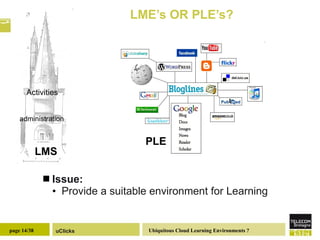
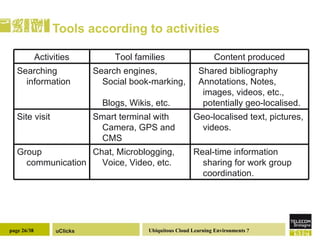
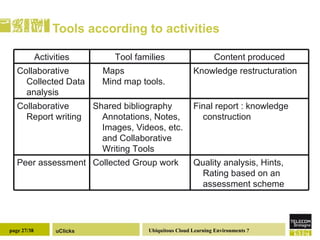
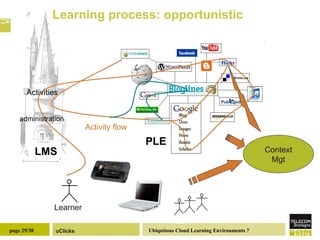
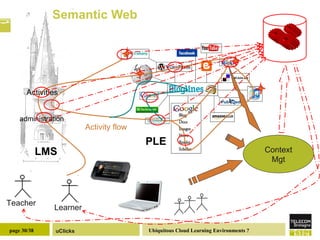
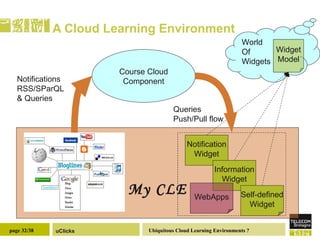
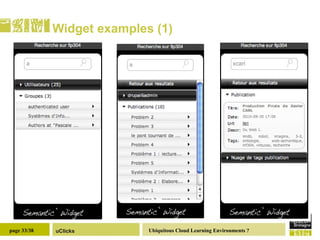
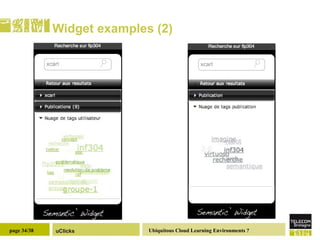
The document discusses the necessity of digital literacy for 21st-century learners, emphasizing the blending of formal and informal learning within cloud environments and the significance of Web 2.0 tools. It outlines various teaching scenarios, including inquiry-based science teaching, and the use of mobile devices for collaborative and real-time data sharing among students. The conclusion highlights the need for flexible learning environments to adapt to evolving educational practices.