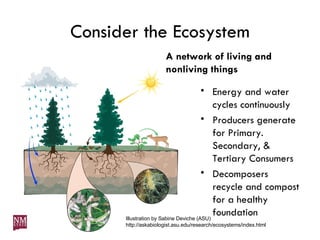
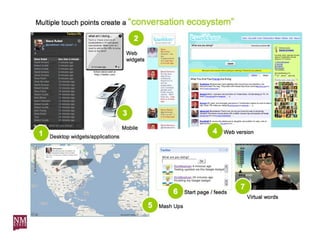
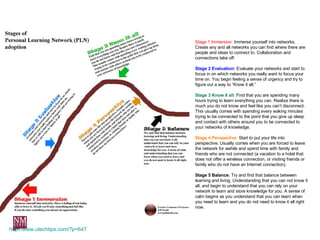
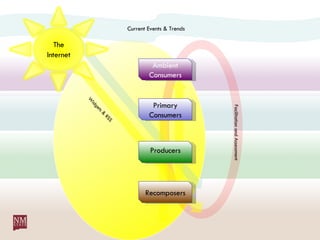
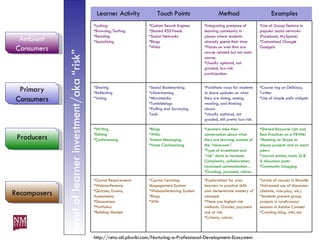
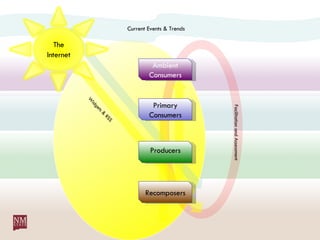
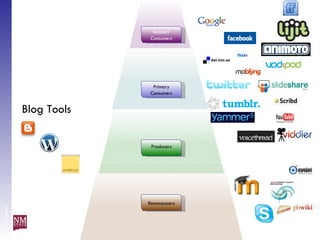
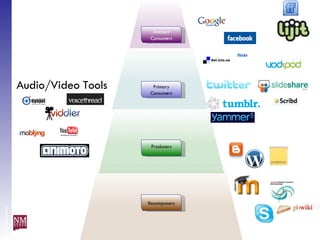
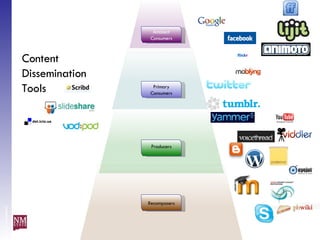
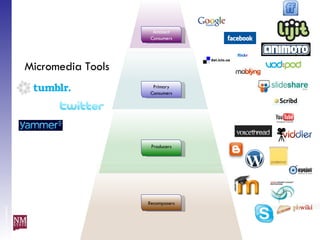
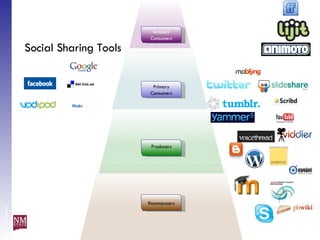
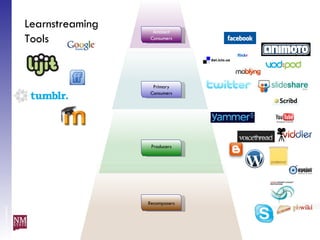
The document discusses nurturing a professional development ecosystem using an analogy to biological ecosystems. It describes using an ecosystem approach to professional development by viewing it as a network of interconnected systems with various roles like producers, consumers, and decomposers. Tools like blogs, wikis, and social networks can help facilitate information sharing and learning at different levels of engagement within this professional development ecosystem.