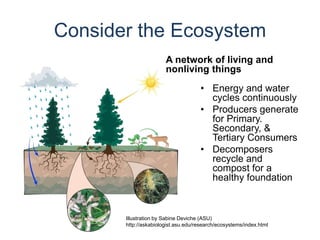
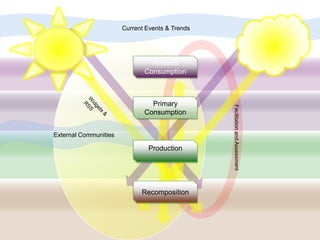
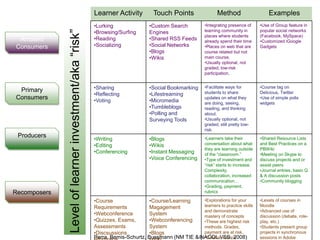
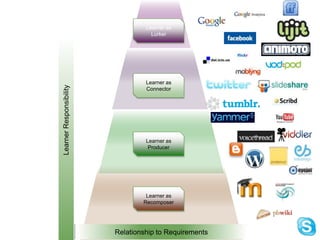
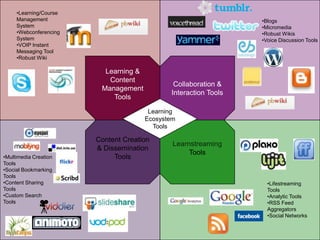
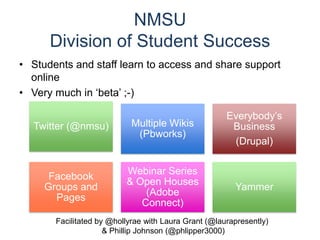
The document discusses the creation and nurturing of new learning communities and ecosystems in educational contexts. It emphasizes the importance of connectivism, personal learning skills, and the use of various technologies to enhance experiential learning for K-20 educators. Key themes include the characteristics of learning ecosystems, the role of social media, and strategies for developing and assessing these communities.