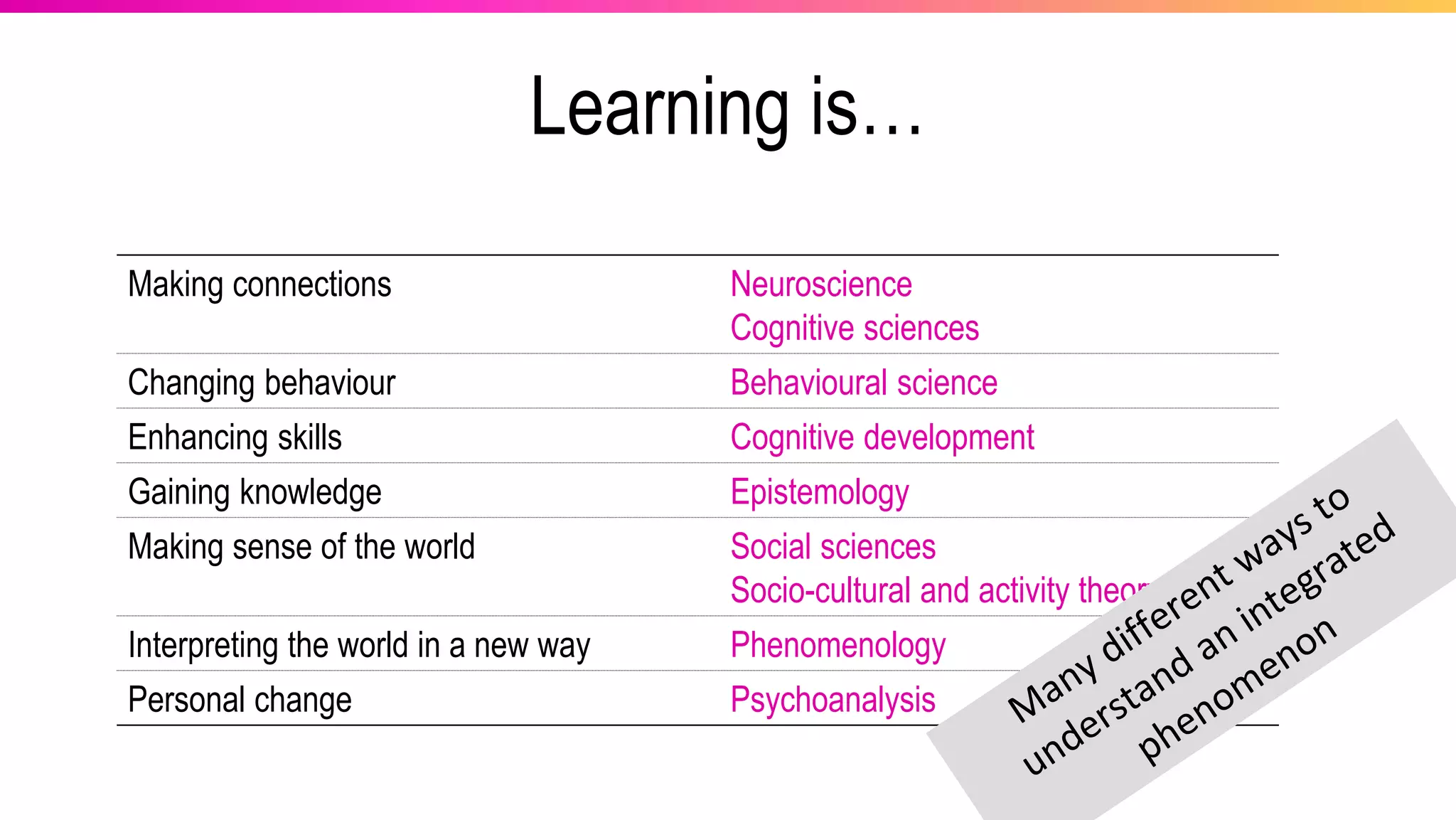
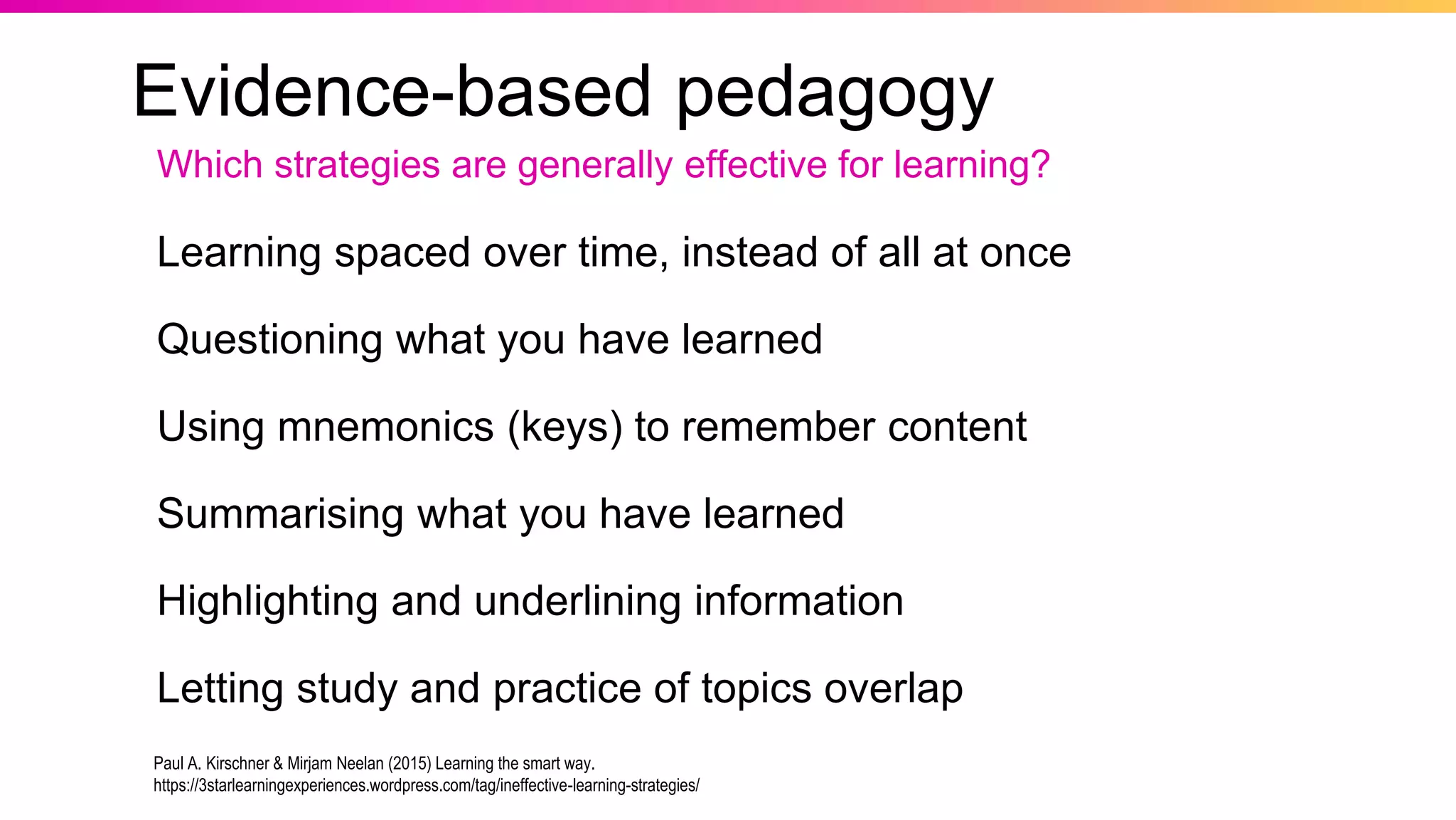
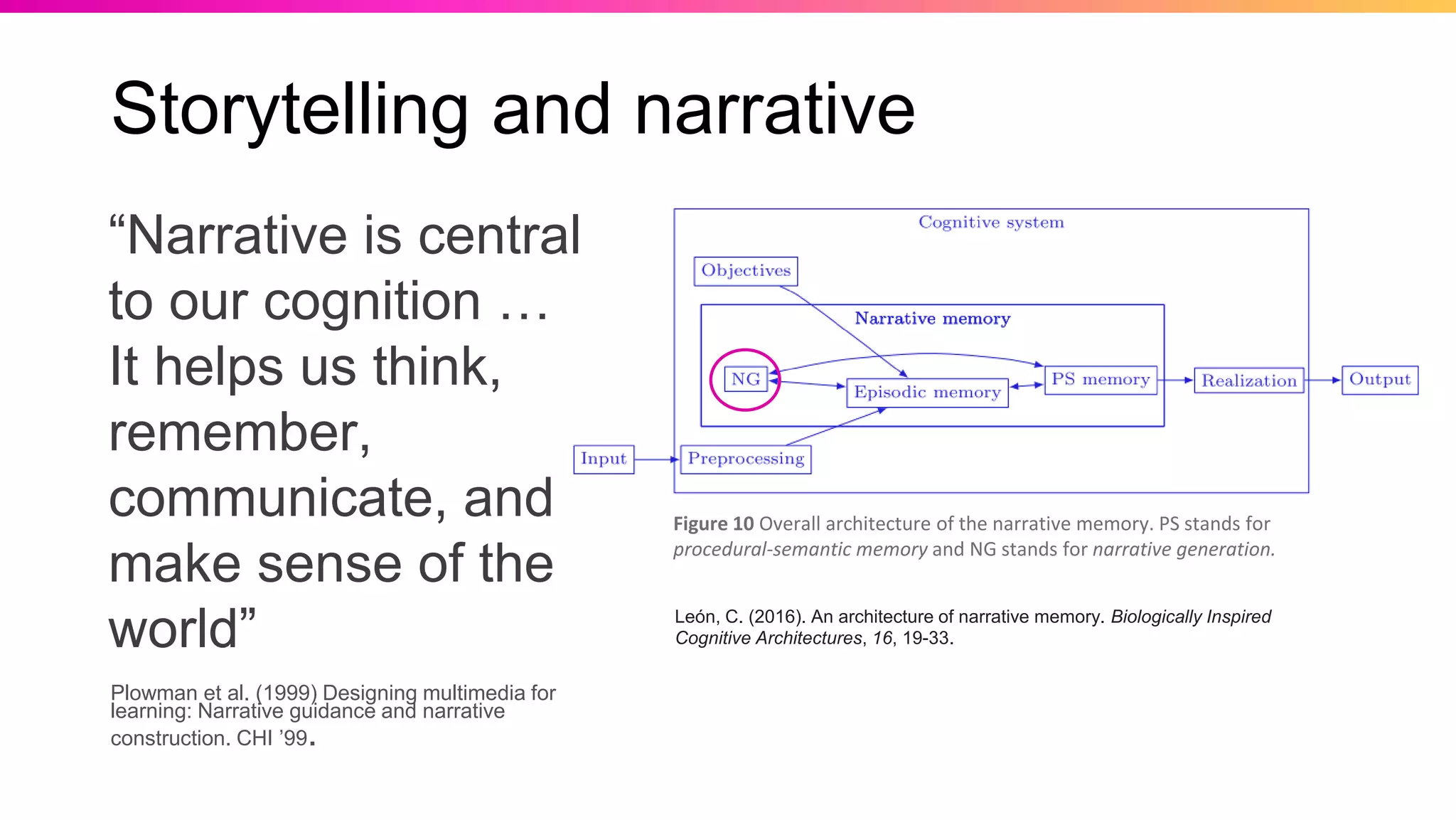
