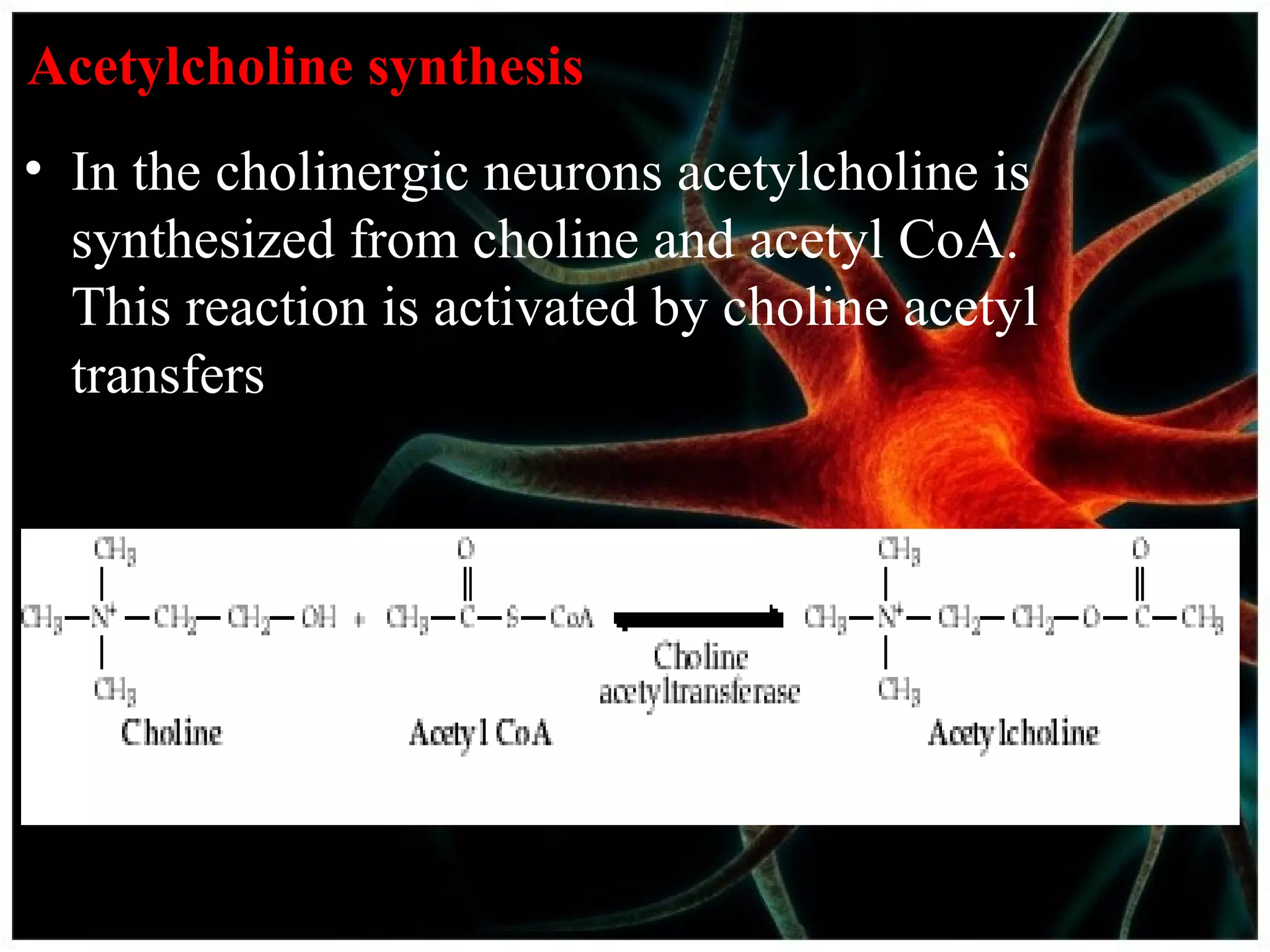
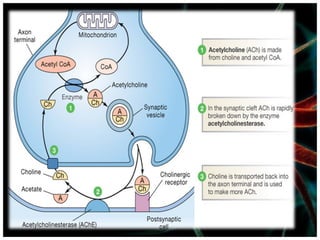
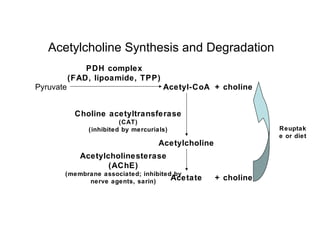
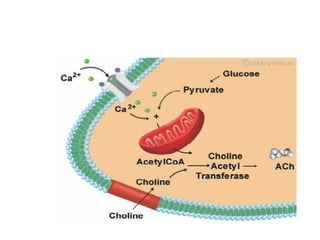
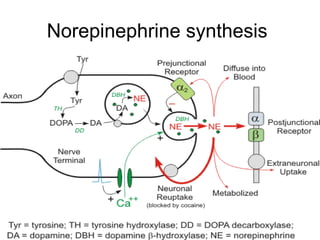
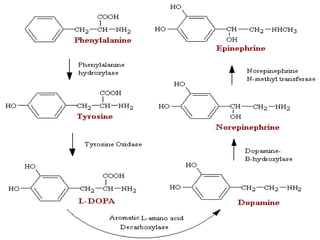
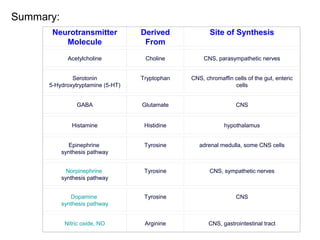
The document discusses acetylcholine synthesis and degradation. Acetylcholine is synthesized from choline and acetyl-CoA by the enzyme choline acetyltransferase. It is degraded by acetylcholinesterase into inactive metabolites choline and acetate. Acetylcholinesterase is abundant in the synaptic cleft and clears acetylcholine, which is essential for proper muscle function. Deficiency of acetylcholinesterase can cause paralysis.