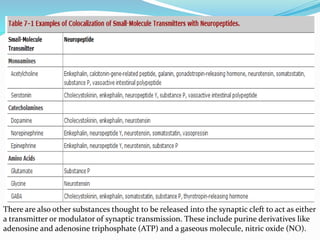
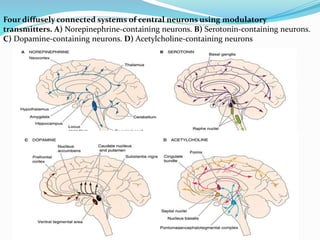
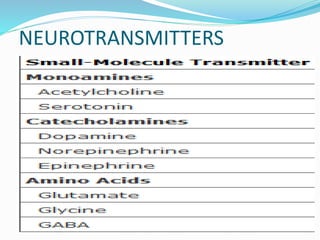
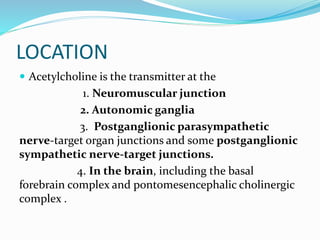
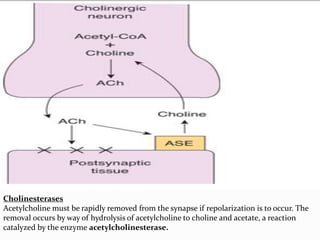
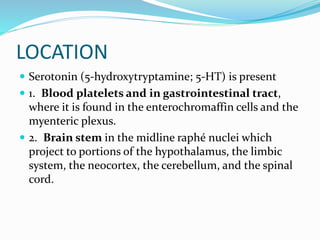
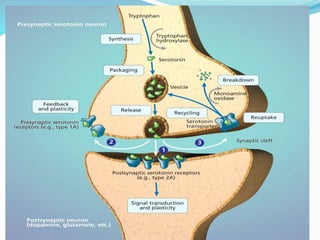
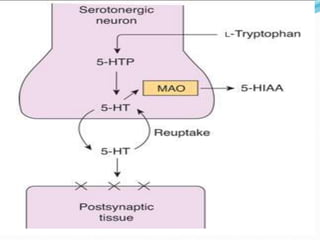
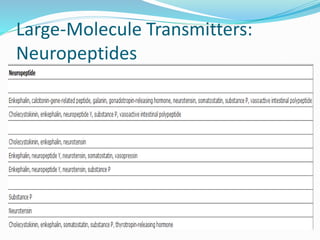
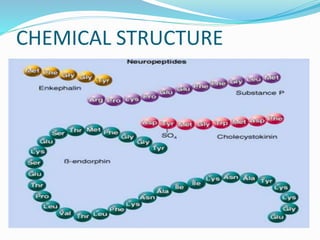
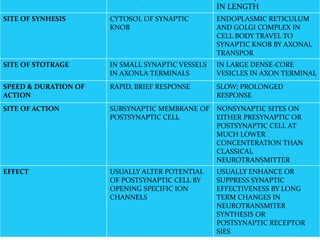
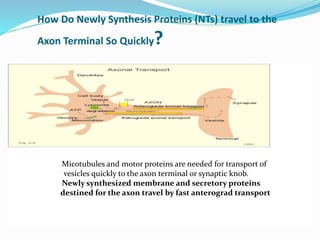
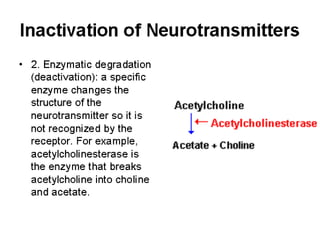
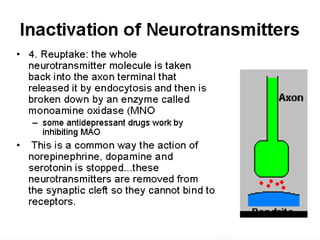
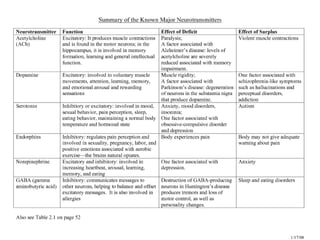
This document summarizes neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. It discusses how nerve endings called transducers convert electrical to chemical energy by synthesizing and storing neurotransmitters in vesicles. Upon stimulation, vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft to act on receptors and be removed. Neuromodulators modify neurotransmitter effects. Transmitters are divided into small molecules like acetylcholine, serotonin, catecholamines, and amino acids, as well as large neuropeptides. Specific locations of different transmitters are highlighted. Biosynthesis, release, and effects of various transmitters are described, including excitatory glutamate and inhibitory GABA and glycine. Finally, comparisons are made between classical transmitters and neurope