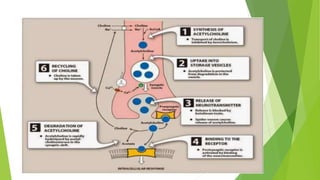
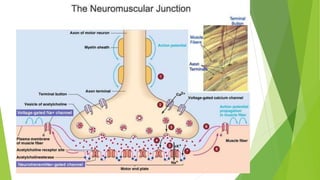
Acetylcholine (Ach) is a key neurotransmitter in the human body that facilitates communication between nerve cells and muscle fibers, important for muscle activation and autonomic nervous system functions. It is synthesized from choline and acetyl-CoA and binds to either nicotinic or muscarinic receptors to exert its effects. Ach plays a crucial role in both voluntary muscle movement and various involuntary functions, and its modulation through drugs can have significant medical applications.