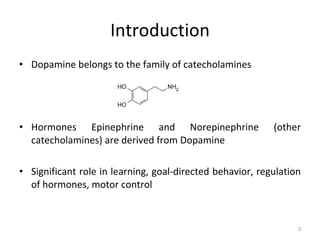
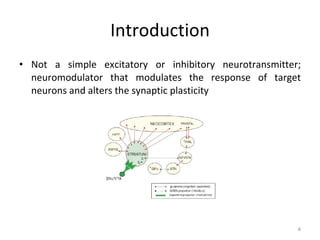
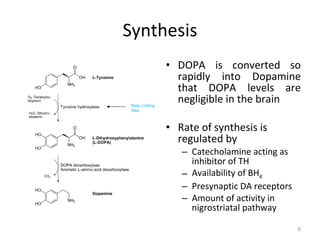
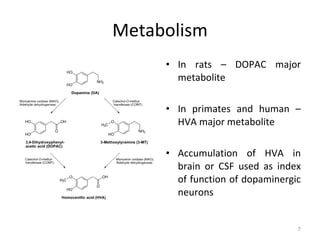
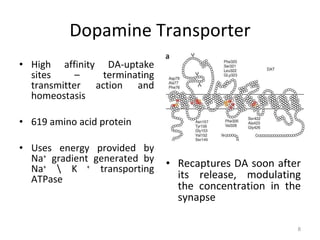
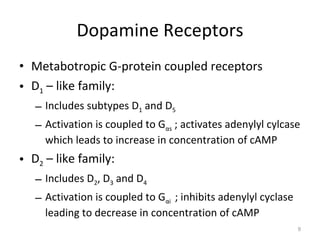
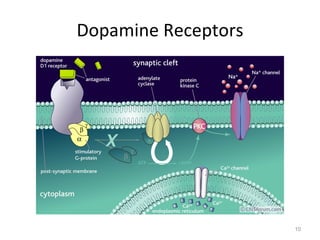
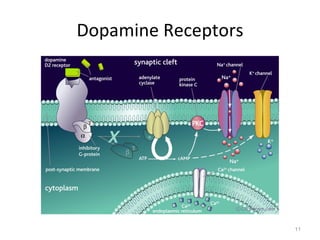
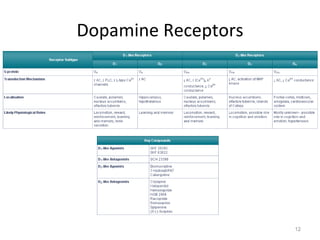
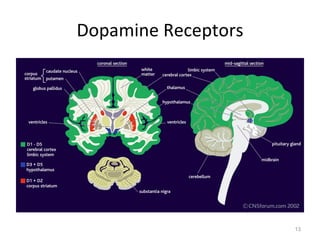
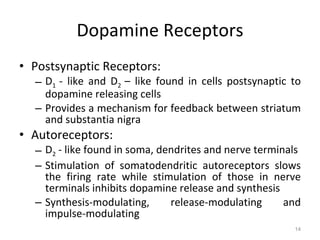
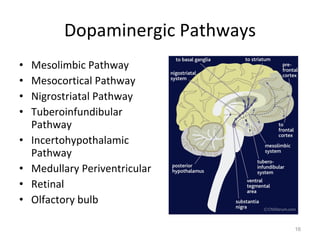
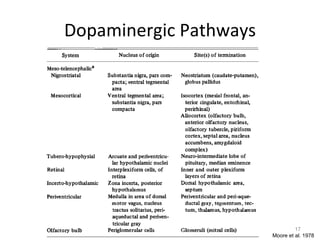
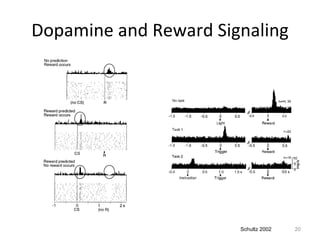
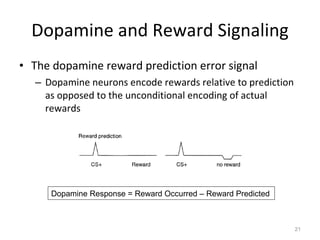
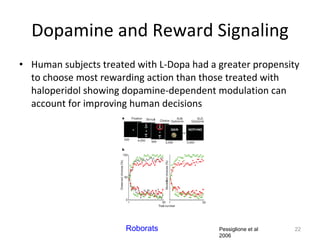
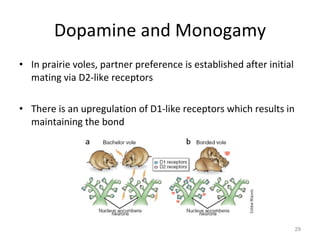
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in reward processing, motor control, and addiction. It acts through two families of G protein-coupled receptors and is synthesized and transported via specific pathways in the brain, notably the mesolimbic pathway associated with reward. Dopamine neurons fire in response to unexpected rewards and encode reward prediction errors, helping to reinforce rewarding behaviors. Imbalances in dopamine signaling are implicated in various disorders like addiction, Parkinson's disease, and schizophrenia.