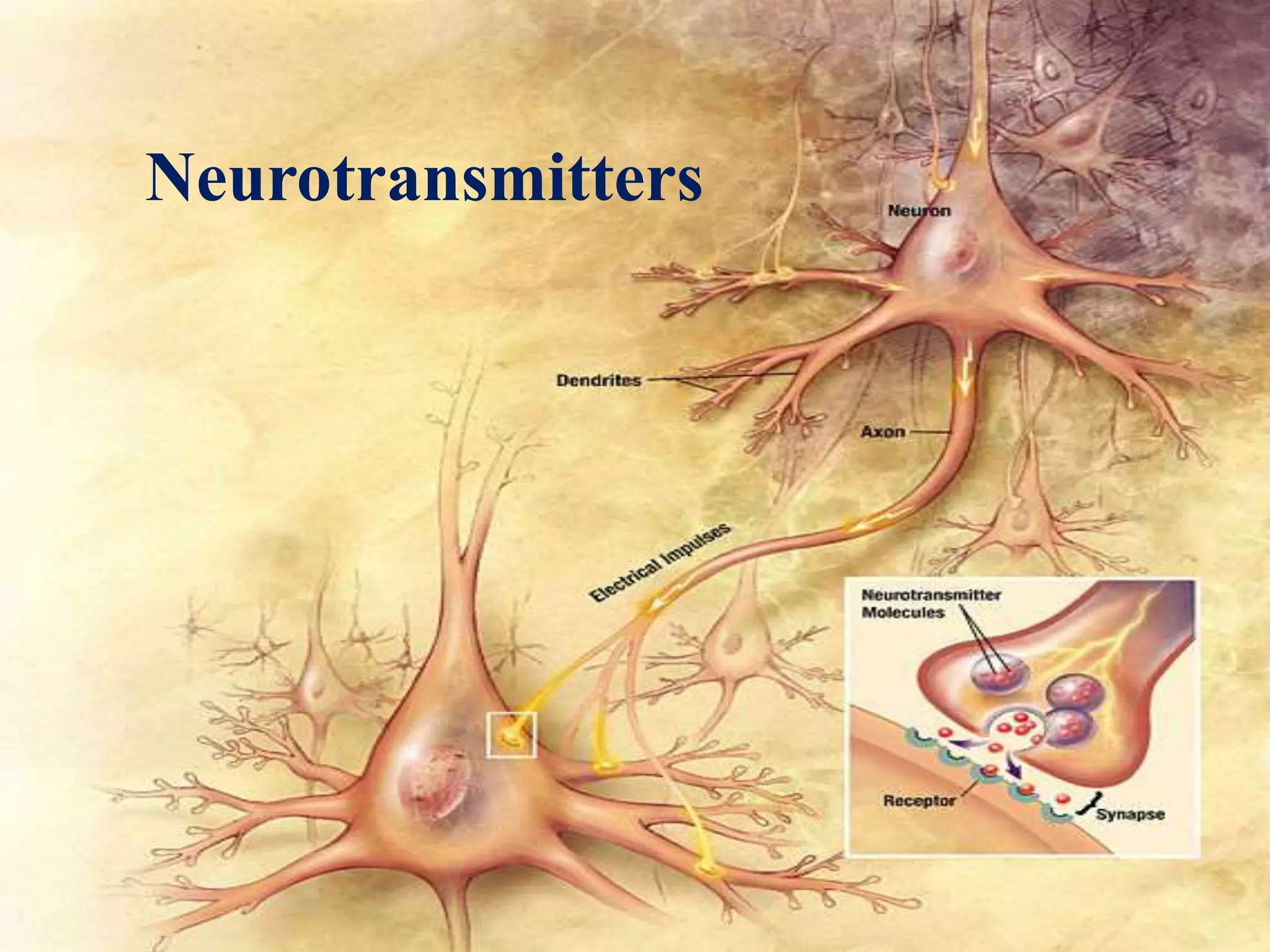
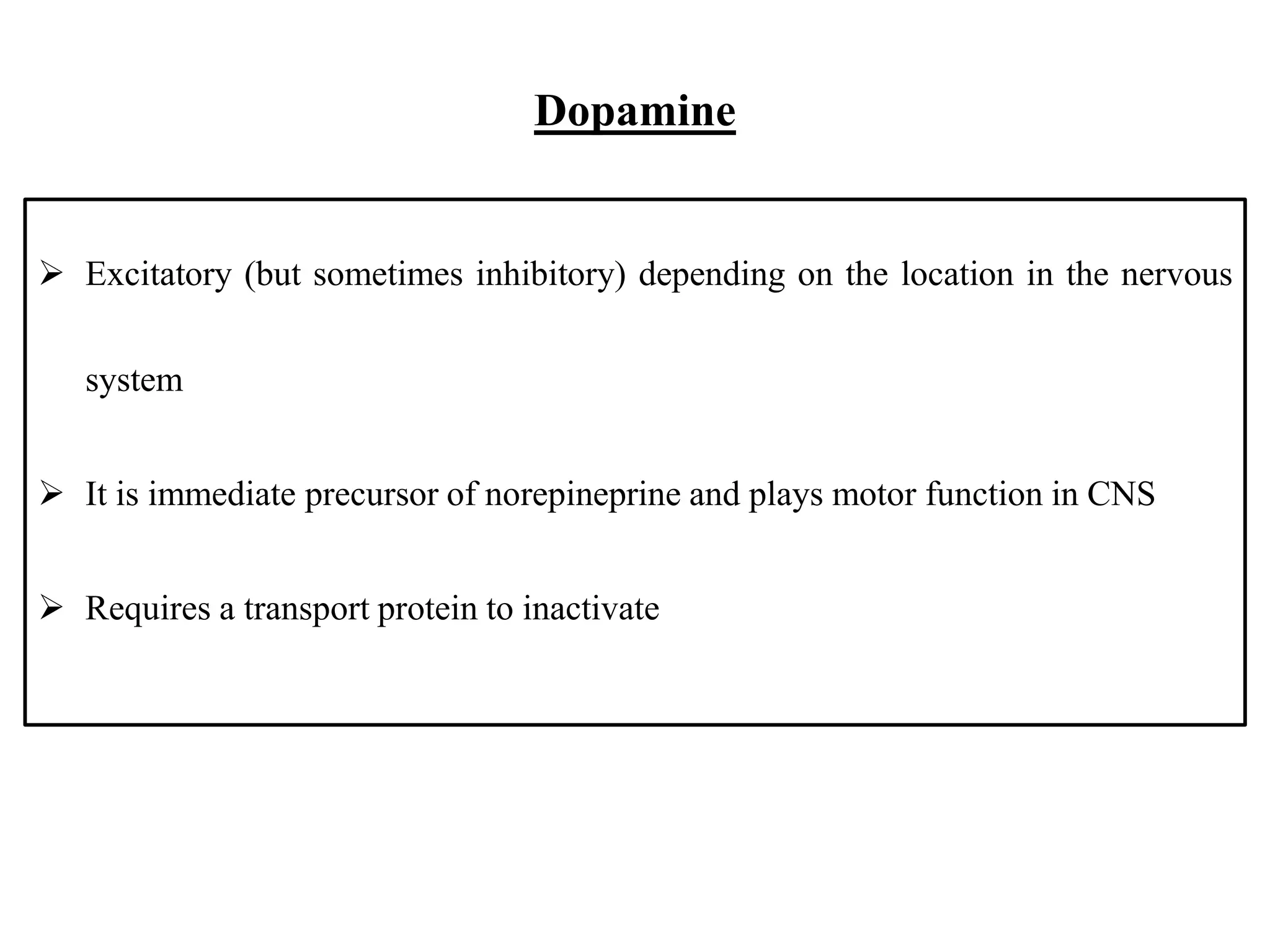
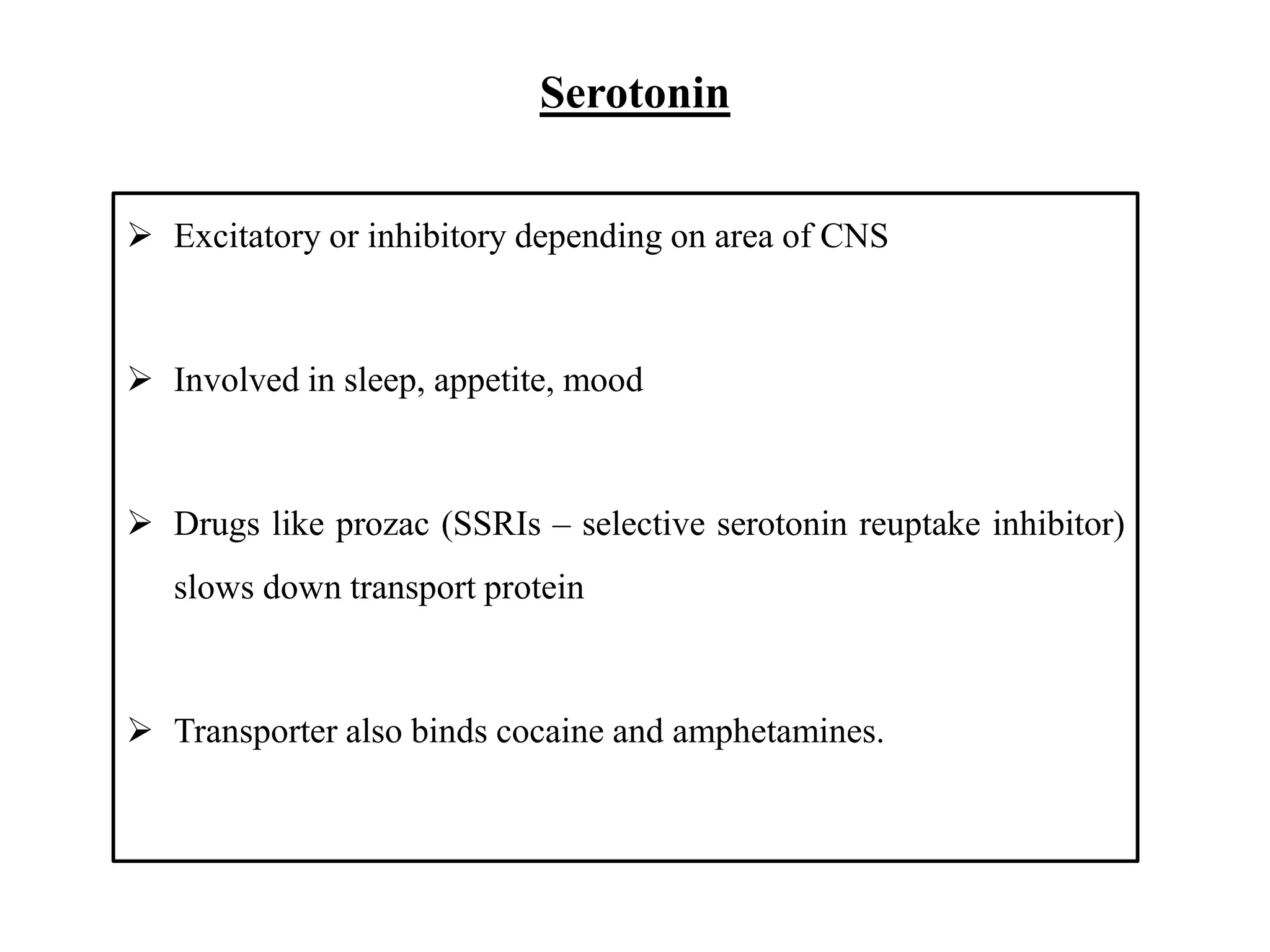
