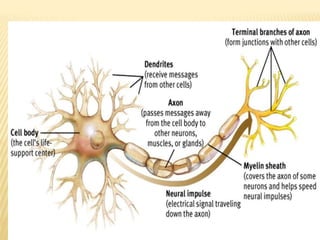
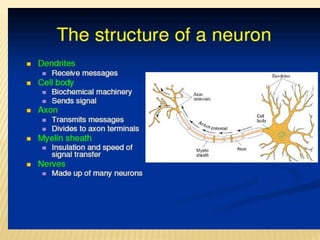
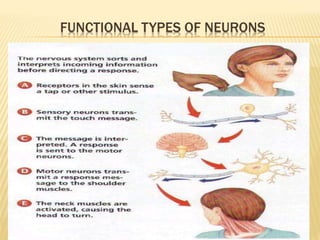
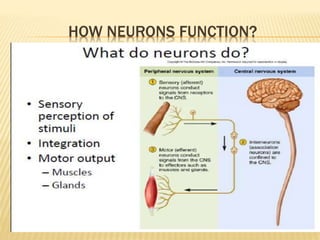
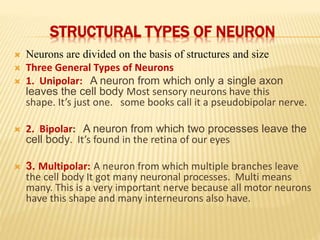
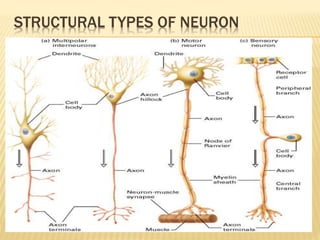
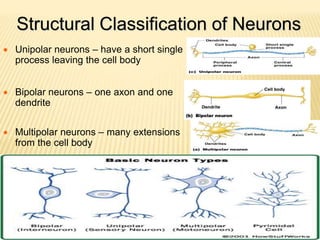
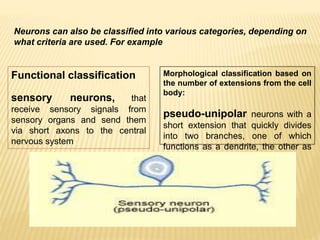
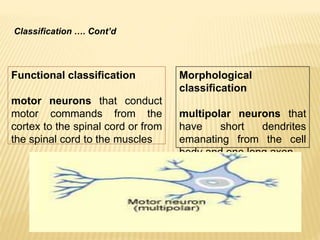
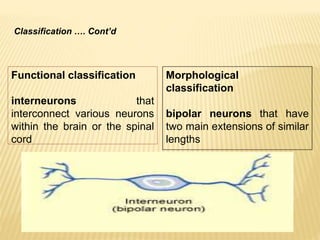
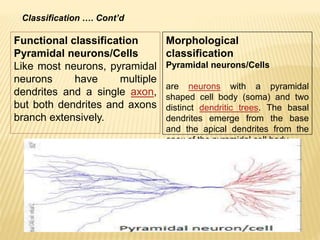
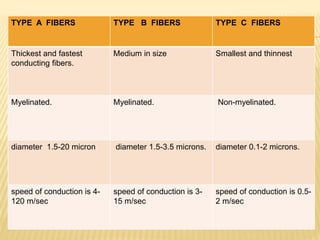
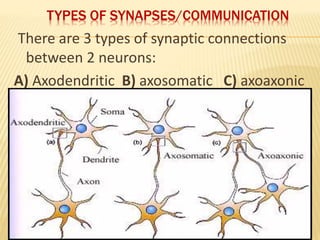
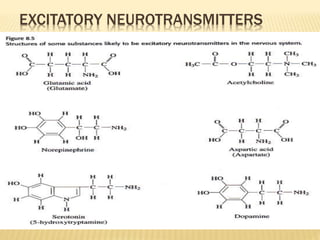
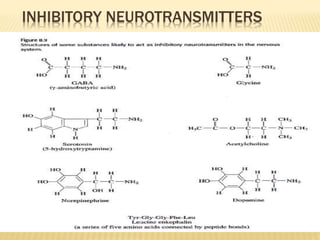
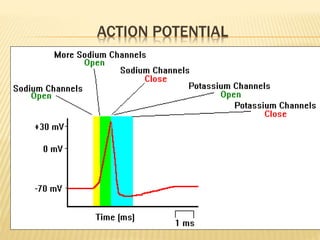
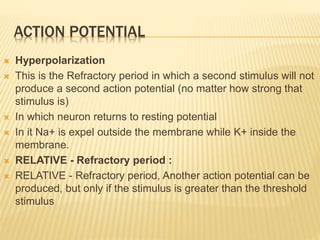
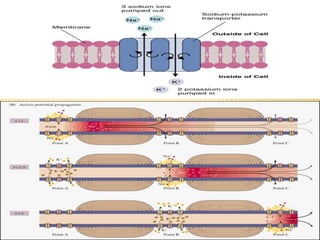
This document discusses neurons and their structural and functional types. It begins by defining neurons as the functional units of the nervous system, consisting of a cell body, axon, and dendrites. It then describes the three main types of neurons based on their structures - unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar. The document also covers the functional classifications of neurons into sensory, motor and interneurons. It provides details on the structural components of neurons including axons, nerve fibers, and synapses. Finally, it explains the phases and propagation of action potentials in neurons.