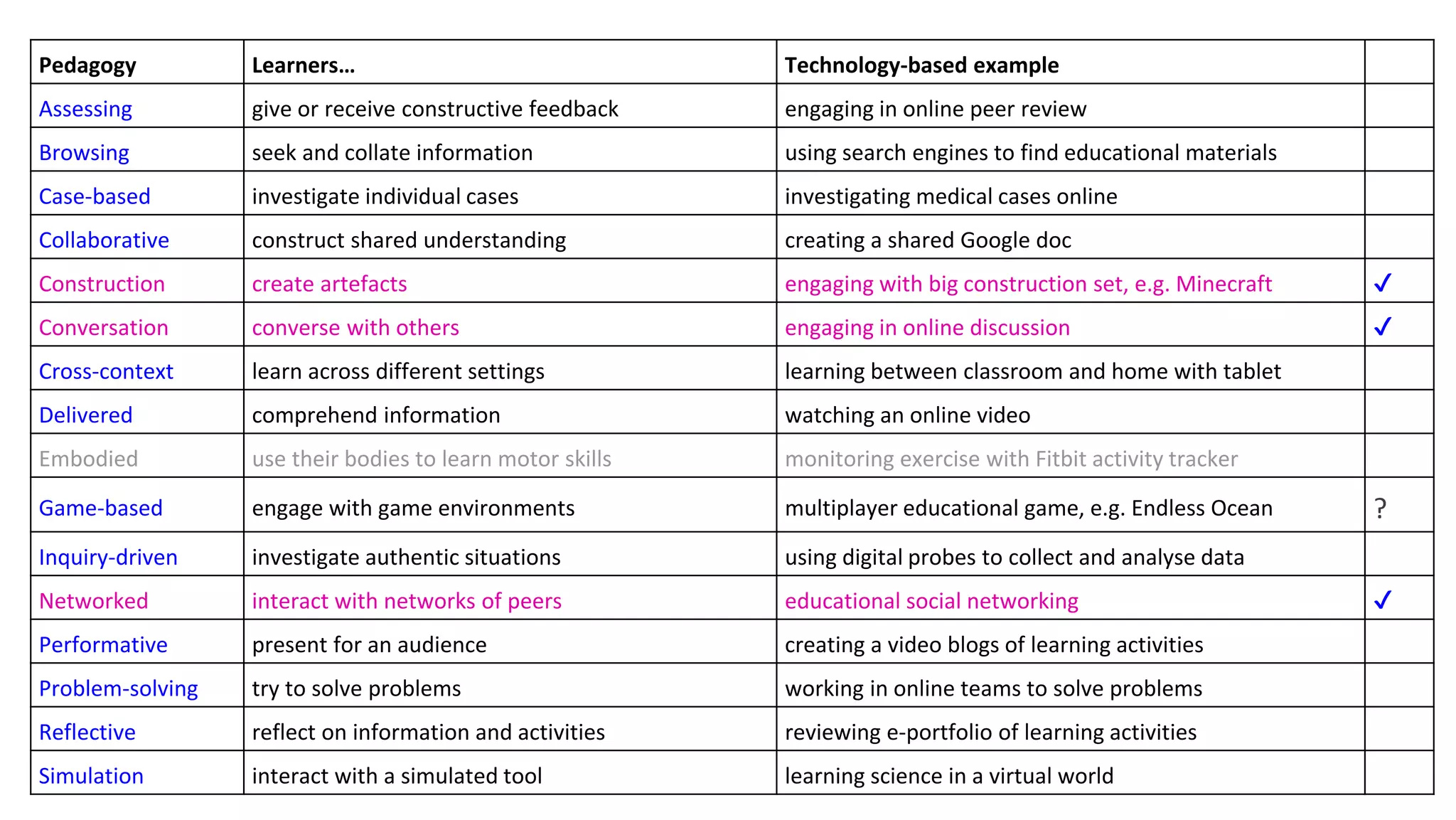
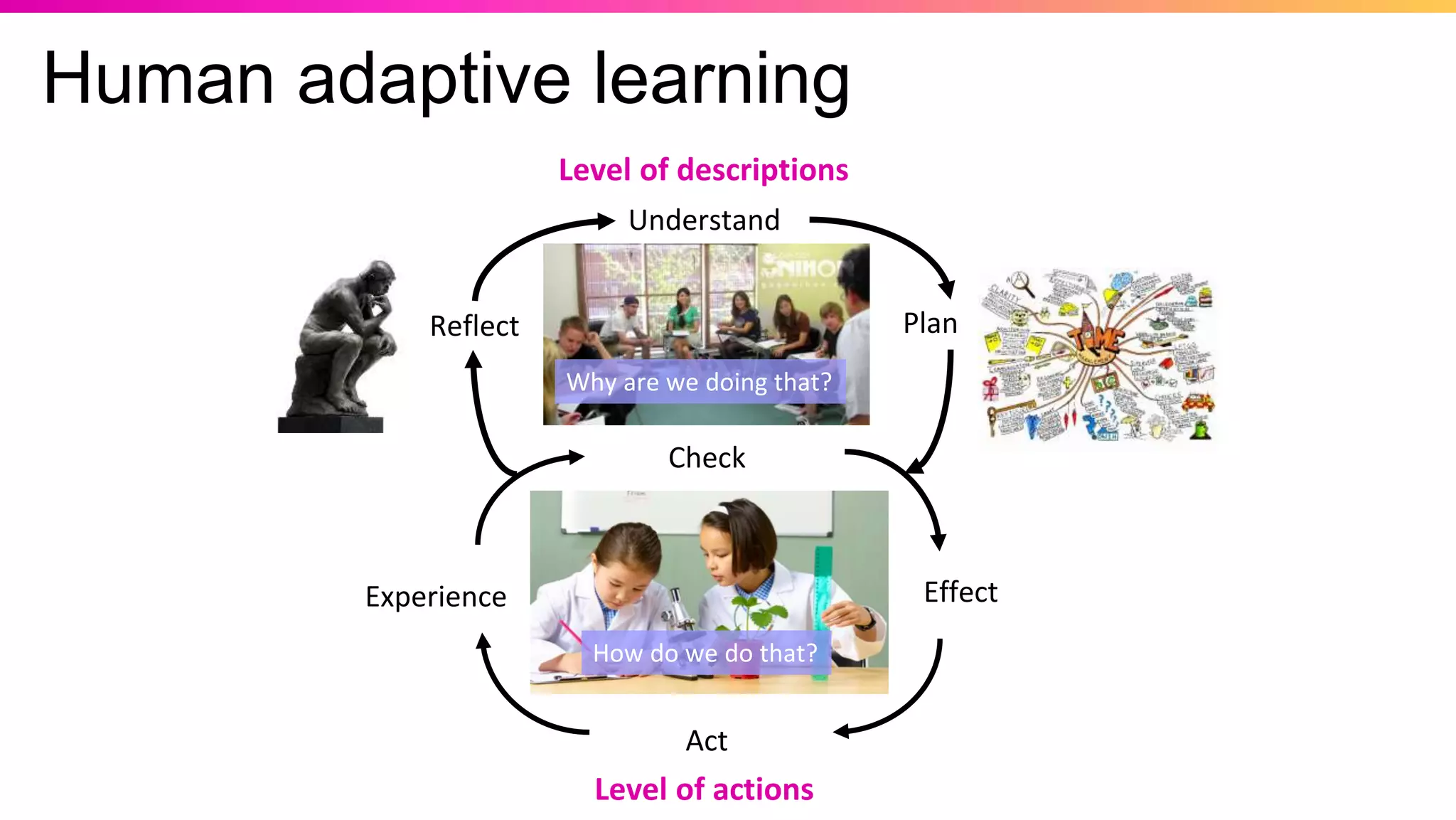
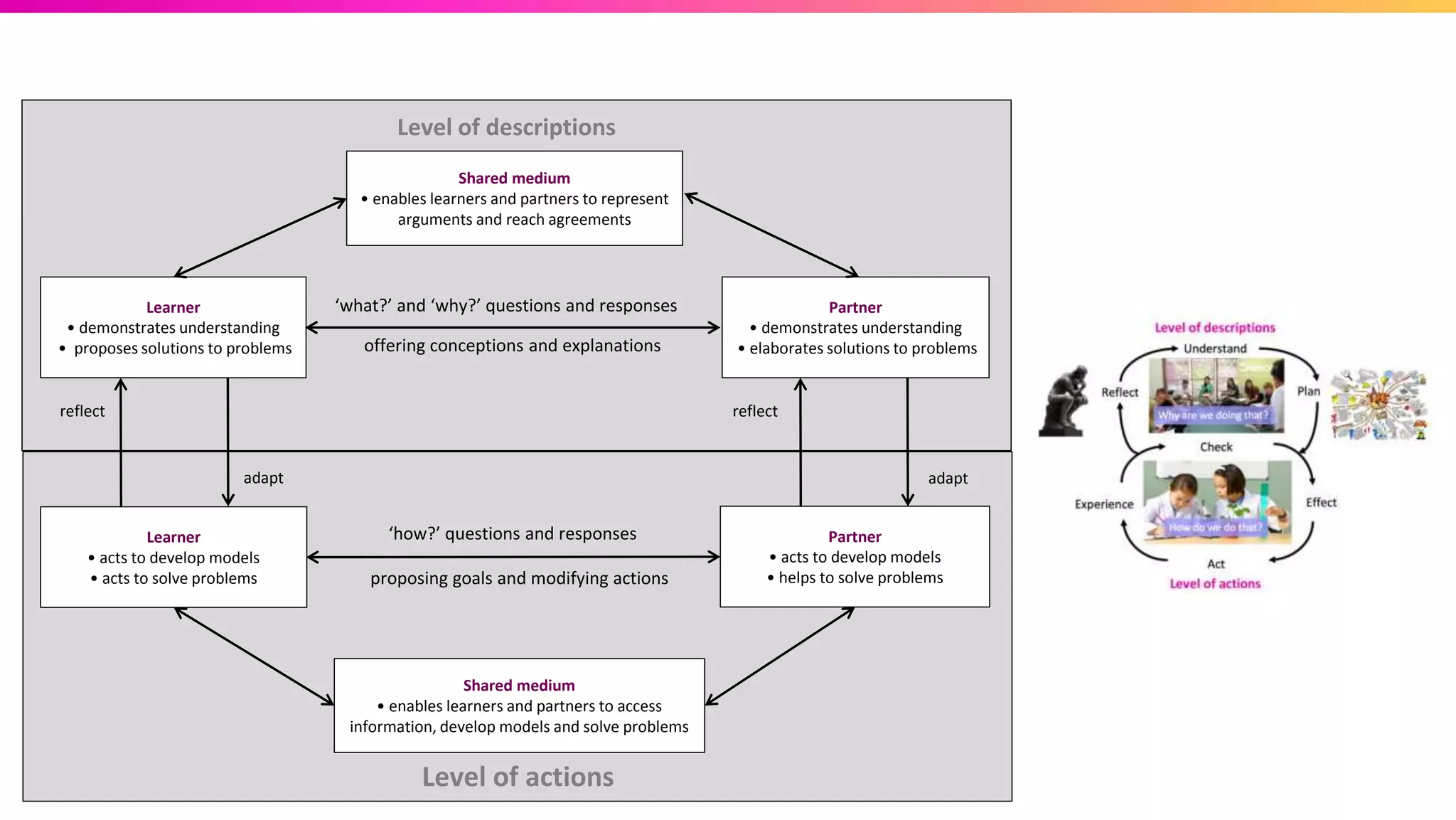