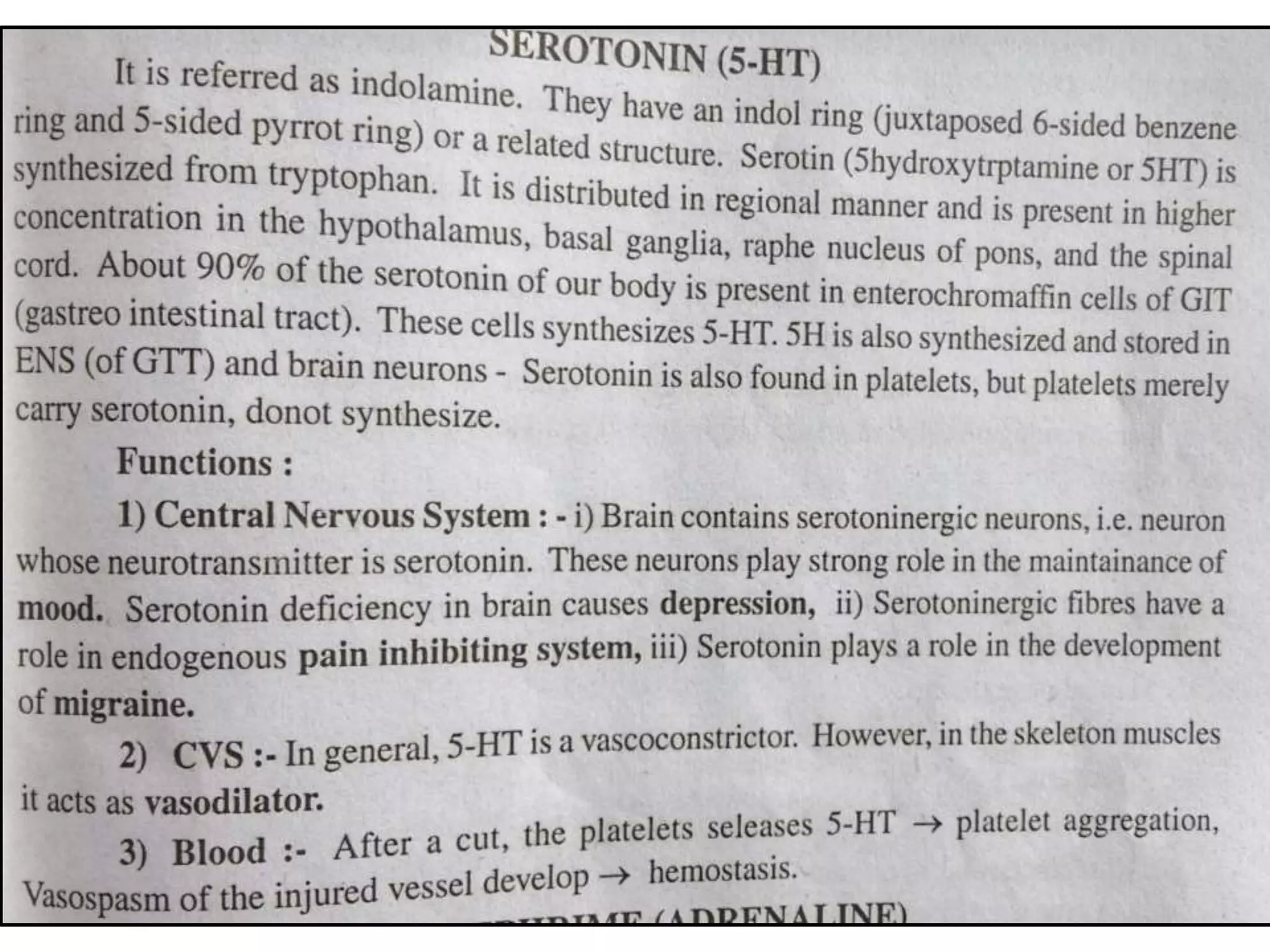
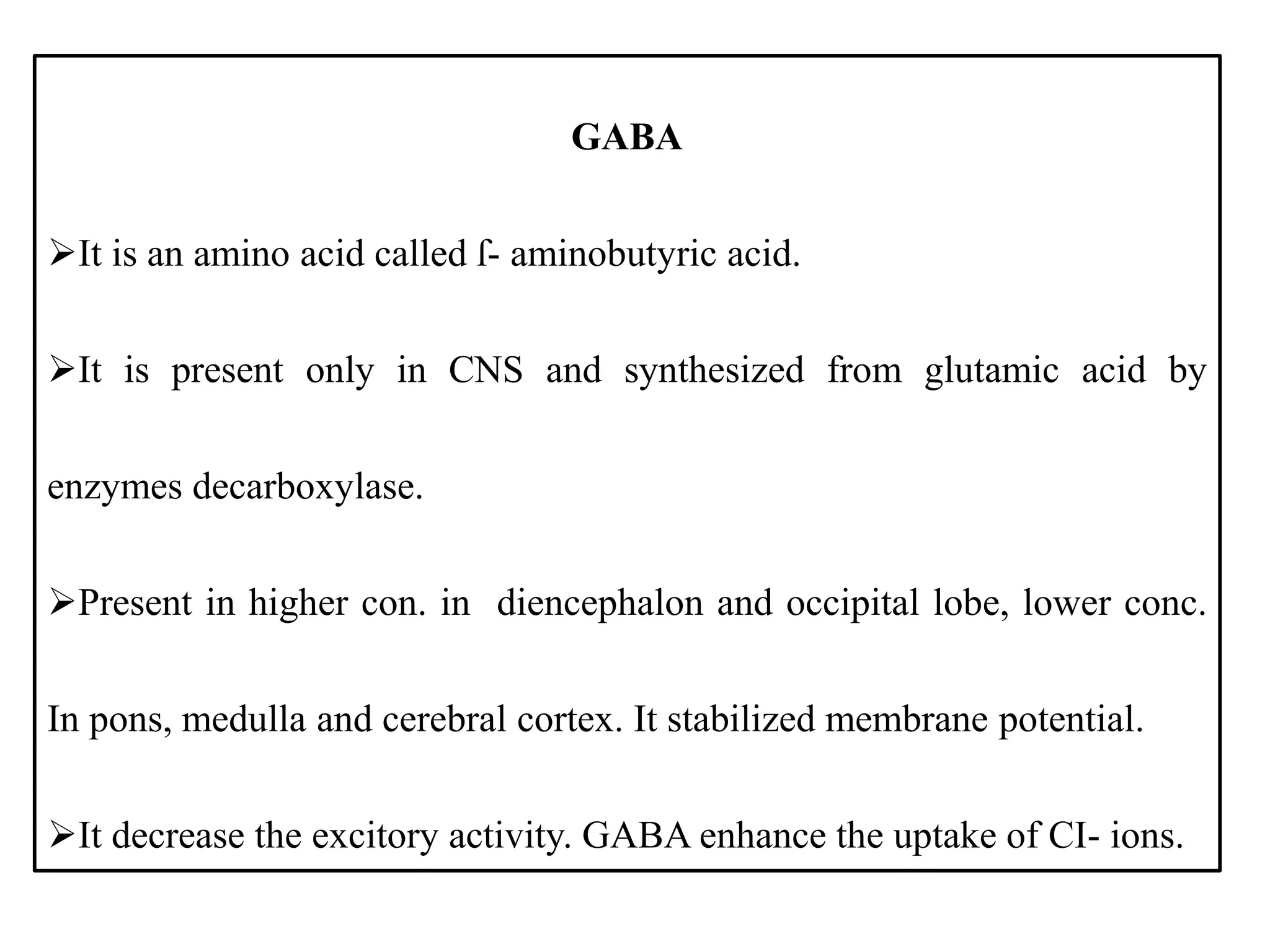
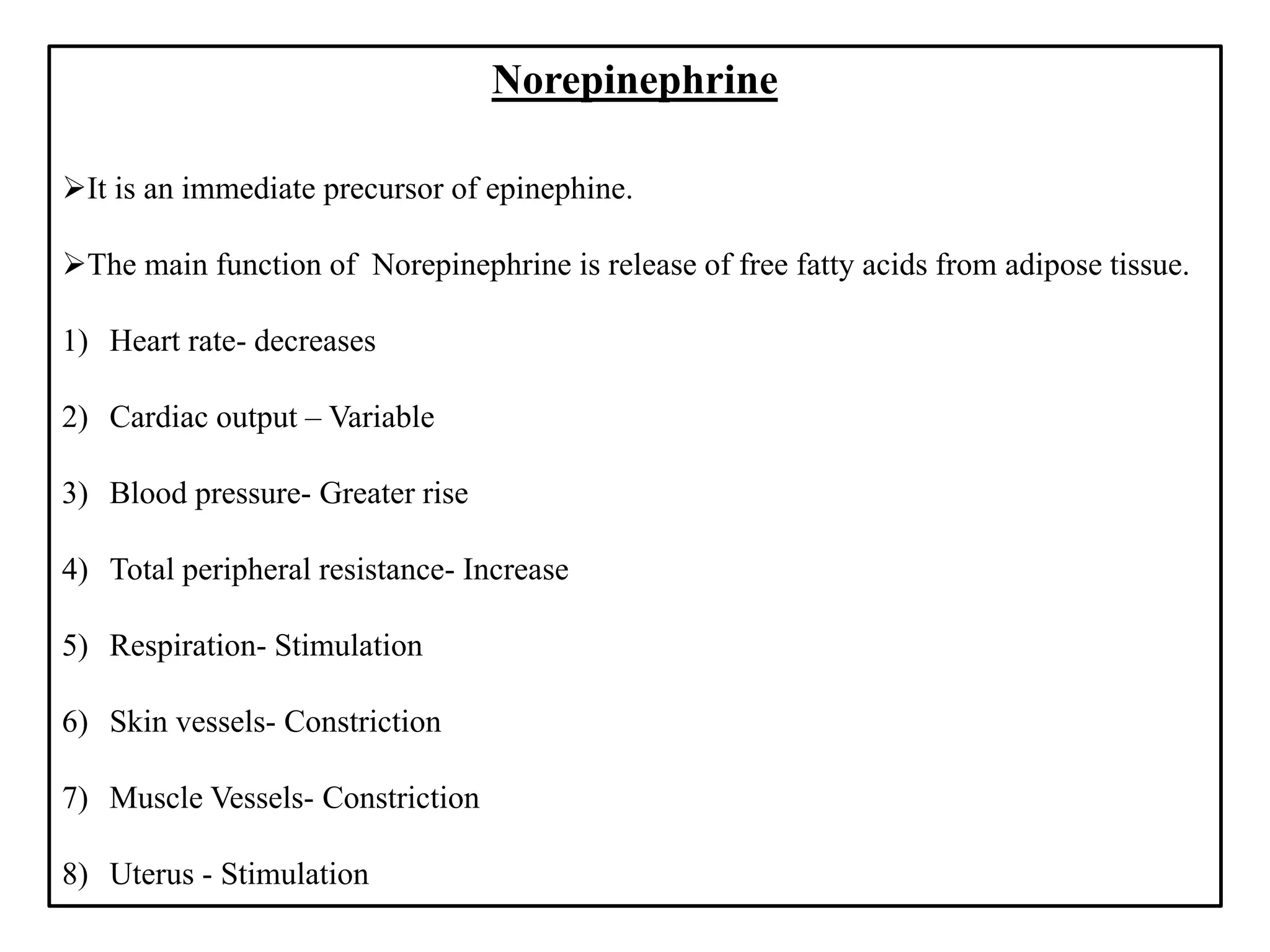
There are over 100 known neurotransmitters that transmit signals between neurons in the nervous system. The major excitatory neurotransmitters are glutamate, acetylcholine, and dopamine. Glutamate, glycine, and GABA are the primary inhibitory neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine is involved in muscle movement and is both excitatory and inhibitory depending on the receptor. Serotonin and dopamine play important roles in behaviors and mood, while GABA decreases excitatory activity in the nervous system.