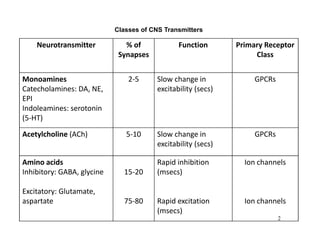
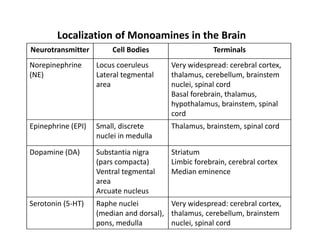
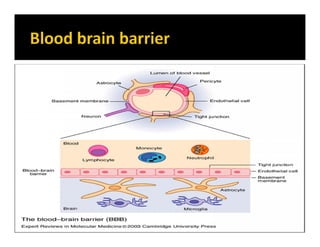
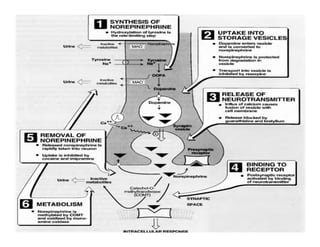
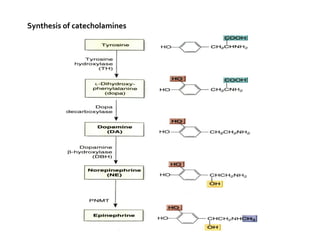
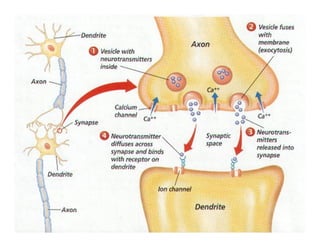
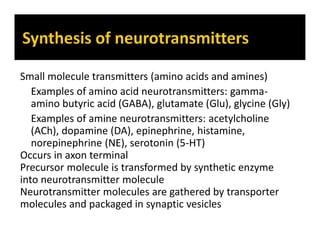
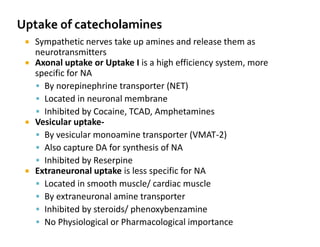
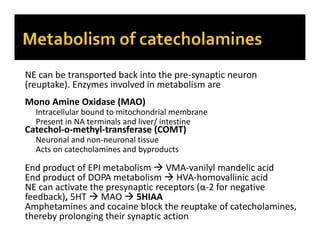
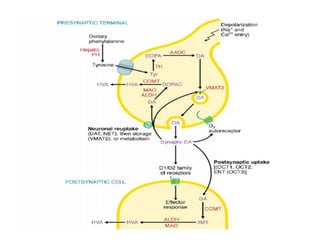
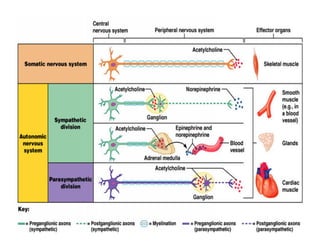
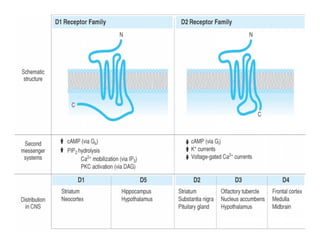
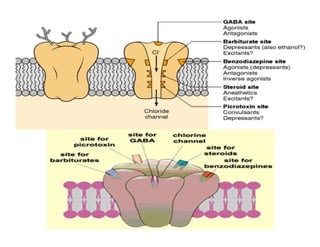
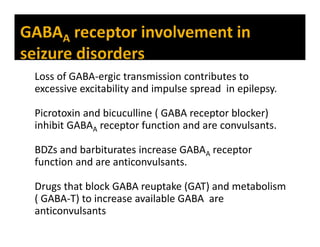
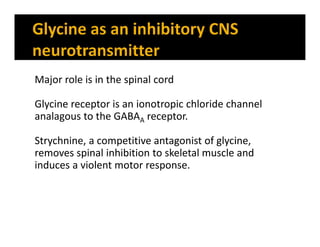
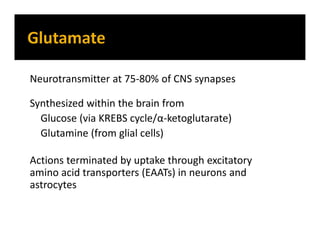
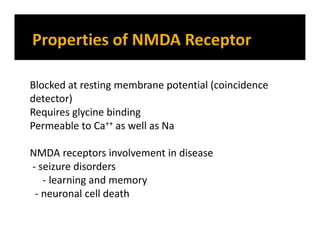
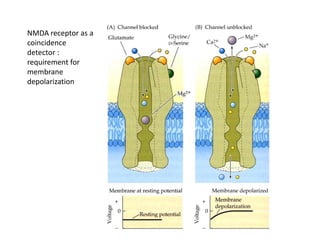
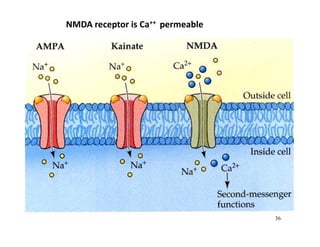
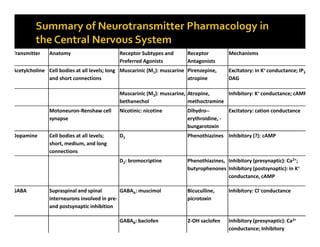
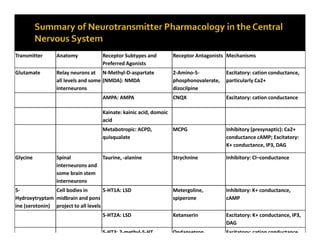
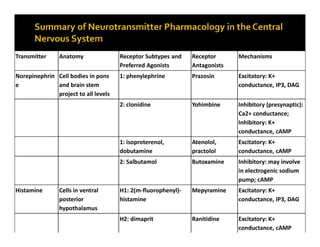
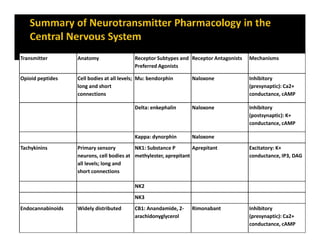
The document discusses various neurotransmitters in the central nervous system including their classes, functions, receptor types, and localization. It describes the monoamine neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin. It discusses their synthesis pathways and the receptors they act on like dopamine receptors. It also covers acetylcholine, amino acid neurotransmitters like GABA and glutamate, and how they are involved in various functions and diseases.