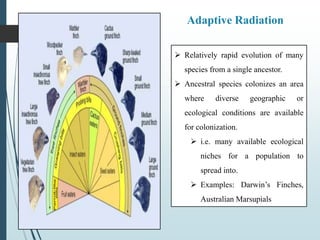
Speciation occurs through three main types: allopatric speciation, sympatric speciation, and adaptive radiation. Allopatric speciation involves reproductive isolation of populations separated by geographic barriers. Sympatric speciation can occur through balanced polymorphism, polyploidy, or hybridization without a geographic barrier. Adaptive radiation is the rapid evolution of many species from a single ancestor as it colonizes areas with diverse ecological niches. Evolution can occur through four patterns: divergent evolution of isolated populations, convergent evolution of unrelated species adapting to similar environments, parallel evolution of related lineages making similar changes, and coevolution of interacting species influencing each other's adaptations.