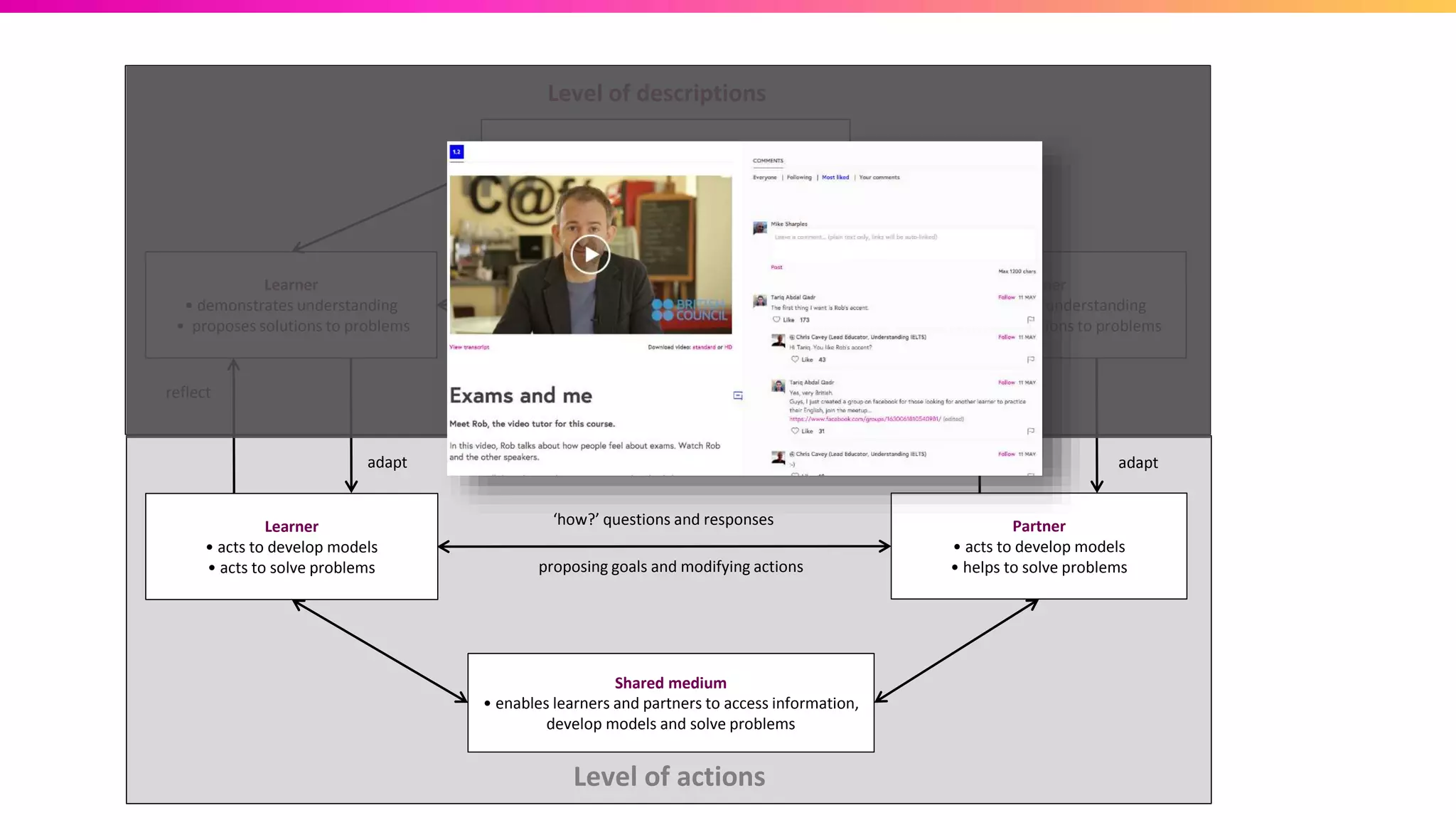
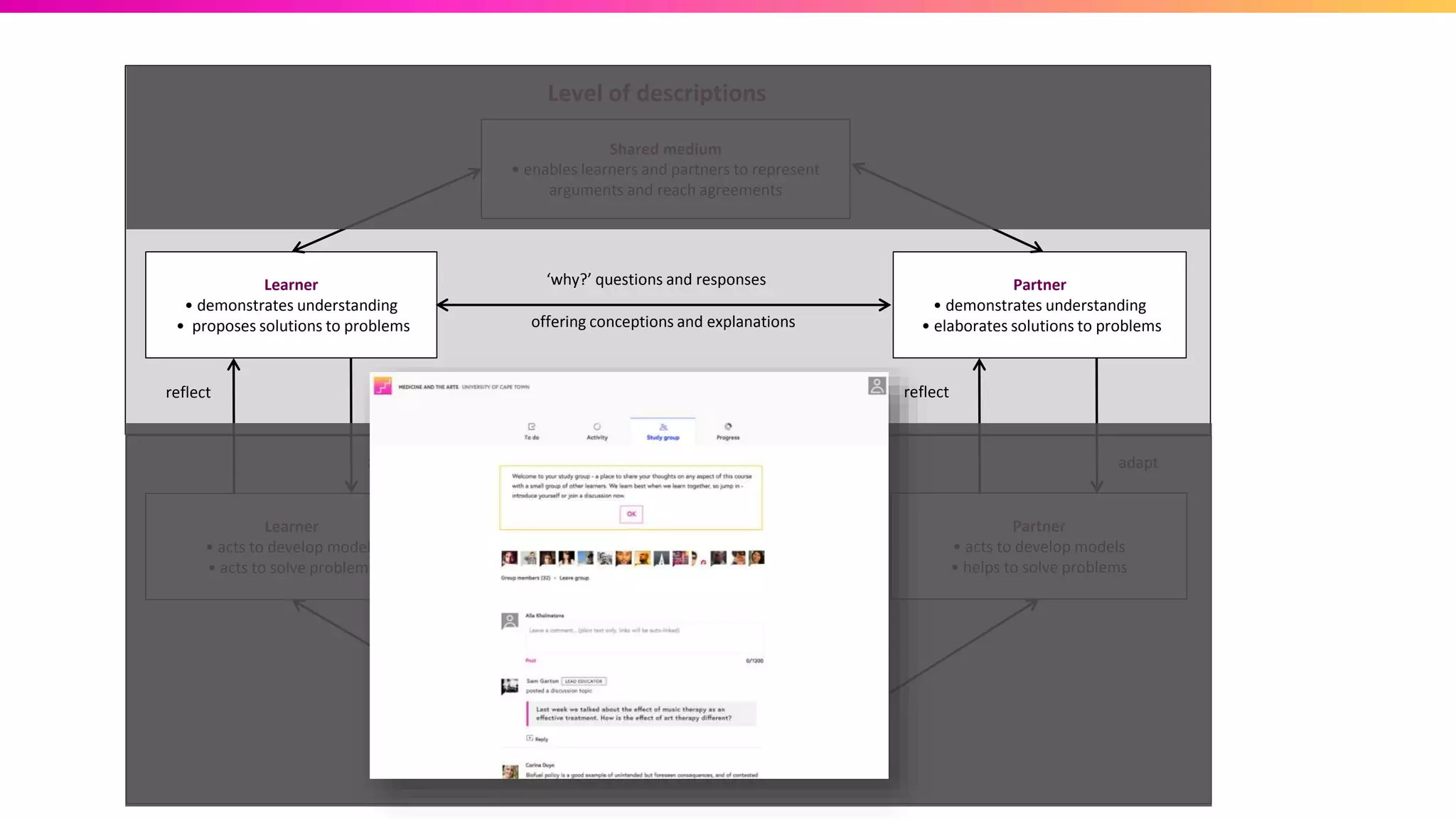
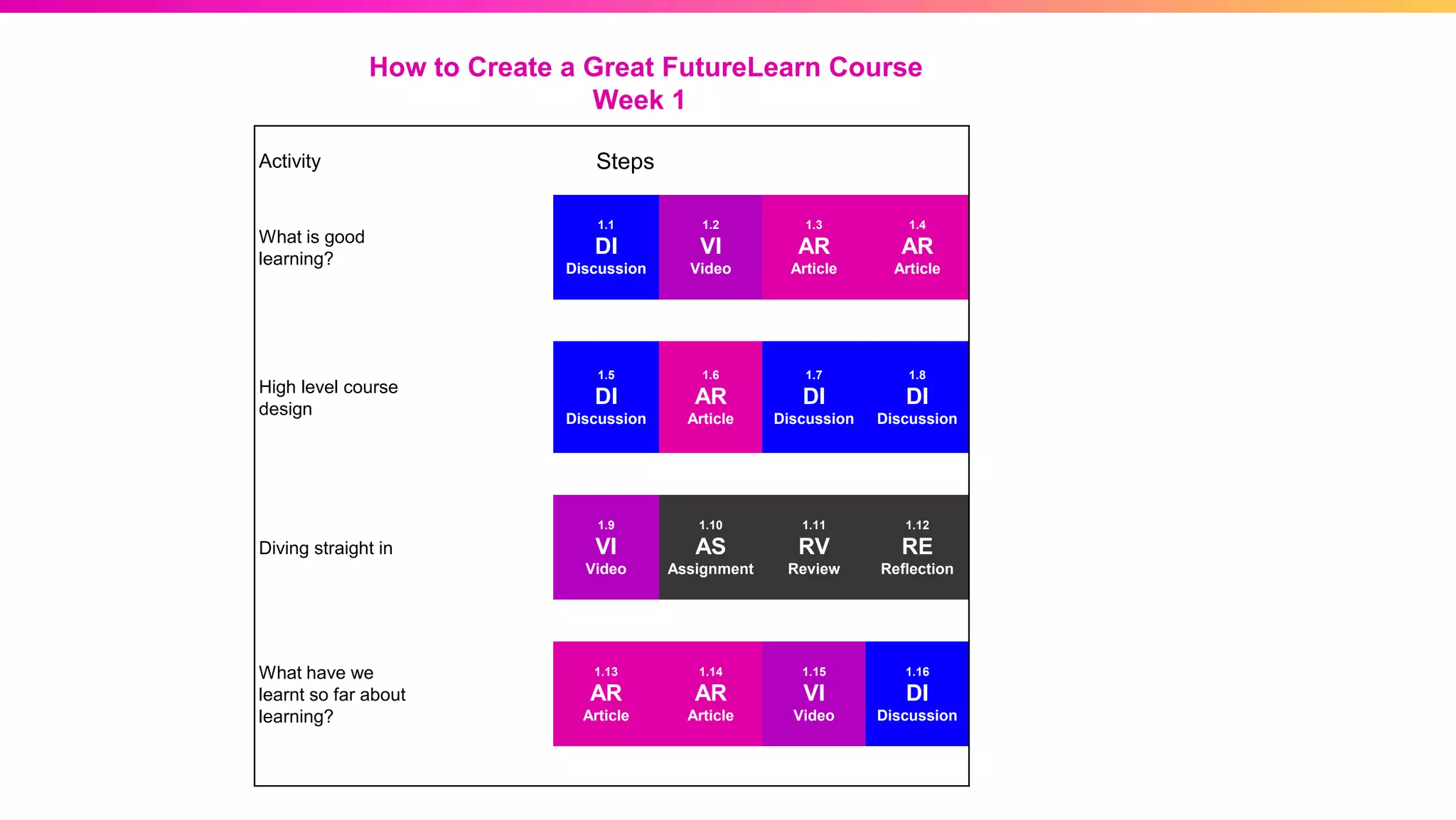
