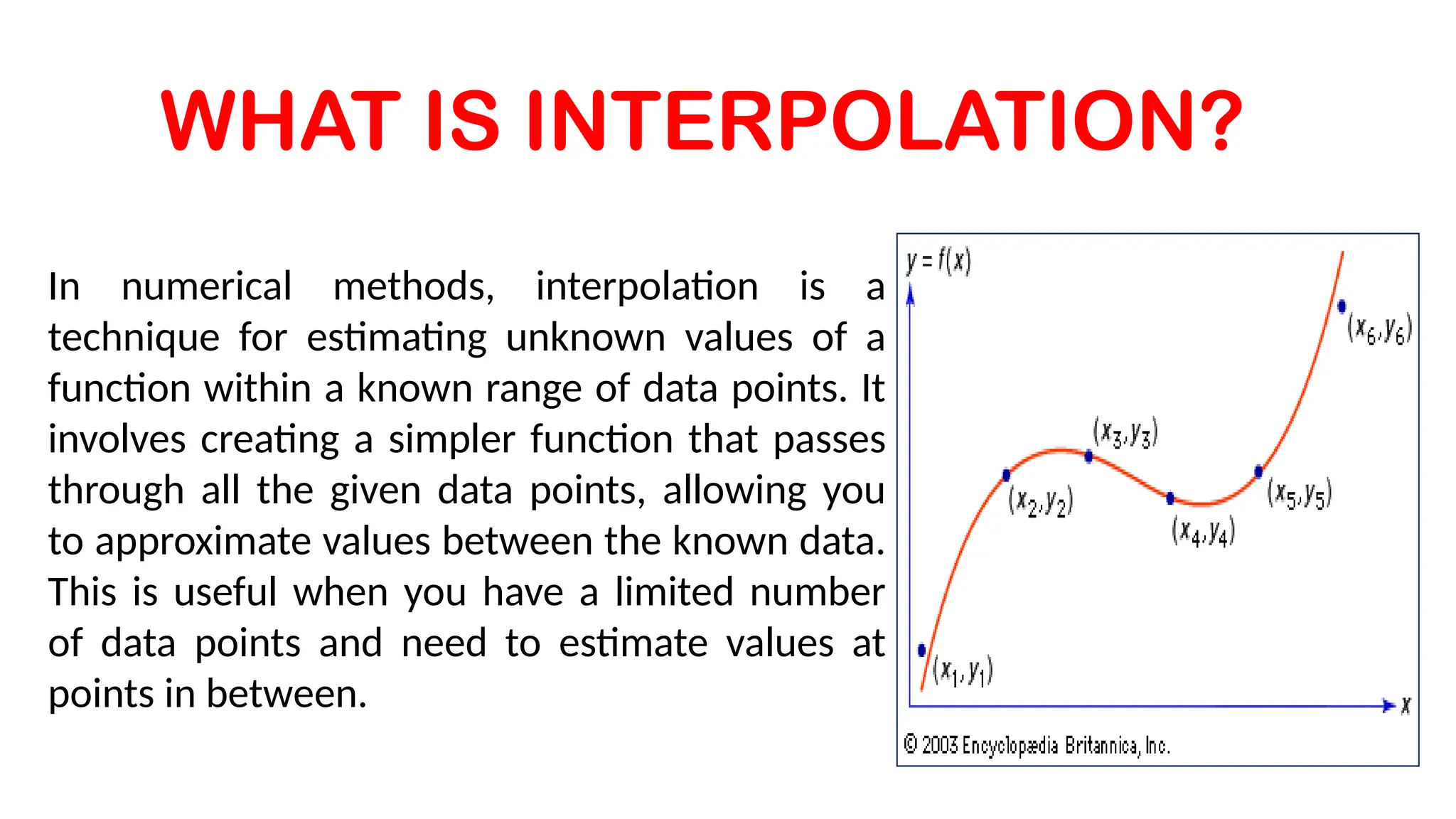
hello! I am Pralay sarkar.I posted a ppt on a topic of newton's divided difference. it is a part of B.Sc. Mathematics and Engineering. Newton's divided difference is a recursive algorithm for finding an interpolating polynomial that passes through a given set of data points, allowing for the estimation of values between known points, even if the x-values are not equally spaced. The method involves calculating a series of divided differences—which represent successive approximations of the function's derivatives—to construct the final polynomial, which takes the form of a sum of terms with these divided differences as coefficients. Some advantage of Newton's divided difference are These are useful for interpolation.
Through difference table, we can find out the differences in higher order.
Differences at each stage in each of the columns are easily measured by subtracting the previous value from its immediately succeeding value.
The differences are found out successively between the two adjacent values of the y variable till the ultimate difference vanishes or become a constant.