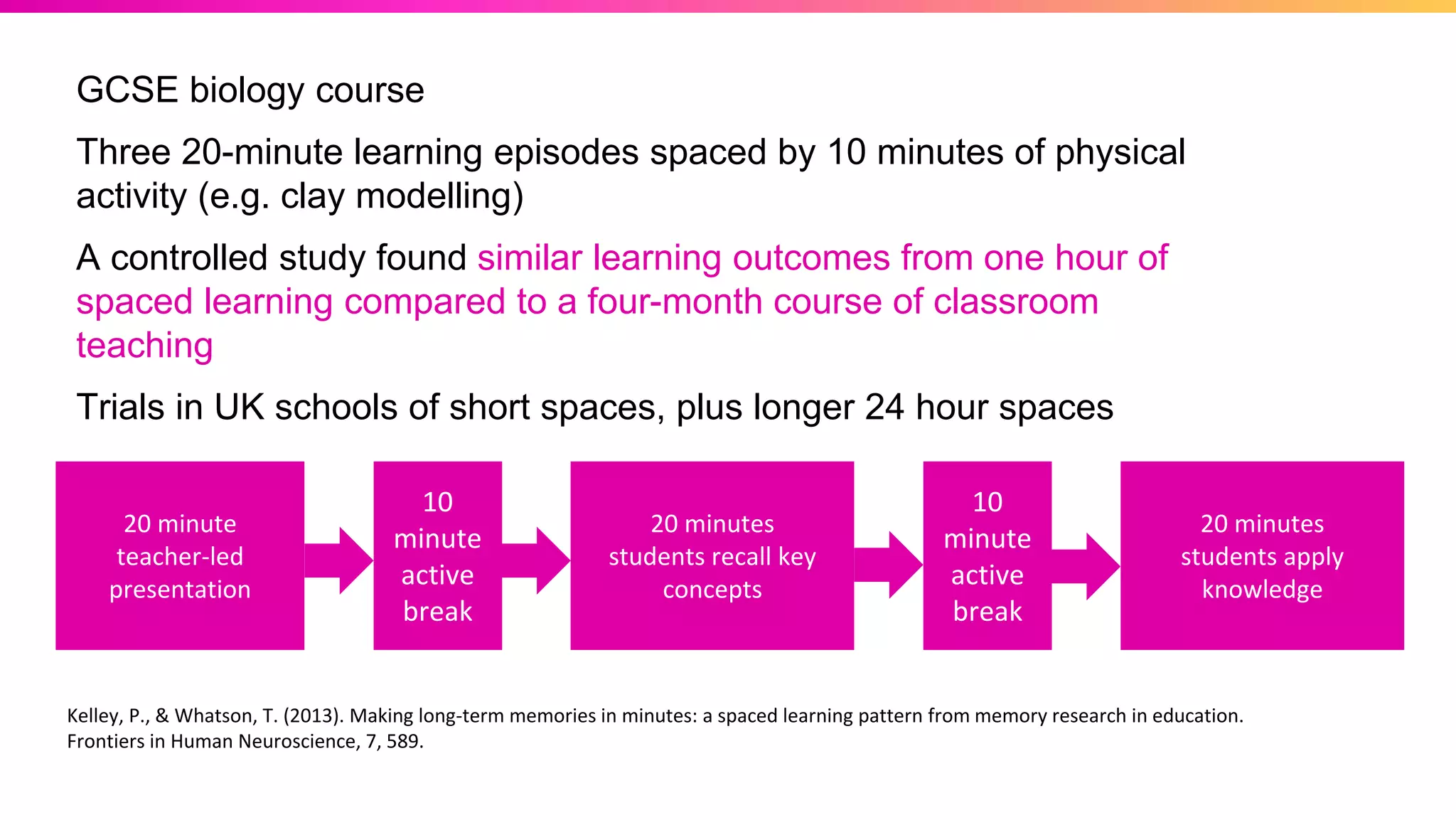
The document discusses the pedagogy of FutureLearn and how learners learn online. It explores evidence-based strategies like spaced learning and questioning what is learned. Storytelling, conversation, and visible progress are highlighted as key aspects of FutureLearn's pedagogy. The role of social interaction in catalyzing learning is also discussed. The document considers how certain educational methods can improve with massive scale online learning environments through techniques like peer review and collaborative documents.